Abstract
Background
The efficacy of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) differs in patients with lung adenocarcinoma harboring EGFR-activating mutations. Although lung adenocarcinoma with EGFR-activating mutations has heterogeneous morphologic features, the predictive role of histologic subtype of lung adenocarcinoma with regard to the effectiveness of EGFR-TKIs in patients with EGFR-activating mutations has not been well defined.
Methods
Among 134 postoperative recurrence patients with lung adenocarcinoma harboring EGFR-activating mutation (L858R or exon 19 deletion) treated with EGFR-TKIs, we retrospectively analyzed 61 patients treated with EGFR-TKIs as first-line chemotherapy. All the tumors were classified according to the new histologic classification proposed by the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer (IASLC), American Thoracic Society (ATS), and European Respiratory Society (ERS) into the following subtypes: lepidic, papillary, acinar, micropapillary, or solid predominant subtype. We evaluated the correlation between the histologic subtype and the clinical efficacy of EGFR-TKIs.
Results
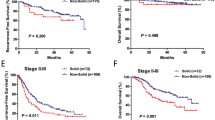
In overall response rate, adenocarcinoma with solid predominant subtype is significantly worse than with non-solid predominant subtype (61 vs. 88 %, P = 0.03). The median progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival after EGFR-TKI treatment were significantly shorter for the patients with solid predominant subtype than for those with non-solid predominant subtype (median PFS of 7.7 vs. 13.5 months, P = 0.002, and median OS of 21.5 vs. 31.0 months, P = 0.028).
Conclusions
This study indicated that among patients with lung adenocarcinoma harboring activating EGFR mutations treated with EGFR-TKIs, solid predominant subtype according to IASLC/ATS/ERS classification is a response predictor for EGFR-TKI.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- EGFR:
-
Epidermal growth factor receptor
- TKI:
-
Tyrosine kinase inhibitor
- NSCLC:
-
Non-small cell lung cancer
- PFS:
-
Progression-free survival
- IASLC:
-
International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer
- ATS:
-
American Thoracic Society
- ERS:
-
European Respiratory Society
- RECIST:
-
Response evaluation criteria solid tumor criteria
- ORR:
-
Objective response rate
- OS:
-
Overall survival
- HR:
-
Hazard ratio
- CI:
-
Confidence interval
- HGF:
-
Hepatocyte growth factor
References
Azuma K, Okamoto I, Kawahara A, Taira T, Nakashima K, Hattori S, Kinoshita T, Takeda M, Nakagawa K, Takamori S, Kuwano M, Ono M, Kage M (2012) Association of the expression of mutant epidermal growth factor receptor protein as determined with mutation-specific antibodies in non-small cell lung cancer with progression-free survival after gefitinib treatment. J Thorac Oncol 7(1):122–127. doi:10.1097/JTO.0b013e31822eeba2
Bean J, Brennan C, Shih JY, Riely G, Viale A, Wang L, Chitale D, Motoi N, Szoke J, Broderick S, Balak M, Chang WC, Yu CJ, Gazdar A, Pass H, Rusch V, Gerald W, Huang SF, Yang PC, Miller V, Ladanyi M, Yang CH, Pao W (2007) MET amplification occurs with or without T790M mutations in EGFR mutant lung tumors with acquired resistance to gefitinib or erlotinib. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104(52):20932–20937. doi:10.1073/pnas.0710370104
Birchmeier C, Birchmeier W, Gherardi E, Vande Woude GF (2003) Met, metastasis, motility and more. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 4(12):915–925. doi:10.1038/nrm1261
Calvo E, Baselga J (2006) Ethnic differences in response to epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors. J Clin Oncol 24(14):2158–2163. doi:10.1200/JCO.2006.06.5961
Cappuzzo F, Janne PA, Skokan M, Finocchiaro G, Rossi E, Ligorio C, Zucali PA, Terracciano L, Toschi L, Roncalli M, Destro A, Incarbone M, Alloisio M, Santoro A, Varella-Garcia M (2009) MET increased gene copy number and primary resistance to gefitinib therapy in non-small-cell lung cancer patients. Ann Oncol 20(2):298–304. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdn635
