Abstract
Purpose
The aim of this study was to investigate whether resveratrol (Res) combined with artemisinin (ART) possess synergistic effect on different cancer cells.
Materials and methods
The viability of HepG2 and HeLa cells treated with ART and Res was detected by 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay. Combination index (CI) analysis and isobologram were used to assess the synergistic effect of ART and Res in different ratios. Wound-healing assay was used to investigate the migration rate. AO staining and fluorescent microscopy measurements were performed to detect the cell apoptosis. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) was measured with 2′7′-dichlorofluorescein diacetate (DCFH-DA).
Results
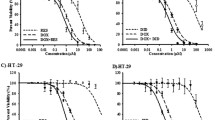
MTT assay indicated that ART and Res inhibited the growth of HeLa and HepG2 cells in a dose-dependent manner. The combination of ART and Res exhibited the strongest anticancer effect at the ratio of 1:2 (ART to Res). The combination of the two drugs also markedly reduced the ability of cell migration. Apoptosis analysis showed that combination of ART and Res significantly increased the apoptosis and necrosis rather than use singly. Additionally, ROS levels were elevated by combining ART with Res.
Conclusions
Taken together, the present study suggested that ART and Res possessed the synergistic anti-tumor effect. ART in combination with Res could be an effective therapeutic strategy for cancer.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aggarwal BB, Bhardwaj A, Aggarwal RS, Seeram NP, Shishodia S, Takada Y (2004) Role of resveratrol in prevention and therapy of cancer: preclinical and clinical studies. Anticancer Res 24(5A):2783–2840
Aziz MH, Kumar R, Ahmad N (2003) Cancer chemoprevention by resveratrol: in vitro and in vivo studies and the underlying mechanisms (review). Int J Oncol 23(1):17–28
Baxevanis CN, Perez SA, Papamichail M (2009) Combinatorial treatments including vaccines, chemotherapy and monoclonal antibodies for cancer therapy. Cancer Immunol Immunother 58(3):317–324
Berger TG, Dieckmann D, Efferth T, Schultz ES, Funk JO, Baur A, Schuler G (2005) Artesunate in the treatment of metastatic uveal melanoma-first experiences. Oncol Rep 14(6):1599–1603
Bostwick DG, Alexander EE, Singh R, Shan A, Qian J, Santella RM, Oberley TD et al (2000) Antioxidant enzyme expression and reactive oxygen species damage in prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia and cancer. Cancer 89(1):123–134
Cakir Z, Saydam G, Sahin F et al (2011) The roles of bioactive sphingolipids in resveratrol-induced apoptosis in HL60 acute myeloid leukemia cells. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 137(2):279–286
Canel M, Serrels A, Frame MC, Brunton VG (2013) E-cadherin–integrin crosstalk in cancer invasion and metastasis. J Cell Sci 126(2):393–401
Chou TC (2006) Theoretical basis, experimental design, and computerized simulation of synergism and antagonism in drug combination studies. Pharmacol Rev 58(3):621–681
Chou TC, Talalay P (1984) Quantitative analysis of dose-effect relationships: the combined effects of multiple drugs or enzyme inhibitors. Adv Enzyme Regul 22:27–55
Fatemi MH, Izadiyan P (2011) Cytotoxicity estimation of ionic liquids based on their effective structural features. Chemosphere 84(5):553–563
Firestone GL, Sundar SN (2009) Anticancer activities of artemisinin and its bioactive derivatives. Expert Rev Mol Med 11:e32
Frazzi R, Valli R, Tamagnini I, Casali B, Latruffe N, Merli F (2013) Resveratrol-mediated apoptosis of hodgkin lymphoma cells involves SIRT1 inhibition and FOXO3a hyperacetylation. Int J Cancer 132(5):1013–1021
Hou J, Wang D, Zhang R, Wang H (2008) Experimental therapy of hepatoma with artemisinin and its derivatives: in vitro and in vivo activity, chemosensitization, and mechanisms of action. Clin Cancer Res 14(17):5519–5530
Jang M, Cai L, Udeani GO, Slowing KV, Thomas CF, Beecher CW, Pezzuto JM et al (1997) Cancer chemopreventive activity of resveratrol, a natural product derived from grapes. Science 275(5297):218–220
Khan MA, Chen HC, Wan XX, Tania, M, Xu AH, Chen FZ, Zhang DZ (2013) Regulatory effects of resveratrol on antioxidant enzymes: A mechanism of growth inhibition and apoptosis induction in cancer cells. Mol Cells, 1–7
Lai H, Nakase I, Lacoste E, Singh NP, Sasaki T (2009) Artemisinin-transferrin conjugate retards growth of breast tumors in the rat. Anticancer Res 29(10):3807–3810
Lai HC, Singh NP, Sasaki T (2013) Development of artemisinin compounds for cancer treatment. Invest New Drugs 31(1):230–246
Leite M, Quinta-Costa M, Leite PS, Guimarães JE (1999) Critical evaluation of techniques to detect and measure cell death–study in a model of UV radiation of the leukaemic cell line HL60. Anal Cell Pathol 19(3):139–151
Li PC, Lam E, Roos WP, Zdzienicka MZ, Kaina B, Efferth T (2008) Artesunate derived from traditional Chinese medicine induces DNA damage and repair. Cancer Res 68(11):4347–4351
Liu WM, Gravett AM, Dalgleish AG (2011) The antimalarial agent artesunate possesses anticancer properties that can be enhanced by combination strategies. Int J Cancer 128(6):1471–1480
Liu P, Liang H, Xia Q, Li P, Kong H, Lei P, Tu Z et al (2013) Resveratrol induces apoptosis of pancreatic cancers cells by inhibiting miR-21 regulation of BCL-2 expression. Clin Transl Oncol pp 1–6
