Abstract
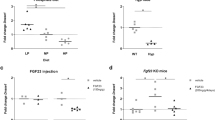
The phosphatonin, secreted frizzled-related protein-4 (sFRP-4), induces phosphaturia and inhibits 25-hydroxyvitamin D 1α-hydroxylase activity normally induced in response to hypophosphatemia. To determine the mechanism by which sFRP-4 alters renal phosphate (Pi) transport, we examined the effect of sFRP-4 on renal brush border membrane (BBMV) Na+-dependent Pi uptake, and the abundance and localization of the major Na+–Pi-IIa co-transporter in proximal tubules and opossum kidney (OK) cells. Infusion of sFRP-4 increased renal fractional excretion of Pi and decreased renal β-catenin concentrations. The increase in renal Pi excretion with sFRP-4 infusion was associated with a 21.9±3.4% decrease in BBMV Na+-dependent Pi uptake (P<0.001) compared with a 39.5±2.1% inhibition of Na+-dependent Pi transport in renal BBMV induced by PTH (P<0.001). sFRP-4 infusion was associated with a 30.7±4.8% decrease in Na+–Pi-IIa co-transporter protein abundance (P<0.01) assessed by immunoblotting methods compared to a 45.4±8.8% decrease induced by PTH (P<0.001). In OK cells, sFRP-4 reduced surface expression of a heterologous Na+–Pi-IIa co-transporter. We conclude that sFRP-4 increases renal Pi excretion by reducing Na+–Pi-IIa transporter abundance in the brush border of the proximal tubule through enhanced internalization of the protein.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Autosomal dominant hypophosphataemic rickets is associated with mutations in FGF23 (2000) Nat Genet 26:345–348
Bacic D, Capuano P, Baum M, Zhang J, Stange G, Biber J, Kaissling B, Moe OW, Wagner CA, Murer H (2005) Activation of dopamine D1-like receptors induces acute internalization of the renal Na+/phosphate cotransporter NaPi-IIa in mouse kidney and OK cells. Am J Physiol Ren Physiol 288:F740–F747
Berndt T, Craig TA, Bowe AE, Vassiliadis J, Reczek D, Finnegan R, Jan De Beur SM, Schiavi SC, Kumar R (2003) Secreted frizzled-related protein 4 is a potent tumor-derived phosphaturic agent. J Clin Invest 112:785–794
Berndt T, Knox FG (1992) Renal regulation of phosphate excretion. Raven Press, New York
Biber J, Murer H (1994) A molecular view of renal Na-dependent phosphate transport. Ren Physiol Biochem 17:212–215
Biber J, Murer H (1993) Towards a molecular view of renal proximal tubular reabsorption of phosphate. Ren Physiol Biochem 16:37–47
Biber J, Stieger B, Haase W, Murer H (1981) A high yield preparation for rat kidney brush border membranes. Different behaviour of lysosomal markers. Biochim Biophys Acta 647:169–176
Bonjour JP, Preston C, Fleisch H (1977) Effect of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 on the renal handling of Pi in thyroparathyroidectomized rats. J Clin Invest 60:1419–1428
Bowe AE, Finnegan R, Jan de Beur SM, Cho J, Levine MA, Kumar R, Schiavi SC (2001) FGF-23 inhibits renal tubular phosphate transport and is a PHEX substrate. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 284:977–981
Cai Q, Hodgson SF, Kao PC, Lennon VA, Klee GG, Zinsmiester AR, Kumar R (1994) Brief report: inhibition of renal phosphate transport by a tumor product in a patient with oncogenic osteomalacia. N Engl J Med 330:1645–1649
Capuano P, Radanovic T, Wagner CA, Bacic D, Kato S, Uchiyama Y, St-Arnoud R, Murer H, Biber J (2005) Intestinal and renal adaptation to a low-Pi diet of type II NaPi cotransporters in vitamin D receptor- and 1alphaOHase-deficient mice. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 288:C429–C434
Carpenter TO, Ellis BK, Insogna KL, Philbrick WM, Sterpka J, Shimkets R (2005) Fibroblast growth factor 7: an inhibitor of phosphate transport derived from oncogenic osteomalacia-causing tumors. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 90:1012–1020
Chen P, Toribara T, Warner H (1956) Microdetermination of phosphorus. Anal Chem 28:1756–1758
Chen TC, Castillo L, Korycka-Dahl M, DeLuca HF (1974) Role of vitamin D metabolites in phosphate transport of rat intestine. J Nutr 104:1056–1060
Custer M, Lotscher M, Biber J, Murer H, Kaissling B (1994) Expression of Na–P(i) cotransport in rat kidney: localization by RT-PCR and immunohistochemistry. Am J Physiol 266:F767–F774
