Abstract
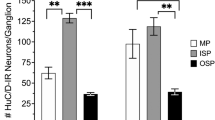
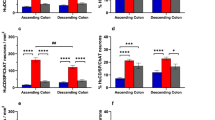
Most myenteric neurons contain one of the two generating enzymes for major excitatory and inhibitory neurotransmitters: choline acetyltransferase (ChAT) or neuronal nitric oxide synthase (NOS). Two minor groups of myenteric neurons contain either both enzymes or neither. Our study had two aims: (1) to compare the proportions of neurons stained for ChAT and/or NOS in human small and large intestinal whole-mounts by co-staining with an antibody against the human neuronal protein Hu C/D (HU); (2) to characterize these neurons morphologically by co-staining with a neurofilament (NF) antibody. In small intestinal whole-mounts co-stained with HU, we counted more ChAT-positive (ChAT+) than NOS+ neurons (52% vs. 38%), whereas the large intestine exhibited fewer ChAT+ than NOS+ neurons (38% vs. 50%). Neurons co-reactive for both ChAT and NOS accounted for about 3% in both regions, whereas neurons negative for both enzymes accounted for 7% in the small intestine and 8% in the large intestine. Co-staining with NF revealed that, in both small and large intestine, ChAT+/NOS+ neurons were either spiny (type I) neurons or displayed smaller perikarya that were weakly or not NF-stained. Of all spiny neurons, almost one third was co-reactive for ChAT and NOS, whereas nearly two thirds were positive only for NOS. Neurons negative for both ChAT and NOS were heterogeneous in size and NF reactivity. Thus, neither the co-existence nor the co-absence of ChAT and NOS in human myenteric neurons is indicative for particular neuron types, with several qualitative and quantitative parameters showing a wide range of interindividual variability.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bernard CE, Gibbons SJ, Gomez-Pinilla PJ, Lurken MS, Schmalz PF, Roeder JL, Linden D, Cima RR, Dozois EJ, Larson DW, Camilleri M, Zinsmeister AR, Pozo MJ, Hicks GA, Farrugia G (2009) Effect of age on the enteric nervous system of the human colon. Neurogastroenterol Motil 21:746–754
Brehmer A (2006) Structure of enteric neurons. Adv Anat Embryol Cell Biol 186:1–94
Brehmer A, Schrödl F, Neuhuber W (2002) Correlated morphological and chemical phenotyping in myenteric type V neurons of porcine ileum.J Comp Neurol 453:1–9
Brehmer A, Blaser B, Seitz G, Schrödl F, Neuhuber W (2004a) Pattern of lipofuscin pigmentation in nitrergic and non-nitrergic, neurofilament immunoreactive myenteric neuron types of human small intestine. Histochem Cell Biol 121:13–20
Brehmer A, Croner R, Dimmler A, Papadopoulos T, Schrödl F, Neuhuber W (2004b) Immunohistochemical characterization of putative primary afferent (sensory) myenteric neurons in human small intestine. Auton Neurosci 112:49–59
Brehmer A, Schrödl F, Neuhuber W, Tooyama I, Kimura H (2004c) Co-expression pattern of neuronal nitric oxide synthase and two variants of choline acetyltransferase in myenteric neurons of porcine ileum. J Chem Neuroanat 27:33–41
Brehmer A, Schrödl F, Neuhuber W (2006) Morphology of VIP/nNOS-immunoreactive myenteric neurons in the human gut. Histochem Cell Biol 125:557–565
Brookes SJ (2001) Classes of enteric nerve cells in the guinea-pig small intestine. Anat Rec 262:58–70
Brown DR, Timmermans JP (2004) Lessons from the porcine enteric nervous system. Neurogastroenterol Motil 16(Suppl 1):50–54
Chiocchetti R, Poole DP, Kimura H, Aimi Y, Robbins HL, Castelucci P, Furness JB (2003) Evidence that two forms of choline acetyltransferase are differentially expressed in subclasses of enteric neurons. Cell Tissue Res 311:11–22
Costa M, Brookes SJ, Steele PA, Gibbins I, Burcher E, Kandiah CJ (1996) Neurochemical classification of myenteric neurons in the guinea-pig ileum. Neuroscience 75:949–967
De Giorgio R, Camilleri M (2004) Human enteric neuropathies: morphology and molecular pathology. Neurogastroenterol Motil 16:515–531
Dogiel AS (1899) Ueber den Bau der Ganglien in den Geflechten des Darmes und der Gallenblase des Menschen und der Säugethiere. Arch Anat Physiol Anat Abt (Leipzig) 1899:130-158
Furness JB (2006) The enteric nervous system. Blackwell, Oxford
Furness JB, Trussell DC, Pompolo S, Bornstein JC, Smith TK (1990) Calbindin neurons of the guinea-pig small intestine: quantitative analysis of their numbers and projections. Cell Tissue Res 260:261–272
Ganns D, Schrödl F, Neuhuber W, Brehmer A (2006) Investigation of general and cytoskeletal markers to estimate numbers and proportions of neurons in the human intestine. Histol Histopathol 21:41–51
