Abstract
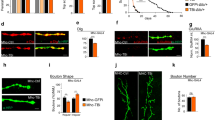
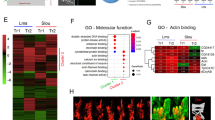
In humans, mutations in ZASP (the gene for Z-band alternatively spliced PDZ-motif protein) are associated with dilated cardiomyopathy and left ventricular non-compaction. In particular, mutations in or around the Zasp motif seem to be related to myofibrillar myopathy. Thus, “zaspopathies” include symptoms such as Z-line disgregation, proximal and distal muscle weakness, cardiomyopathies, and peripheral neuropathies. In order to understand the role of ZASP in muscle structure and function, we have performed a molecular characterization of the Drosophila ortholog of human ZASP and a functional analysis following the post-transcriptional silencing of the Drosophila gene. Transcriptional analysis of dzasp has revealed six additional exons, with respect to the known 16, and multiple splice variants. We have produced transgenic lines harboring constructs that, through the use of the UAS/Gal4 binary system, have enabled us to drive dsRNA interference of dzasp in a tissue-specific manner. Knockdown individuals show locomotor defects associated with alterations of muscle structure and ultrastructure, consistent with a role of dzasp specifically in the maintenance of muscular integrity.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arimura T, Hayashi T, Terada H, Lee SY, Zhou Q, Takahashi M, Ueda K, Nouchi T, Hohda S, Shibutani M, Hirose M, Chen J, Park JE, Yasunami M, Hayashi H, Kimura A (2004) A Cypher/ZASP mutation associated with dilated cardiomyopathy alters the binding affinity to protein kinase C. J Biol Chem 279:6746–6752
Au Y, Atkinson RA, Guerrini R, Kelly G, Joseph C, Martin SR, Muskett FW, Pallavicini A, Faulkner G, Pastore A (2004) Solution structure of ZASP PDZ domain; implications for sarcomere ultrastructure and enigma family redundancy. Structure 12:611–622
Beramendi A, Peron S, Megighian A, Reggiani C, Cantera R (2005) The inhibitor kappaB-ortholog Cactus is necessary for normal neuromuscular function in Drosophila melanogaster. Neuroscience 134:397–406
Bilen J, Bonini NM (2005) Drosophila as a model for human neurodegenerative disease. Annu Rev Genet 39:153–171
Brand AH, Perrimon N (1993) Targeted gene expression as a means of altering cell fates and generating dominant phenotypes. Development 118:401–415
Crowther DC, Page R, Chandraratna D, Lomas DA (2006) A Drosophila model of Alzheimer’s disease. Methods Enzymol 412:234–255
Faulkner G, Lanfranchi G, Valle G (2001) Telethonin and other new proteins of the Z-disc of skeletal muscle. IUBMB Life 51:275–282
Faulkner G, Pallavicini A, Formentin E, Comelli A, Ievolella C, Trevisan S, Bortoletto G, Scannapieco P, Salamon M, Mouly V, Valle G, Lanfranchi G (1999) ZASP: a new Z-band alternatively spliced PDZ-motif protein. J Cell Biol 146:465–475
Feany MB, Bender WW (2000) A Drosophila model of Parkinson’s disease. Nature 404:394–398
Fristrom DK, Fristrom JW (1993) The metamorphic development of the adult epidermis. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, NY
Griggs R, Vihola A, Hackman P, Talvinen K, Haravuori H, Faulkner G, Eymard B, Richard I, Selcen D, Engel A, Carpen O, Udd B (2007) Zaspopathy in a large classic late-onset distal myopathy family. Brain 130:1477–1484
Guan B, Hartmann B, Kho YH, Gorczyca M, Budnik V (1996) The Drosophila tumor suppressor gene, dlg, is involved in structural plasticity at a glutamatergic synapse. Curr Biol 6:695–706
Huang C, Zhou Q, Liang P, Hollander MS, Sheikh F, Li X, Greaser M, Shelton GD, Evans S, Chen J (2003) Characterization and in vivo functional analysis of splice variants of Cypher. J Biol Chem 278:7360–7365
Jani K, Schock F (2007) Zasp is required for the assembly of functional integrin adhesion sites. J Cell Biol 179:1583–1597
Klaavuniemi T, Ylanne J (2006) Zasp/Cypher internal ZM-motif containing fragments are sufficient to co-localize with alpha-actinin–analysis of patient mutations. Exp Cell Res 312:1299–1311