Eisenhauer EA, Therasse P, Bogaerts J, Schwartz LH, Sargent D, Ford R, Dancey J, Arbuck S, Gwyther S, Mooney M, Rubinstein L, Shankar L, Dodd L, Kaplan R, Lacombe D, Verweij J (2009) New response evaluation criteria in solid tumours: revised RECIST guideline (version 1.1). Eur J Cancer 45(2):228–247. doi:10.1016/j.ejca.2008.10.026
Engelman JA, Zejnullahu K, Mitsudomi T, Song Y, Hyland C, Park JO, Lindeman N, Gale CM, Zhao X, Christensen J, Kosaka T, Holmes AJ, Rogers AM, Cappuzzo F, Mok T, Lee C, Johnson BE, Cantley LC, Janne PA (2007) MET amplification leads to gefitinib resistance in lung cancer by activating ERBB3 signaling. Science 316(5827):1039–1043. doi:10.1126/science.1141478
Herbst RS, Heymach JV, Lippman SM (2008) Lung cancer. N Engl J Med 359(13):1367–1380. doi:10.1056/NEJMra0802714
Jackman D, Pao W, Riely GJ, Engelman JA, Kris MG, Janne PA, Lynch T, Johnson BE, Miller VA (2010) Clinical definition of acquired resistance to epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors in non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol 28(2):357–360. doi:10.1200/JCO.2009.24.7049
Kobayashi S, Boggon TJ, Dayaram T, Janne PA, Kocher O, Meyerson M, Johnson BE, Eck MJ, Tenen DG, Halmos B (2005) EGFR mutation and resistance of non-small-cell lung cancer to gefitinib. N Engl J Med 352(8):786–792. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa044238
Kosaka T, Yatabe Y, Endoh H, Kuwano H, Takahashi T, Mitsudomi T (2004) Mutations of the epidermal growth factor receptor gene in lung cancer: biological and clinical implications. Cancer Res 64(24):8919–8923. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-2818
Kosaka T, Yatabe Y, Endoh H, Yoshida K, Hida T, Tsuboi M, Tada H, Kuwano H, Mitsudomi T (2006) Analysis of epidermal growth factor receptor gene mutation in patients with non-small cell lung cancer and acquired resistance to gefitinib. Clin Cancer Res 12(19):5764–5769. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-06-0714
Lynch TJ, Bell DW, Sordella R, Gurubhagavatula S, Okimoto RA, Brannigan BW, Harris PL, Haserlat SM, Supko JG, Haluska FG, Louis DN, Christiani DC, Settleman J, Haber DA (2004) Activating mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor underlying responsiveness of non-small-cell lung cancer to gefitinib. N Engl J Med 350(21):2129–2139. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa040938
Maemondo M, Inoue A, Kobayashi K, Sugawara S, Oizumi S, Isobe H, Gemma A, Harada M, Yoshizawa H, Kinoshita I, Fujita Y, Okinaga S, Hirano H, Yoshimori K, Harada T, Ogura T, Ando M, Miyazawa H, Tanaka T, Saijo Y, Hagiwara K, Morita S, Nukiwa T (2010) Gefitinib or chemotherapy for non-small-cell lung cancer with mutated EGFR. N Engl J Med 362(25):2380–2388. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa0909530
Maheswaran S, Sequist LV, Nagrath S, Ulkus L, Brannigan B, Collura CV, Inserra E, Diederichs S, Iafrate AJ, Bell DW, Digumarthy S, Muzikansky A, Irimia D, Settleman J, Tompkins RG, Lynch TJ, Toner M, Haber DA (2008) Detection of mutations in EGFR in circulating lung-cancer cells. N Engl J Med 359(4):366–377. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa0800668
Mitsudomi T, Kosaka T, Endoh H, Horio Y, Hida T, Mori S, Hatooka S, Shinoda M, Takahashi T, Yatabe Y (2005) Mutations of the epidermal growth factor receptor gene predict prolonged survival after gefitinib treatment in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer with postoperative recurrence. J Clin Oncol 23(11):2513–2520. doi:10.1200/JCO.2005.00.992
Mitsudomi T, Morita S, Yatabe Y, Negoro S, Okamoto I, Tsurutani J, Seto T, Satouchi M, Tada H, Hirashima T, Asami K, Katakami N, Takada M, Yoshioka H, Shibata K, Kudoh S, Shimizu E, Saito H, Toyooka S, Nakagawa K, Fukuoka M (2010) Gefitinib versus cisplatin plus docetaxel in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer harbouring mutations of the epidermal growth factor receptor (WJTOG3405): an open label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol 11(2):121–128. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(09)70364-X
