Abstract
Purpose
This work employs pharmacological targeting of phosphoinositide 3-kinases (PI3K) in selected neuroblastoma (NB) tumors with the inhibitor AS605240, which has been shown to express low toxicity and relative specificity for the PI3K species γ.
Methods
The expression pattern of PI3K isoforms in 7 NB cell lines and 14 tumor patient samples was determined by Western blotting and immunocytochemistry. The effect of AS605240 on the growth of four selected tumor cell lines was assessed. Two cell lines exhibiting (SK-N-LO) or lacking (SK-N-AS) PI3Kγ expression were chosen for further in vitro analysis, which involved propidium iodide (PI)-based cell cycle staining, terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase–mediated dUTP-biotin nick end labeling (TUNEL-staining) of apoptotic cells and analysis of PI3K/Akt-related signaling pathways via Western blotting and translocation experiments. The action of AS605240 in vivo was addressed by xenograft experiments in severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID) mice, thereby comparing SK-N-LO and SK-N-AS derived tumors. Apoptosis induced in SK-N-LO tumors was shown by immunohistochemical TUNEL-staining.
Results
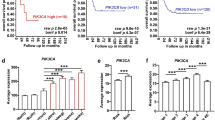
Significant expression of PI3Kγ in neuroblastoma patient biopsies and tumor cell lines was detected. AS605240 induced apoptosis in NB cell lines proportional to this expression and suppressed growth of PI3Kγ positive, but not negative, tumors in a xenograft mouse model. No adverse effects of the inhibitor treatment were observed.
Conclusions
Our observations hint to an oncogenic function of PI3Kγ in distinct neuroblastoma entities and reveal PI3K targeting by AS605240 as a promising molecular therapy of these tumors.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ambros PF, Ambros IM, Brodeur GM et al (2009) International consensus for neuroblastoma molecular diagnostics: report from the international neuroblastoma risk group (INRG) biology committee. Br J Cancer 100(9):1471–1482
Barbier M, Attoub S, Calvez R et al (2001) Tumour biology. Weakening link to colorectal cancer? Nature 413(6858):796
Billottet C, Grandage VL, Gale RE et al (2006) A selective inhibitor of the p110delta isoform of PI 3-kinase inhibits AML cell proliferation and survival and increases the cytotoxic effects of VP16. Oncogene 25(50):6648–6659
Birkenkamp KU, Coffer PJ (2003) FOXO transcription factors as regulators of immune homeostasis: molecules to die for? J Immunol 171(4):1623–1629
Camps M, Ruckle T, Ji H et al (2005) Blockade of PI3Kgamma suppresses joint inflammation and damage in mouse models of rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Med 11(9):936–943
Cohn SL, Pearson AD, London WB et al (2009) The international neuroblastoma risk group (INRG) classification system: an INRG task force report. J Clin Oncol 27(2):289–297
Denley A, Kang S, Karst U, Vogt PK (2008) Oncogenic signaling of class I PI3K isoforms. Oncogene 27(18):2561–2574
Dunn T, Praissman L, Hagag N, Viola MV (1994) ERG gene is translocated in an Ewing’s sarcoma cell line. Cancer Genet Cytogenet 76(1):19–22
Hirsch E, Ciraolo E, Ghigo A, Costa C (2008) Taming the PI3K team to hold inflammation and cancer at bay. Pharmacol Ther 118(2):192–205
Horn S, Bergholz U, Jucker M et al (2008) Mutations in the catalytic subunit of class IA PI3K confer leukemogenic potential to hematopoietic cells. Oncogene 27(29):4096–4106
Johnson EE, Lum HD, Rakhmilevich AL et al (2008) Intratumoral immunocytokine treatment results in enhanced antitumor effects. Cancer Immunol Immunother 57(12):1891–1902
Kang S, Denley A, Vanhaesebroeck B, Vogt PK (2006) Oncogenic transformation induced by the p110beta, -gamma, and -delta isoforms of class I phosphoinositide 3-kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103(5):1289–1294
Maris JM, Hogarty MD, Bagatell R, Cohn SL (2007) Neuroblastoma. Lancet 369(9579):2106–2120
Marone R, Cmiljanovic V, Giese B, Wymann MP (2008) Targeting phosphoinositide 3-kinase: moving towards therapy. Biochim Biophys Acta 1784(1):159–185
Opel D, Poremba C, Simon T et al (2007) Activation of Akt predicts poor outcome in neuroblastoma. Cancer Res 67(2):735–745
Parashar B, Shafit-Zagardo B (2006) Inhibition of human neuroblastoma in SCID mice by low-dose of selective Cox-2 inhibitor nimesulide. J Neurooncol 78(2):129–134
Patrucco E, Notte A, Barberis L et al (2004) PI3Kgamma modulates the cardiac response to chronic pressure overload by distinct kinase-dependent and -independent effects. Cell 118(3):375–387
Samuels Y, Wang Z, Bardelli A et al (2004) High frequency of mutations of the PIK3CA gene in human cancers. Science 304(5670):554
Sasaki T, Irie-Sasaki J, Horie Y et al (2000) Colorectal carcinomas in mice lacking the catalytic subunit of PI(3)Kgamma. Nature 406(6798):897–902
Sasaki T, Irie-Sasaki J, Horie Y et al (2003) Corrigendum: colorectal carcinomas in mice lacking the catalytic subunit of PI(3)Kgamma. Nature 426(6966):584
Sims TL, Williams RF, Ng CY et al (2008) Bevacizumab suppresses neuroblastoma progression in the setting of minimal disease. Surgery 144(2):269–275
Smith LD, Hickman ES, Parry RV et al (2007) PI3Kgamma is the dominant isoform involved in migratory responses of human T lymphocytes: effects of ex vivo maintenance and limitations of non-viral delivery of siRNA. Cell Signal 19(12):2528–2539
Stoyanov B, Volinia S, Hanck T et al (1995) Cloning and characterization of a G protein-activated human phosphoinositide-3 kinase. Science 269(5224):690–693
Wang J, Tucker LA, Stavropoulos J et al (2008) Correlation of tumor growth suppression and methionine aminopetidase-2 activity blockade using an orally active inhibitor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105(6):1838–1843
Wetzker R, Rommel C (2004) Phosphoinositide 3-kinases as targets for therapeutic intervention. Curr Pharm Des 10(16):1915–1922
Wymann MP, Schneiter R (2008) Lipid signalling in disease. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 9(2):162–176
Zhao L, Vogt PK (2008) Class I PI3K in oncogenic cellular transformation. Oncogene 27(41):5486–5496
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Deutsche Krebshilfe and Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft SFB 604. The authors gratefully acknowledge significant contributions of Christian Rommel (San Diego) and Thomas Ruckle (Geneva) in the initial state of this study and the kind support of the histochemical department of the FLI (Jena) and Bernhard Schlott (Jena) for providing the p53 antibody.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
V. Spitzenberg and C. König are contributed equally.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Spitzenberg, V., König, C., Ulm, S. et al. Targeting PI3K in neuroblastoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 136, 1881–1890 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-010-0847-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-010-0847-2