May J, Cuatrecasas P et al (1985) Transferrin receptor: its biological significance. J Membr Biol 88(3):205–215
Muqbil I, Beck WJ, Bao F, Sarkar BH, Mohammad FM, Hadi RM et al (2012) Old wine in a new bottle: the Warburg effect and anticancer mechanisms of resveratrol. Curr Pharm Des 18(12):1645–1654
Nakase I, Gallis B, Takatani-Nakase T, Oh S, Lacoste E, Singh NP et al (2009) Ransferrin receptor-dependent cytotoxicity of artemisinin–transferrin conjugates on prostate cancer cells and induction of apoptosis. Cancer Lett 274(2):290–298
Notas G, Nifli AP, Kampa M, Vercauteren J, Kouroumalis E, Castanas E (2006) Resveratrol exerts its antiproliferative effect on HepG2 hepatocellular carcinoma cells, by inducing cell cycle arrest, and NOS activation. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-General Subjects 1760(11):1657–1666
Rasheed SA, Efferth T, Asangani IA, Allgayer H (2010) First evidence that the antimalarial drug artesunate inhibits invasion and in vivo metastasis in lung cancer by targeting essential extracellular proteases. Int J Cancer 127(6):1475–1485
Riganti C, Doublier S, Costamagna C, Aldieri E, Pescarmona G, Ghigo D, Bosia A (2008) Activation of nuclear factor-kappa B pathway by simvastatin and RhoA silencing increases doxorubicin cytotoxicity in human colon cancer HT29 cells. Mol Pharmacol 74(2):476–484
Tallarida RJ (2001) Drug synergism: its detection and applications. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 298(3):865–872
Tan WF, Shen F, Luo XJ, Su CQ et al (2011) Artemisinin inhibits in vitro and in vivo invasion and metastasis of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Phytomedicine 18(2):158–162
Tin AS, Sundar SN, Tran KQ, Park AH, Poindexter KM, Firestone GL (2012) Antiproliferative effects of artemisinin on human breast cancer cells requires the downregulated expression of the E2F1 transcription factor and loss of E2F1-target cell cycle genes. Anticancer Drugs 23(4):370–379
Trung LQ, Espinoza JL, Takami A, Nakao S (2013) Resveratrol induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in malignant NK cells via JAK2/STAT3 pathway inhibition. PLoS ONE 8(1):e55183
Vishchuk OS, Ermakova SP, Zvyagintseva TN (2013) The effect of sulfated (1 → 3)-α-l-fucan from the brown alga Saccharina cichorioides miyabe on resveratrol-induced apoptosis in colon carcinoma cells. Marine Drugs 11(1):194–212
Wang Z, Hu W, Zhang JL, Wu XH, Zhou HJ (2012) Dihydroartemisinin induces autophagy and inhibits the growth of iron-loaded human myeloid leukemia K562 cells via ROS toxicity. FEBS Open Biol 2:103–112
Willoughby JA, Sundar SN, Cheung M, Tin AS, Modiano J, Firestone GL (2009) Artemisinin blocks prostate cancer growth and cell cycle progression by disrupting Sp1 interactions with the cyclin-dependent kinase-4 (CDK4) promoter and inhibiting CDK4 gene expression. J Biol Chem 284(4):2203–2213
World Health Organization (2006) Guidelines for the treatment of malaria. World Health Organization
Xu H, He Y, Yang X, Liang L, Zhan Z, Ye Y, Sun L et al (2007) Anti-malarial agent artesunate inhibits TNF-α-induced production of proinflammatory cytokines via inhibition of NF-κB and PI3 kinase/Akt signal pathway in human rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Rheumatology 46(6):920–926
Xu Q, Li ZX, Peng HQ, Sun ZW, Cheng RL, Ye ZM, Li WX (2011) Artesunate inhibits growth and induces apoptosis in human osteosarcoma HOS cell line in vitro and in vivo. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B 12(4):247–255
Yang L, Tian W et al (2014) Resveratrol plays dual roles in pancreatic cancer cells[J]. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 140(5):749–755
Zhang J, Tong N, Chen Y, Li P, Yang S, Zhao X (2013) Resveratrol protects against vinorelbine-induced vascular endothelial cell injury. Toxicol Mech Methods 23(9):665–671
Zhao L, Wientjes MG, Au JL (2004) Evaluation of combination chemotherapy integration of nonlinear regression, curve shift, isobologram, and combination index analyses. Clin Cancer Res 10(23):7994–8004
Zhao XY, Li GY, Liu Y, Chai LM, Chen JX, Zhang Y, Yang BF (2008) Resveratrol protects against arsenic trioxide-induced cardiotoxicity in vitro and in vivo. Br J Pharmacol 154(1):105–113
Zhou S, Guo Y, Wang X, Wang PJ, Zhang B (2014) Effects of resveratrol on oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) cells in vitro. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 140:371–374
Zhu HL, Huang X (2011) Resveratrol and its analogues: promising antitumor agents. Anti-Cancer Agents in Medicinal Chemistry (Formerly Current Medicinal Chemistry-Anti-Cancer Agents) 11(5):479–490
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81001454), the fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (XDJK2014B024), and the Fund for Construction of Scientific and Technical Innovation of Chongqing (CSTC, 2009CB1010).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
J. Zhang and X. Zhao contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, P., Yang, S., Dou, M. et al. Synergic effects of artemisinin and resveratrol in cancer cells. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 140, 2065–2075 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-014-1771-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-014-1771-7