Abstract
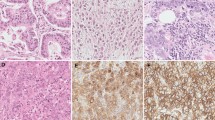
The aim of the present study was to correlate tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TIL) with bladder cancer recurrence in patients with solitary low-grade non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer (NMIBC). We retrospectively identified from the institutional database 115 patients with solitary low-grade NMIBC after transurethral resection (TURBT) without adjuvant therapy and with complete follow-up, between 1996 and 2006. Tumor specimens were retrieved and tissue microarrays were constructed. Patients were divided in two groups: those who developed recurrent disease (n = 69) and those without recurrence (n = 46) during a follow-up period of a minimum of 5 years. Immunohistochemical staining for TIL with anti-CD3, CD4, CD8, CD20, CD56, CD68, and granzyme B (GrB) was performed. Student’s t test, Mann–Whitney U test, as well as uni- and multivariate analyses were applied to compare the two patient groups. TIL were predominantly observed in cancer stroma. The number of CD3+ and CD8+ lymphocytes observed in the non-recurrent group of patients was lower than that in recurrent patients (p = 0.0001, p = 0.0002, respectively). Also, in uni- and multivariate analyses, levels of CD3+ TIL (OR = 5.4035; p = 0.0001 and OR = 5.8280; p = 0.0102) and CD8+ TIL (OR = 3.2857; p = 0.0036 and OR = 5.3257; p = 0.0092) showed prognostic value with regard to NMIBC recurrence. Our results suggest that CD3+ and CD8+ TIL are predictive of bladder cancer recurrence in patients with solitary low-grade NMIBC which might facilitate identification of patients with higher risk of recurrence. However, prospective validating studies have to confirm these results before immunohistochemical staining for CD3 and CD8 TIL can be included in the clinical workup of these patients.

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AUC:
-
Area under the curve
- CD:
-
Cluster of differentiation
- CI:
-
Confidence interval
- HR:
-
Hazard ratio
- NMIBC:
-
Non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer
- OR:
-
Odds ratio
- TIL:
-
Tumor-infiltrating leukocytes
- TURBT:
-
Transurethral resection of bladder tumor
References
Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A (2012) Cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin 62:10–29
Knowles MA (2008) Molecular pathogenesis of bladder cancer. Int J Clin Oncol 13:287–297
Kikuchi E, Fujimoto H, Mizutani Y, Okajima E, Koga H, Hinotsu S, Shinohara N, Oya M, Miki T, Cancer Registration Committee of the Japanese Urological Association (2009) Clinical outcome of tumor recurrence for Ta, T1 non-muscle invasive bladder cancer from the data on registered bladder cancer patients in Japan: 1999–2001 report from the Japanese Urological Association. Int J Urol 16(3):279–86
Bryan RT, Collins SI, Daykin MC, Zeegers MP, Cheng KK, Wallace DM, Sole GM (2010) Mechanisms of recurrence of Ta/T1 bladder cancer. Ann R Coll Surg Engl 92(6):519–24
Sylvester RJ, van der Meijden AP, Oosterlinck W, Witjes JA, Bouffioux C, Denis L, Newling DW, Kurth K (2006) Predicting recurrence and progression in individual patients with stage Ta T1 bladder cancer using EORTC risk tables: a combined analysis of 2596 patients from seven EORTC trials. Eur Urol 49:466–477
Lv S, Turlova E, Zhao S, Kang H, Han M, Sun HS (2014) Prognostic and clinicopathological significance of survivin expression in bladder cancer patients: a meta-analysis. Tumor Biol 35(2):1565–1574
Zachos I, Tzortzis V, Mitrakas L, Samarinas M, Karatzas A, Gravas S, Vandoros GP, Melekos MD, Papavassiliou AG (2014) Tumor size and T stage correlate independently with recurrence and progression in high-risk non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer patients treated with adjuvant BCG. Tumor Biol 35(5):4185–4189