Mok TS, Wu YL, Thongprasert S, Yang CH, Chu DT, Saijo N, Sunpaweravong P, Han B, Margono B, Ichinose Y, Nishiwaki Y, Ohe Y, Yang JJ, Chewaskulyong B, Jiang H, Duffield EL, Watkins CL, Armour AA, Fukuoka M (2009) Gefitinib or carboplatin-paclitaxel in pulmonary adenocarcinoma. N Engl J Med 361(10):947–957. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa0810699
Motoi N, Szoke J, Riely GJ, Seshan VE, Kris MG, Rusch VW, Gerald WL, Travis WD (2008) Lung adenocarcinoma: modification of the 2004 WHO mixed subtype to include the major histologic subtype suggests correlations between papillary and micropapillary adenocarcinoma subtypes, EGFR mutations and gene expression analysis. Am J Surg Pathol 32(6):810–827. doi:10.1097/PAS.0b013e31815cb162
Paez JG, Janne PA, Lee JC, Tracy S, Greulich H, Gabriel S, Herman P, Kaye FJ, Lindeman N, Boggon TJ, Naoki K, Sasaki H, Fujii Y, Eck MJ, Sellers WR, Johnson BE, Meyerson M (2004) EGFR mutations in lung cancer: correlation with clinical response to gefitinib therapy. Science 304(5676):1497–1500. doi:10.1126/science.1099314
Pao W, Miller VA, Politi KA, Riely GJ, Somwar R, Zakowski MF, Kris MG, Varmus H (2005) Acquired resistance of lung adenocarcinomas to gefitinib or erlotinib is associated with a second mutation in the EGFR kinase domain. Plos Med 2(3):e73. doi:10.1371/journal.pmed.0020073
Rosell R, Carcereny E, Gervais R, Vergnenegre A, Massuti B, Felip E, Palmero R, Garcia-Gomez R, Pallares C, Sanchez JM, Porta R, Cobo M, Garrido P, Longo F, Moran T, Insa A, De Marinis F, Corre R, Bover I, Illiano A, Dansin E, de Castro J, Milella M, Reguart N, Altavilla G, Jimenez U, Provencio M, Moreno MA, Terrasa J, Munoz-Langa J, Valdivia J, Isla D, Domine M, Molinier O, Mazieres J, Baize N, Garcia-Campelo R, Robinet G, Rodriguez-Abreu D, Lopez-Vivanco G, Gebbia V, Ferrera-Delgado L, Bombaron P, Bernabe R, Bearz A, Artal A, Cortesi E, Rolfo C, Sanchez-Ronco M, Drozdowskyj A, Queralt C, de Aguirre I, Ramirez JL, Sanchez JJ, Molina MA, Taron M, Paz-Ares L (2012) Erlotinib versus standard chemotherapy as first-line treatment for European patients with advanced EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (EURTAC): a multicentre, open-label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol 13(3):239–246. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(11)70393-X
Russell PA, Wainer Z, Wright GM, Daniels M, Conron M, Williams RA (2011) Does lung adenocarcinoma subtype predict patient survival?: a clinicopathologic study based on the new International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer/American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society international multidisciplinary lung adenocarcinoma classification. J Thorac Oncol 6(9):1496–1504. doi:10.1097/JTO.0b013e318221f701
Sica G, Yoshizawa A, Sima CS, Azzoli CG, Downey RJ, Rusch VW, Travis WD, Moreira AL (2010) A grading system of lung adenocarcinomas based on histologic pattern is predictive of disease recurrence in stage I tumors. Am J Surg Pathol 34(8):1155–1162. doi:10.1097/PAS.0b013e3181e4ee32
Su KY, Chen HY, Li KC, Kuo ML, Yang JC, Chan WK, Ho BC, Chang GC, Shih JY, Yu SL, Yang PC (2012) Pretreatment epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) T790M mutation predicts shorter EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor response duration in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol 30(4):433–440. doi:10.1200/JCO.2011.38.3224
Takano T, Ohe Y, Sakamoto H, Tsuta K, Matsuno Y, Tateishi U, Yamamoto S, Nokihara H, Yamamoto N, Sekine I, Kunitoh H, Shibata T, Sakiyama T, Yoshida T, Tamura T (2005) Epidermal growth factor receptor gene mutations and increased copy numbers predict gefitinib sensitivity in patients with recurrent non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol 23(28):6829–6837. doi:10.1200/JCO.2005.01.0793
