Abstract
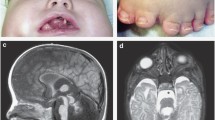
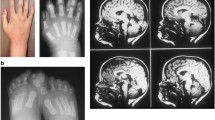
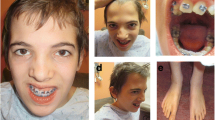
Oral-facial-digital syndrome type 1 (OFD1) is an X-linked dominant disease characterized by malformations of the face, oral cavity, and digits. Thus far, 18 small mutations in the OFD1 gene have been reported. Here, we describe, in one Japanese sporadic female OFD1 case, the presence of a novel pair of deletion mutations: a 4,094-bp deletion encompassing exon 7 to intron 9, and a 14-bp deletion in intron 9, both of which are present in her paternal X-chromosome. The first deletion, the largest known to affect OFD1, was revealed by identifying four novel transcripts that all lacked exons 7–9. The most likely cause of the double deletion is two unequal recombinations between homologous sequences. Identification of the 4,094-bp deletion was made possible only by analyzing OFD1 mRNA, underscoring the utility of mRNA analysis in the mutational analysis of OFD1.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aradhya S, Woffendin H, Jakins T, Bardaro T, Esposito T, Smahi A, Shaw C, Levy M, Munnich A, D’Urso M, Lewis RA, Kenwrick S, Nelson DL (2001) A recurrent deletion in the ubiquitously expressed NEMO (IKK-gamma) gene accounts for the vast majority of incontinentia pigmenti mutations. Hum Mol Genet 10:2171–2179
Buyse IM, Fang P, Hoon KT, Amir RE, Zoghbi HY, Roa BB (2000) Diagnostic testing for Rett syndrome by DHPLC and direct sequencing analysis of the MECP2 gene: identification of several novel mutations and polymorphisms. Am J Hum Genet 67:1428–1436
Conciliis L de, Marchitiello A, Wapenaar MC, Borsani G, Giglio S, Mariani M, Consalez GG, Zuffardi O, Franco B, Ballabio A, Banfi S (1998) Characterization of Cxorf5 (71-7A), a novel human cDNA mapping to Xp22 and encoding a protein containing coiled-coil alpha-helical domains. Genomics 51:243–250
Connacher A, Forsyth C, Stewart W (1987) Orofaciodigital syndrome type 1 associated with polycystic kidneys and agenesis of tne corpus callosum. J Med Genet 24:116–118
Fang LJ, Simard MJ, Vidaud D, Assouline B, Lemieux B, Vidaud M, Chabot B, Thirion JP (2001) A novel mutation in the neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1) gene promotes skipping of two exons by preventing exon definition. J Mol Biol 307:1261–1270
Feather S, Woolf A, Donnani D, Malcolm S, Winter R (1997) The oral-facial-digital syndrome type 1 (OFD1), a cause of polycystic kidney disease and associated malformations, maps to Xp22.2–Xp22.3. Hum Mol Genet 6:1163–1167
Ferrante M, Giorgio G, Feather S, Bulfone A, Wright V, Ghiani M, Selicorni A, Gammaro L, Scolari F, Woolf A, Odent S, Le Marec B, Malcolm S, Winter R, Ballabio A, Franco B (2001) Identification of the gene for oral facial digital syndrome type 1. Am J Hum Genet 68:569–576
Gedeon AK (1999) Gene localization for oral-facial-digital syndrome type1(OFD1:MIM 311200) Proximal to DXS 85. Am J Med Genet 82:352–355
Girard M, Couvert P, Carrie A, Tardieu M, Chelly J, Beldjord C, Bienvenu T (2001) Parental origin of de novo MECP2 mutations in Rett syndrome. Eur J Hum Genet 9:231–236
Gotoda T, Yamada N, Murase T, Inaba T, Ishibashi S, Shimano H, Koga S, Yazaki Y, Furuichi Y, Takaku F (1991) Occurrence of multiple aberrantly spliced mRNAs upon a donor splice site mutation that causes familial lipoprotein lipase deficiency. J Biol Chem 266:24757–24762
Huopaniemi L, Tyynismaa H, Rantala A, Rosenberg T, Alitalo T (2000) Characterization of two unusual RS1 gene deletions segregating in Danish retinoschisis families. Hum Mutat 16:307–314
Ketterling RP, Vielhaber E, Bottema CD, Schaid DJ, Cohen MP, Sexauer CL, Sommer SS (1993) Germ-line origins of mutation in families with hemophilia B: the sex ratio varies with the type of mutation. Am J Hum Genet 52:152–166
Lakich D, Kazazian HH Jr, Antonarakis SE, Gitschier J (1993) Inversions disrupting the factor VIII gene are a common cause of severe haemophilia A. Nat Genet 5:236–241
Lebo RV, Ikuta T, Milunsky JM, Milunsky A (2001) Rett syndrome from quintuple and triple deletions within the MECP2 deletion hotspot region. Clin Genet 59:406–417