Wieder T, Braumüller H, Kneilling M, Pichler B, Röcken M (2008) T cell-mediated help against tumors. Cell Cycle 7(19):2974–2977
Liakou CI, Narayanan S, Ng Tang D, Logothetis CJ, Sharma P (2007) Focus on TILs: prognostic significance of tumor infiltrating lymphocytes in human bladder cancer. Cancer Immun 7:10–16
Lipponen PK, Eskelinen MJ, Jauhiainen K, Harju E, Terho R (1993) Tumour infiltrating lymphocytes as an independent prognostic factor in transitional cell bladder cancer. Eur J Cancer 29A(1):69–75
Gakis G, Todenhöfer T, Renninger M, Schilling D, Sievert KD, Schwentner C, Stenzl A (2011) Development of a new outcome prediction model in carcinoma invading the bladder based on preoperative serum C-reactive protein and standard pathological risk factors: the TNR-C score. BJU Int 108(11):1800–1805
Agarwal A, Verma S, Burra U, Murthy NS, Mohanty NK, Saxena S (2006) Flow cytometric analysis of Th1 and Th2 cytokines in PBMCs as a parameter of immunological dysfunction in patients of superficial transitional cell carcinoma of bladder. Cancer Immunol Immunother 55:734–743
Loskog A, Ninalga C, Paul-Wetterberg G, de laTorre M, Malmstrom PU, Totterman TH (2007) Human bladder carcinoma is dominated by T-regulatory cells and Th1 inhibitory cytokines. J Urol 177:353–358
Ebelt K, Babaryka G, Figel AM, Pohla H, Buchner A, Stief CG, Eisenmenger W, Kirchner T, Schendel DJ, Noessner E (2008) Dominance of CD4+ lymphocytic infiltrates with disturbed effector cell characteristics in the tumor microenvironment of prostate carcinoma. Prostate 68:1–10
Adler AJ (2007) Mechanisms of T cell tolerance and suppression in cancer mediated by tumor-associated antigens and hormones. Curr Cancer Drug Targets 7:3–14
Leong PP, Mohammad RI, Ibrahim N, Abdalla NH, Davis WC, Scow HF (2006) Phenotyping of lymphocytes expressing regulatory and effector markers in infiltrating ductal carcinoma of the breast. Immunol Lett 102(2):229–236
Unitt E, Rushbrook SM, Marshal A, Davies S, Gibbs P, Morris LS (2005) Compromised lymphocytes infiltrate hepatocellular carcinoma, the role of T-regulatory cells. Hepatol 41(4):700–2
Lamagna C, Aurrand-Lions M, Imhof BA (2006) Dual role of macrophages in tumor growth and angiogenesis. Step of the angiogenesis cascade. J Leukoc Biol 80:705–713
Stout RD, Watkins SK, Suttles J (2009) Functional plasticity of macrophages: in situ reprogramming of tumor-associated macrophages. J Leukoc Biol 86:1105–1109
Ayari C, Larue H, Hovington H, Decobert M, Harel F, Bergeron A, Têtu B, Lacombe L, Fradet Y (2009) Bladder tumor infiltrating mature dendritic cells and macrophages as predictors of response to Bacillus Calmette-Guerin immunotherapy. Eur Urol 55(6):1386–1396
Koide N, Nishio A, Sato T, Sugiyama A, Miyagawa S (2004) Significance of macrophage chemoattractant protein-1 expression and macrophage infiltration in squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus. Am J Gastroenterol 99:1667–74
Ishigami S, Natsugoe S, Tokuda K (2003) Tumor-associated macrophage (TAM) infiltration in gastric cancer. Anticancer Res 23:4079–83
Acknowledgments
We would like to express our gratitude to Ozren Štanfel, Ankica Brajenić, and Ivan Dašek for the excellent technical assistance.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Krpina, K., Babarović, E. & Jonjić, N. Correlation of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes with bladder cancer recurrence in patients with solitary low-grade urothelial carcinoma. Virchows Arch 467, 443–448 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00428-015-1808-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00428-015-1808-6