Abstract
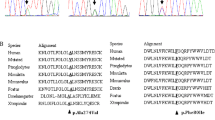
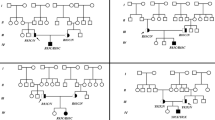
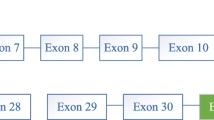
Glycogen storage disease (GSD) type Ib is an autosomal recessive disorder caused by a deficiency in microsomal glucose 6-phosphate (G6P) translocase. A gene mutated in GSD type Ib patients has recently been isolated. We have determined the entire sequence of the human G6P translocase gene by PCR-directed sequencing. The gene spans approximately 5 kb of genomic DNA and contains eight exons. Analysis of DNA from a Japanese patient with GSD type Ib revealed new compound heterozygous mutations; a T to C transition at cDNA position 521 resulting in W118R, and an A to C transversion at the –2 splicing acceptor site of intron 1. Reverse transcription (RT)-PCR from leukocyte RNA of the patient revealed the abnormally spliced transcript. These results further support the suggestion that the gene is causative for GSD Ib and should be useful in the molecular diagnosis of such patients.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 11 May 1998 / Accepted: 25 July 1998
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ihara, K., Kuromaru, R. & Hara, T. Genomic structure of the human glucose 6-phosphate translocase gene and novel mutations in the gene of a Japanese patient with glycogen storage disease type Ib. Hum Genet 103, 493–496 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004390050856
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004390050856