Klaavuniemi T, Kelloniemi A, Ylanne J (2004) The ZASP-like motif in actinin-associated LIM protein is required for interaction with the alpha-actinin rod and for targeting to the muscle Z-line. J Biol Chem 279:26402–26410
Lin DM, Goodman CS (1994) Ectopic and increased expression of Fasciclin II alters motoneuron growth cone guidance. Neuron 13:507–523
Machuca-Tzili L, Thorpe H, Robinson TE, Sewry C, Brook JD (2006) Flies deficient in Muscleblind protein model features of myotonic dystrophy with altered splice forms of Z-band associated transcripts. Hum Genet 120:487–499
Passier R, Zeng H, Frey N, Naya FJ, Nicol RL, McKinsey TA, Overbeek P, Richardson JA, Grant SR, Olson EN (2000) CaM kinase signaling induces cardiac hypertrophy and activates the MEF2 transcription factor in vivo. J Clin Invest 105:1395–1406
Piccin A, Salameh A, Benna C, Sandrelli F, Mazzotta G, Zordan M, Rosato E, Kyriacou CP, Costa R (2001) Efficient and heritable functional knock-out of an adult phenotype in Drosophila using a GAL4-driven hairpin RNA incorporating a heterologous spacer. Nucleic Acids Res 29:E55
Roberts DB, Standen GN (1998) The elements of Drosophila biology and genetics. IRL, Oxford
Rubin GM, Spradling AC (1982) Genetic transformation of Drosophila with transposable element vectors. Science 218:348–353
Selcen D, Engel AG (2005) Mutations in ZASP define a novel form of muscular dystrophy in humans. Ann Neurol 57:269–276
Te Velthuis AJ, Isogai T, Gerrits L, Bagowski CP (2007) Insights into the molecular evolution of the PDZ/LIM family and identification of a novel conserved protein motif. PLoS ONE 2:e189
Vatta M, Mohapatra B, Jimenez S, Sanchez X, Faulkner G, Perles Z, Sinagra G, Lin JH, Vu TM, Zhou Q, Bowles KR, Di Lenarda A, Schimmenti L, Fox M, Chrisco MA, Murphy RT, McKenna W, Elliott P, Bowles NE, Chen J, Valle G, Towbin JA (2003) Mutations in Cypher/ZASP in patients with dilated cardiomyopathy and left ventricular non-compaction. J Am Coll Cardiol 42:2014–2027
Wolf MJ, Amrein H, Izatt JA, Choma MA, Reedy MC, Rockman HA (2006) Drosophila as a model for the identification of genes causing adult human heart disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:1394–1399
Xing Y, Ichida F, Matsuoka T, Isobe T, Ikemoto Y, Higaki T, Tsuji T, Haneda N, Kuwabara A, Chen R, Futatani T, Tsubata S, Watanabe S, Watanabe K, Hirono K, Uese K, Miyawaki T, Bowles KR, Bowles NE, Towbin JA (2006) Genetic analysis in patients with left ventricular noncompaction and evidence for genetic heterogeneity. Mol Genet Metab 88:71–77
Zhou Q, Ruiz-Lozano P, Martone ME, Chen J (1999) Cypher, a striated muscle-restricted PDZ and LIM domain-containing protein, binds to alpha-actinin-2 and protein kinase C. J Biol Chem 274:19807–19813
Zhou Q, Chu PH, Huang C, Cheng CF, Martone ME, Knoll G, Shelton GD, Evans S, Chen J (2001) Ablation of Cypher, a PDZ-LIM domain Z-line protein, causes a severe form of congenital myopathy. J Cell Biol 155:605–612
Zordan MA, Cisotto P, Benna C, Agostino A, Rizzo G, Piccin A, Pegoraro M, Sandrelli F, Perini G, Tognon G, De Caro R, Peron S, Kronnie TT, Megighian A, Reggiani C, Zeviani M, Costa R (2006) Post-transcriptional silencing and functional characterization of the Drosophila melanogaster homolog of human Surf1. Genetics 172:229–241
Acknowledgements
Thanks are due to Mr. M. Sturnega, ICGEB, Trieste, for excellent technical assistance in the immunization of the animals used for antibody production.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The authors wish the first three authors to be regarded as joint first authors.
Financial support was provided by the Telethon Foundation, Italy (GGP04088 to G.F., GP0048Y01 to R.C.) and the Italian Centro Nazionale delle Ricerche and Ministero dell’Universita’ e della Ricerca “Legge 449/97” (CU04.00067 to R.C.)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Benna, C., Peron, S., Rizzo, G. et al. Post-transcriptional silencing of the Drosophila homolog of human ZASP: a molecular and functional analysis. Cell Tissue Res 337, 463–476 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-009-0813-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-009-0813-y