Abstract
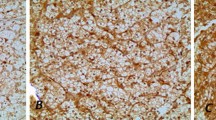
p27 (p27/kip1) is involved in cell-cycle control, and loss of p27 expression may result in tumour development and/or progression. Association with Skp2 targets p27 for degradation. Using a tissue microarray technique, 171 primary renal cell carcinomas (RCCs) and 58 RCC metastases were immunostained for p27 and Skp2. p27 Immunoreactivity was noted in 83 of 129 (64%) clear cell, 6 of 22 (27%) chromophobe and 15 of 20 (75%) papillary tumours as well as 44 of 58 (76%) metastases. In clear cell cancers, high p27 expression (≥50% of tumour cells) decreased with rising tumour stage (50% pT1/pT2 versus 20% pT3; P<0.001) and grade (44% G1/G2 versus 21% G3/G4; P=0.008). None of 22 chromophobe cancers showed high expression in contrast to 46 of 129 (36%) clear cell tumours (P<0.001). Skp2 expression was noted in 8 of 129 (6%) clear cell cancers and 11 of 55 (20%) metastases (P=0.008). Immunoreactivity increased with rising tumour stage (1% pT1/pT2 versus 11% pT3; P=0.03) and grade (1% G1/G2 versus 15% G3/G4; P=0.004) and was associated with sarcomatoid morphology (P<0.001). In multivariate analysis, patients with low p27 expression and Skp2 immunoreactivity in clear cell cancers had a less favourable outcome. In conclusion, p27 and Skp2 proved to be additional biomarkers in renal cancer pathology with both prognostic and diagnostic impact.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ben-Izhak O, Lahaz-Baratz S, Meretyk S, Ben-Eliezer S, Sabo E, Dirnfeld M, Cohen S, Ciechanover A (2003) Inverse relationship between Skp2 ubiquitin ligase and the cyclin dependent kinase inhibitor p27kip1 in prostate cancer. J Urol 170:241–245
Carrano AC, Pagano M (2001) Role of the F-box protein Skp2 in adhesion-dependent cell cycle progression. J Cell Biol 153:1381–1389
Carrano AC, Eytan E, Hershko A, Pagano M (1999) Skp2 is required for ubiquitin-mediated degradation of the CDK inhibitor p27. Nat Cell Biol 1:193–199
Cheville JC, Lohse CM, Zincke H, Weaver AL, Blute ML (2003) Comparison of outcome and prognostic features among histologic subtypes of renal cell carcinoma. Am J Surg Pathol 27:612–624
Chiarle R, Fan Y, Piva R, Boggino H, Skolnik J, Novero D, Palestro G, De Wolf-Peeters C, Chilosi M, Pagano M, Inghirami G (2002) S-phase kinase-associated protein 2 expression in non-Hodgkin’ lymphoma inversely correlates with p27 expression and defines cells in S phase. Am J Pathol 160:1457–1466
Eble JN, Togashi K, Pisani P (2004) Renal cell carcinoma. In: Eble JN, Sauter G, Epstein JI, Sesterhenn IA (eds) World Health Organization classification of tumours. Pathology & genetics, tumours of the urinary system and male genital organs. IARC Press, Lyon, pp 12–43
Fuhrman SA, Lasky LC, Limas C (1982) Prognostic significance of morphologic parameters in renal cell carcinoma. Am J Surg Pathol 6:655–663
Gstaiger M, Jordan R, Lim M, Catzavelos C, Mestan J, Slingerland J, Krek W (2001) Skp2 is oncogenic and overexpressed in human cancers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 98:5043–5048
Haitel A, Wiener HG, Neudert B, Marberger M, Susani M (2001) Expression of the cell cycle proteins p21, p27, and pRb in clear cell renal cell carcinoma and their prognostic significance. Urology 58:477–481
Hara T, Kamura T, Nakayama K, Oshikawa K, Hatekeyama S, Nakayama K (2001) Degradation of p27kip1 at the G0–G1 transition mediated by a skp2-independent ubiquitination pathway. J Biol Chem 276:48937–48943
Hedberg Y, Davoodi E, Ljungberg B, Roos G, Landberg G (2002) Cyclin E and p27 protein content in human renal cell carcinoma: Clinical outcome and associations with cyclin D. Int J Cancer 102:601–607
Hedberg Y, Ljungberg B, Roos G, Landberg G (2003) Expression of cyclin D1, D3, E, and p27 in human renal cell carcinoma analysed by tissue microarray. Br J Cancer 88:1417–1423
Hershko D, Bornstein G, Ben-Izhak O, Carrano A, Pagano M, Krausz MM, Hershko A (2001) Inverse relation between levels of p27kip1 and of its ubiquitin ligase subunit Skp2 in colorectal carcinomas. Cancer 91:1745–1751
