Abstract
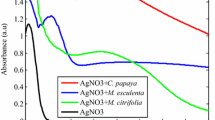
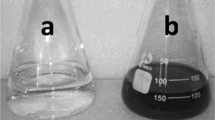
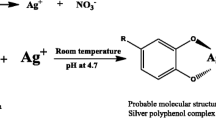
Five plant leaf extracts (Pine, Persimmon, Ginkgo, Magnolia and Platanus) were used and compared for their extracellular synthesis of metallic silver nanoparticles. Stable silver nanoparticles were formed by treating aqueous solution of AgNO3 with the plant leaf extracts as reducing agent of Ag+ to Ag0. UV-visible spectroscopy was used to monitor the quantitative formation of silver nanoparticles. Magnolia leaf broth was the best reducing agent in terms of synthesis rate and conversion to silver nanoparticles. Only 11 min was required for more than 90% conversion at the reaction temperature of 95 °C using Magnolia leaf broth. The synthesized silver nanoparticles were characterized with inductively coupled plasma spectrometry (ICP), energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), and particle analyzer. The average particle size ranged from 15 to 500 nm. The particle size could be controlled by changing the reaction temperature, leaf broth concentration and AgNO3 concentration. This environmentally friendly method of biological silver nanoparticles production provides rates of synthesis faster or comparable to those of chemical methods and can potentially be used in various human contacting areas such as cosmetics, foods and medical applications.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Willems, van den Wildenberg (2005) Roadmap report on nanoparticles. W&W Espana sl, Barcelona, Spain
Simi CK, Abraham TE (2007) Hydrophobic grafted and cross-linked starch nanoparticles for drug delivery. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 30:173–180
Jiang H, Manolache S, Wong ACL, Denes FS (2004) Plasma-enhanced deposition of silver nanoparticles onto polymer and metal surfaces for the generation of antimicrobial characteristics. J Appl Polym Sci 93:1411–1422
Becker RO (1999) Silver ions in the treatment of local infections. Met Based Drugs 6:297–300
Silver S (2003) Bacterial silver resistance: molecular biology and uses and misuses of silver compounds. FEMS Microbiol Rev 27:341–353
Klaus T, Joerger R, Olsson E, Granqvist C-G (1999) Silver-based crystalline nanoparticles, microbially fabricated. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:13611–13614
Konishi Y, Ohno K, Saitoh N, Nomura T, Nagamine S, Hishida H, Takahashi Y, Uruga T (2007) Bioreductive deposition of platinum nanoparticles on the bacterium Shewanella algae. J Biotechnol 128:648–653
Nair B, Pradeep T (2002) Coalescense of nanoclusters and formation of submicron crystallites assisted by Lactobacillus strains. Cryst Growth Des 2:293–298
Willner I, Baron R, Willner B (2006) Growing metal nanoparticles by enzymes. Adv Mater 18:1109–1120
Shankar SS, Rai A, Ahmad A, Sastry M (2004) Rapid synthesis of Au, Ag, and bimetallic Au core Ag shell nanoparticles using Neem (Azadirachta indica) leaf broth. J Colloid Interface Sci 275:496–502
Rai A, Singh A, Ahmad A, Sastry M (2006) Role of halide ions and temperature on the morphology of biologically synthesized gold nanotriangles. Langmuir 22:736–741
Chandran SP, Chaudhary M, Pasricha R, Ahmad A, Sastry M (2006) Synthesis of gold nanotriangles and silver nanoparticles using Aloe vera plant extract. Biotechnol Prog 22:577–583
Shahverdi A, Minaeian S, Shahverdi HR, Jamalifar H, Nohi A-A (2007) Rapid synthesis of silver nanoparticles using culture supernatants of Enterobacteria: a novel biological approach. Proc Biochem 42:919–923
Mukherjee P, Senapati S, Mandal D, Ahmad A, Khan MI, Kumar R, Sastri M (2002) Extracellular synthesis of gold nanoparticles by the fungus Fusarium oxysporum. Chembiochem 5:461–463
Li S, Shen Y, Xie A, Yu X, Qiu L, Zhang L, Zhang Q (2007) Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Capsicum annuum L. extract. Green Chem 9:852–858
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Song, J.Y., Kim, B.S. Rapid biological synthesis of silver nanoparticles using plant leaf extracts. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 32, 79–84 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-008-0224-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-008-0224-6