Lee SS, Wan M, Francke U (2001) Spectrum of MECP2 mutations in Rett syndrome. Brain Dev 23:S138–S143
Lelli N, Garuti R, Ghisellini M, Tiozzo R, Rolleri M, Aimale V, Ginocchio E, Naselli A, Bertolini S, Calandra S (1995) Occurrence of multiple aberrantly spliced mRNAs of the LDL-receptor gene upon a donor splice site mutation that causes familial hypercholesterolemia (FHBenevento). J Lipid Res 36:1315–1324
Lemahieu V, Gastier JM, Francke U (1999) Novel mutations in the Wiskott–Aldrich syndrome protein gene and their effects on transcriptional, translational, and clinical phenotypes. Hum Mutat 14:54–66
Matsuo M, Masumura T, Nishio H, Nakajima T, Kitoh Y, Takumi T, Koga J, Nakamura H (1991) Exon skipping during splicing of dystrophin mRNA precursor due to an intraexon deletion in the dystrophin gene of Duchenne muscular dystrophy kobe. J Clin Invest 87:2127–2131
Moloney DM, Slaney SF, Oldridge M, Wall SA, Sahlin P, Stenman G, Wilkie AO (1996) Exclusive paternal origin of new mutations in Apert syndrome. Nat Genet 13:48–53
Parrish JE, Scheuerle AE, Lewis RA, Levy ML, Nelson DL (1996) Selection against mutant alleles in blood leukocytes is a consistent feature in Incontinentia Pigmenti type 2. Hum Mol Genet 5:1777–1783
Rakkolainen A, Ala-mello S, Kristo P, Orpana A, Jarvela I (2002) Four novel mutations in the OFD1(Cxorf5) gene in Finnish patients with oral-facial-digital syndrome 1. J Med Genet 39:292–296
Romio L, Wright V, Price K, Winyard PJD, Donnani D, Porteous ME, Franco B, Giorgio G, Malcolm S, Woolf AS, Feather SA (2003) OFD1, the gene mutated in oral-facial-digital syndrome type 1, is expressed in the metanephros and in human embryonic renal mesenchymal cells. J Am Soc Nephrol 14:680–689
Rossiter JP, Young M, Kimberland ML, Hutter P, Ketterling RP, Gitschier J, Horst J, Morris MA, Schaid DJ, de Moerloose P (1994) Factor VIII gene inversions causing severe hemophilia A originate almost exclusively in male germ cells. Hum Mol Genet 3:1035–1039
Scolari F, Valzorio B, Carli O, Vizzardi V, Costantino E, Grazioli L, Bondioni M, Savoldi S, Maiorca R (1997) Oral-facial-digital syndrome type 1: an unusual cause of hereditary cystic kidney disease. Nephrol Dial Transplant 12:1247–1250
Stoll C, Sauvage P (2002) Long-term follow-up of a girl with oro-facio-digital syndrome type 1 due to a mutation in the OFD1 gene. Ann Genet 45:58–62
Su TS, Lin LH (1990) Analysis of a splice acceptor site mutation which produces multiple splicing abnormalities in the human argininosuccinate synthetase locus. J Biol Chem 265:19716–19720
Surono A, Takeshima Y, Wibawa T, Ikezawa M, Nonaka I, Matsuo M (1999) Circular dystrophin RNAs consisting of exons that were skipped by alternative splicing. Hum Mol Genet 8:493–500
Takahara K, Schwarze U, Imamura Y, Hoffman GG, Toriello H, Smith LT, Byers PH, Greenspan DS (2002) Order of intron removal influences multiple splice outcomes, including a two-exon skip, in a COL5A1 acceptor-site mutation that results in abnormal pro-alpha1(V) N-propeptides and Ehlers-Danlos syndrome type I. Am J Hum Genet 71:451–465
Toriello HV (1993) Oral-facial-digital-syndromes. Clin Dysmorphol 2:95–105
Towfighi J, Berlin C, et al (1985) Neuropathology of oral-facial-digital syndromes. Arch Pathol Lab Med 109:642–646
Trappe R, Laccone F, Cobilanschi J, Meins M, Huppke P, Hanefeld F, Engel W (2001) MECP2 mutations in sporadic cases of Rett syndrome are almost exclusively of paternal origin. Am J Hum Genet 68:1093–1101
Yasuda M, Shabbeer J, Osawa M, Desnick RJ (2003) Fabry disease: novel alpha-galactosidase A 3′-terminal mutations result in multiple transcripts due to aberrant 3′-end formation. Am J Hum Genet 73:162–173
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Brunella Franco for providing us sequence data for primers used for the amplification of genomic DNA.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Morisawa, T., Yagi, M., Surono, A. et al. Novel double-deletion mutations of the OFD1 gene creating multiple novel transcripts. Hum Genet 115, 97–103 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-004-1139-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-004-1139-1