Kononen J, Bubendorf L, Kallioniemi A, Barlund M, Schraml P, Leighton S, Torhorst J, Mihatsch MJ, Sauter G, Kallioniemi OP (1998) Tissue microarrays for high-throughput molecular profiling of tumor specimens. Nat Med 4:844–847
Kudo Y, Kitajima S, Sato S, Miyauchi M, Ogawa I, Takata T (2001) High expression of S-phase kinase-interacting protein 2, human F-box protein, correlates with poor prognosis in oral squamous cell carcinomas. Cancer Res 61:7044–7047
Latres E, Chiarle R, Schulman BA, Pavletich NP, Pellicer A, Inghirami G, Pagamo M (2001) Role of the F-box protein Skp2 in lymphomagenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 98:2515–2520
Lim MS, Adamson A, Lin Z, Perez-Ordonez B, Jordan RC, Tripp S, Perkins SL, Elenitoba-Johnson KS (2002) Expression of Skp2, a p27 (Kip1) ubiqitin ligase, in malignant lymphoma: correlation with p27 (Kip1) and proliferation index. Blood 100:2950–2956
Lloyd RV, Erickson LA, Jin L, Kulig E, Qian X, Cheville JC, Scheithauer BW (1999) p27kip1: a multifunctional cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor with prognostic significance in human cancers. Am J Pathol 154:313–323
Masuda TA, Inoue H, Sonoda H, Mine S, Yoshikawa Y, Nakayama T, Nakayama T, Mori M (2002) Clinical and biological significance of S-phase kinase-associated protein 2 (Skp2) gene expression in gastric carcinoma: modulation of malignant phenotype by Skp2 overexpression, possibly via p27 proteolysis. Cancer Res 62:3819–3825
McKay JA, Douglas JJ, Ross VG, Curran S, Ahmed FY, Loane JF, Murray GI, McLeod HL (2000) Expression of cell cycle control proteins in primary colorectal tumors does not always predict expression in lymph node metastases. Clin Cancer Res 6:1113–1118
McLaughlin JK, Lipworth L (2000) Epidemiologic aspects of renal cell cancer. Semin Oncol 27:115–123
Méjean A, Oudard S, Thiounn N (2003) Prognostic factors of renal cell carcinoma. J Urol 169:821–827
Migita T, Oda Y, Naito S, Tsuneyoshi M (2002) Low expression of p27kip1 is associated with tumor size and poor prognosis in patients with renal cell carcinoma. Cancer 94:973–979
Oliveira AM, Okuno SH, Nascimento AG, Lloyd RV (2003) Skp2 protein expression in soft tissue sarcomas. J Clin Oncol 21:722–727
Shigemasa K, Gu L, O’Brien TJ, Ohama K (2003) Skp2 overexpression is a prognostic factor in patients with ovarian adenocarcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 9:1756–1763
Shirane M, Harumiya Y, Ishida N, Hirai A, Miyamoto C, Hatakeyama S, Nakayama K, Kitagawa M (1999) Down-regulation of p27kip1 by two mechanisms, ubiquitin-mediated degradation and proteolytic processing. J Biol Chem 274:13886–13893
Signoretti S, Di Marcotullio L, Richardson A, Ramaswamy S, Isaac B, Rue M, Monti F, Loda M, Pagano M (2002) Oncogenic role of the ubiquitin ligase subunit Skp2 in human breast cancer. J Clin Invest 110:633–641
Sobin LH, Wittekind C (eds) (2002) TNM classification of malignant tumors, 6th edn. Wiley–Liss, Inc., New York
Yang G, Ayala G, De Marzo A, Tian W, FrolovA, Wheeler TM, Thompson TC, Harper JW (2002) Elevated Skp2 protein expression in human prostate cancer: association with loss of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p27 and PTEN and with reduced recurrence-free survival. Clin Cancer Res 8:3419–3426
Yokoi S, Yasui K, Mori M, Iizasa T, Fujisawa T, Inazawa J (2004) Amplification and overexpression of Skp2 are associated with metastasis of non-small-cell lung cancers to lymph nodes. Am J Pathol 165:175–180
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to Mrs. M. Gogg-Kamerer, Mrs. M. Lindbauer, Mrs. A. Sommersacher, Mr. M. Al-Effah and Mr. R. Christof for excellent technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Langner, C., von Wasielewski, R., Ratschek, M. et al. Biological significance of p27 and Skp2 expression in renal cell carcinoma. A systematic analysis of primary and metastatic tumour tissues using a tissue microarray technique. Virchows Arch 445, 631–636 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00428-004-1121-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00428-004-1121-2