Toyooka S, Matsuo K, Shigematsu H, Kosaka T, Tokumo M, Yatabe Y, Ichihara S, Inukai M, Suehisa H, Soh J, Kiura K, Fong KM, Lee H, Wistuba II, Gazdar AF, Mitsudomi T, Date H (2007) The impact of sex and smoking status on the mutational spectrum of epidermal growth factor receptor gene in non small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res 13(19):5763–5768. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-07-0216
Travis WD, Brambilla E, Noguchi M, Nicholson AG, Geisinger KR, Yatabe Y, Beer DG, Powell CA, Riely GJ, Van Schil PE, Garg K, Austin JH, Asamura H, Rusch VW, Hirsch FR, Scagliotti G, Mitsudomi T, Huber RM, Ishikawa Y, Jett J, Sanchez-Cespedes M, Sculier JP, Takahashi T, Tsuboi M, Vansteenkiste J, Wistuba I, Yang PC, Aberle D, Brambilla C, Flieder D, Franklin W, Gazdar A, Gould M, Hasleton P, Henderson D, Johnson B, Johnson D, Kerr K, Kuriyama K, Lee JS, Miller VA, Petersen I, Roggli V, Rosell R, Saijo N, Thunnissen E, Tsao M, Yankelewitz D (2011) International association for the study of lung cancer/american thoracic society/european respiratory society international multidisciplinary classification of lung adenocarcinoma. J Thorac Oncol 6(2):244–285. doi:10.1097/JTO.0b013e318206a221
Tsuta K, Kozu Y, Mimae T, Yoshida A, Kohno T, Sekine I, Tamura T, Asamura H, Furuta K, Tsuda H (2012) c-MET/phospho-MET protein expression and MET gene copy number in non-small cell lung carcinomas. J Thorac Oncol 7(2):331–339. doi:10.1097/JTO.0b013e318241655f
Turke AB, Zejnullahu K, Wu YL, Song Y, Dias-Santagata D, Lifshits E, Toschi L, Rogers A, Mok T, Sequist L, Lindeman NI, Murphy C, Akhavanfard S, Yeap BY, Xiao Y, Capelletti M, Iafrate AJ, Lee C, Christensen JG, Engelman JA, Janne PA (2010) Preexistence and clonal selection of MET amplification in EGFR mutant NSCLC. Cancer Cell 17(1):77–88. doi:10.1016/j.ccr.2009.11.022
Wang W, Li Q, Yamada T, Matsumoto K, Matsumoto I, Oda M, Watanabe G, Kayano Y, Nishioka Y, Sone S, Yano S (2009) Crosstalk to stromal fibroblasts induces resistance of lung cancer to epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Clin Cancer Res 15(21):6630–6638. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-09-1001
Warth A, Muley T, Meister M, Stenzinger A, Thomas M, Schirmacher P, Schnabel PA, Budczies J, Hoffmann H, Weichert W (2012) The novel histologic International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer/American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society classification system of lung adenocarcinoma is a stage-independent predictor of survival. J Clin Oncol 30(13):1438–1446. doi:10.1200/JCO.2011.37.2185
Yamada T, Takeuchi S, Kita K, Bando H, Nakamura T, Matsumoto K, Yano S (2012) Hepatocyte growth factor induces resistance to anti-epidermal growth factor receptor antibody in lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol 7(2):272–280. doi:10.1097/JTO.0b013e3182398e69
Yano S, Wang W, Li Q, Matsumoto K, Sakurama H, Nakamura T, Ogino H, Kakiuchi S, Hanibuchi M, Nishioka Y, Uehara H, Mitsudomi T, Yatabe Y, Sone S (2008) Hepatocyte growth factor induces gefitinib resistance of lung adenocarcinoma with epidermal growth factor receptor-activating mutations. Cancer Res 68(22):9479–9487. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-1643
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by National Cancer Center Research and Development Fund (23-A-12 and 23-K-18), the Foundation for the Promotion of Cancer Research, 3rd-Term Comprehensive 10-Year Strategy for Cancer Control, Program for the Promotion of Fundamental Studies in Health Sciences of the National Institute of Biomedical Innovation, and JSPS KAKENHI (24659185).
Conflict of interest
All authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yoshida, T., Ishii, G., Goto, K. et al. Solid predominant histology predicts EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor response in patients with EGFR mutation-positive lung adenocarcinoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 139, 1691–1700 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-013-1495-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-013-1495-0