Giaroni C, De Ponti F, Cosentino M, Lecchini S, Frigo G (1999) Plasticity in the enteric nervous system. Gastroenterology 117:1438–1458
Heinicke EA, Kiernan JA, Wijsman J (1987) Specific, selective and complete staining of neurons of the myenteric plexus, using Cuprolinic blue. J Neurosci Methods 21:45–54
Holzer P, Schicho R, Holzer-Petsche U, Lippe IT (2001) The gut as a neurological organ. Wien Klin Wochenschr 113:647–660
Lindig TM, Kumar V, Kikinis R, Pieper S, Schrödl F, Neuhuber WL, Brehmer A (2009) Spiny versus stubby: 3D reconstruction of human myenteric (type I) neurons. Histochem Cell Biol 131:1–12
Lomax AE, Fernandez E, Sharkey KA (2005) Plasticity of the enteric nervous system during intestinal inflammation. Neurogastroenterol Motil 17:4–15
Murphy EM, Defontgalland D, Costa M, Brookes SJ, Wattchow DA (2007) Quantification of subclasses of human colonic myenteric neurons by immunoreactivity to Hu, choline acetyltransferase and nitric oxide synthase. Neurogastroenterol Motil 19:126–134
Phillips RJ, Kieffer EJ, Powley TL (2003) Aging of the myenteric plexus: neuronal loss is specific to cholinergic neurons. Auton Neurosci 106:69–83
Phillips RJ, Hargrave SL, Rhodes BS, Zopf DA, Powley TL (2004) Quantification of neurons in the myenteric plexus: an evaluation of putative pan-neuronal markers. J Neurosci Methods 133:99–107
Pidsudko Z, Kaleczyc J, Wasowicz K, Sienkiewicz W, Majewski M, Zajac W, Lakomy M (2008) Distribution and chemical coding of intramural neurons in the porcine ileum during proliferative enteropathy. J Comp Pathol 138:23–31
Pimont S, Bruley Des Varannes S, Le Neel JC, Aubert P, Galmiche JP, Neunlist M (2003) Neurochemical coding of myenteric neurones in the human gastric fundus. Neurogastroenterol Motil 15:655–662
Porter AJ, Wattchow DA, Brookes SJH, Schemann M, Costa M (1996) Choline acetyltransferase immunoreactivity in the human small and large intestine. Gastroenterology 111:401–408
Porter AJ, Wattchow DA, Brookes SJ, Costa M (1997) The neurochemical coding and projections of circular muscle motor neurons in the human colon. Gastroenterology 113:1916–1923
Porter AJ, Wattchow DA, Brookes SJ, Costa M (2002) Cholinergic and nitrergic interneurones in the myenteric plexus of the human colon. Gut 51:70–75
Qu ZD, Thacker M, Castelucci P, Bagyanszki M, Epstein ML, Furness JB (2008) Immunohistochemical analysis of neuron types in the mouse small intestine. Cell Tissue Res 334:147–161
Ramón y Cajal S (1911) Histologie du système nerveux de l'homme et des vertébrés. Maloine, Paris
Rivera LR, Thacker M, Furness JB (2009) High- and medium-molecular-weight neurofilament proteins define specific neuron types in the guinea-pig enteric nervous system. Cell Tissue Res 335:529–538
Schemann M, Neunlist M (2004) The human enteric nervous system. Neurogastroenterol Motil 16(Suppl 1):55–59
Schneider J, Jehle EC, Starlinger MJ, Neunlist M, Michel K, Hoppe S, Schemann M (2001) Neurotransmitter coding of enteric neurones in the submucous plexus is changed in non-inflamed rectum of patients with Crohn's disease. Neurogastroenterol Motil 13:255–264
Schnell SA, Staines WA, Wessendorf MW (1999) Reduction of lipofuscin-like autofluorescence in fluorescently labeled tissue. J Histochem Cytochem 47:719–730
Stach W (1989) A revised morphological classification of neurons in the enteric nervous system. In: Singer MV, Goebell H (eds) Nerves and the gastrointestinal tract. Kluwer, Lancaster, pp 29–45
Tooyama I, Kimura H (2000) A protein encoded by an alternative splice variant of choline acetyltransferase mRNA is localized preferentially in peripheral nerve cells and fibers. J Chem Neuroanat 17:217–226
Wattchow D, Brookes S, Murphy E, Carbone S, Fontgalland D de, Costa M (2008) Regional variation in the neurochemical coding of the myenteric plexus of the human colon and changes in patients with slow transit constipation. Neurogastroenterol Motil 20:1298–1305
Acknowledgements
The excellent technical assistance of Karin Löschner, Stephanie Link, Andrea Hilpert, Hedwig Symowski and Inge Zimmermann is gratefully acknowledged. Patricia Simpson provided us with linguistic advice. We also thank Anne Stab, Tony Simpson, Jens Walluschek and Philip Eichhorn (all Erlangen) and Holger Rupprecht and Martin Rexer (Fürth) for their kind cooperation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Beck, M., Schlabrakowski, A., Schrödl, F. et al. ChAT and NOS in human myenteric neurons: co-existence and co-absence. Cell Tissue Res 338, 37–51 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-009-0852-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-009-0852-4