De Beur SM, Finnegan RB, Vassiliadis J, Cook B, Barberio D, Estes S, Manavalan P, Petroziello J, Madden SL, Cho JY, Kumar R, Levine MA, Schiavi SC (2002) Tumors associated with oncogenic osteomalacia express genes important in bone and mineral metabolism. J Bone Miner Res 17:1102–1110
DeLuca HF (2004) Overview of general physiologic features and functions of vitamin D. Am J Clin Nutr 80:1689S–1696S
DeLuca HF (1980) Vitamin D: revisited 1980. Clin Endocrinol Metab 9:1–26
DeLuca HF, Schnoes HK (1983) Vitamin D: recent advances. Annu Rev Biochem 52:411–439
Econs MJ (1999) New insights into the pathogenesis of inherited phosphate wasting disorders. Bone 25:131–135
Econs MJ, Drezner MK (1994) Tumor-induced osteomalacia—unveiling a new hormone. N Engl J Med 330:1679–1681
Führ J, Kazmarczyk J, Krüttgen CD (1955) Eine einfache colorimetrische Methode zur Inulin-Bestimmung für Nieren-clearance-untersuchungen bei StoffwechselGesunden und Diabetikern. Klin Wochenschr 33:729–730
Fukumoto S, Yamashita T (2002) Fibroblast growth factor-23 is the phosphaturic factor in tumor-induced osteomalacia and may be phosphatonin. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 11:385–389
Georgaki H, Puschett JB (1982) Acute effects of a “physiological” dose of 1,25-dihydroxy vitamin D3 on renal phosphate transport. Endocr Res Commun 9:135–143
Hattenhauer O, Traebert M, Murer H, Biber J (1999) Regulation of small intestinal Na–P(i) type IIb cotransporter by dietary phosphate intake. Am J Physiol 277:G756–G762
Helps C, Murer H, McGivan J (1995) Cloning, sequence analysis and expression of the cDNA encoding a sodium-dependent phosphate transporter from the bovine renal epithelial cell line NBL-1. Eur J Biochem 228:927–930
Hernando N, Forster IC, Biber J, Murer H (2000) Molecular characteristics of phosphate transporters and their regulation. Exp Nephrol 8:366–375
Hilfiker H, Hattenhauer O, Traebert M, Forster I, Murer H, Biber J (1998) Characterization of a murine type II sodium-phosphate cotransporter expressed in mammalian small intestine. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:14564–14569
Johnson JA, Kumar R (1994) Vitamin D and renal calcium transport. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 3:424–429
Jonsson KB, Zahradnik R, Larsson T, White KE, Sugimoto T, Imanishi Y, Yamamoto T, Hampson G, Koshiyama H, Ljunggren O, Oba K, Yang IM, Miyauchi A, Econs MJ, Lavigne J, Juppner H (2003) Fibroblast growth factor 23 in oncogenic osteomalacia and X-linked hypophosphatemia. N Engl J Med 348:1656–1663
Karim-Jimenez Z, Hernando N, Biber J, Murer H (2000) A dibasic motif involved in parathyroid hormone-induced down-regulation of the type IIa NaPi cotransporter. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:12896–12901
Kaufmann M, Muff R, Stieger B, Biber J, Murer H, Fischer JA (1994) Apical and basolateral parathyroid hormone receptors in rat renal cortical membranes. Endocrinology 134:1173–1178
Kempson SA, Lotscher M, Kaissling B, Biber J, Murer H, Levi M (1995) Parathyroid hormone action on phosphate transporter mRNA and protein in rat renal proximal tubules. Am J Physiol 268:F784–F791
Keusch I, Traebert M, Lotscher M, Kaissling B, Murer H, Biber J (1998) Parathyroid hormone and dietary phosphate provoke a lysosomal routing of the proximal tubular Na/Pi-cotransporter type II. Kidney Int 54:1224–1232
Kozak SL, Kabat D (1990) Ping-pong amplification of a retroviral vector achieves high-level gene expression: human growth hormone production. J Virol 64:3500–3508
Kumar R (1980) The metabolism of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3. Endocr Rev 1:258–267
Kumar R (2002) New insights into phosphate homeostasis: fibroblast growth factor 23 and frizzled-related protein-4 are phosphaturic factors derived from tumors associated with osteomalacia. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 11:547–553
Kumar R (1997) Phosphatonin—a new phosphaturetic hormone? (lessons from tumour-induced osteomalacia and X-linked hypophosphataemia). Nephrol Dial Transplant 12:11–13
Kumar R (2000) Tumor-induced osteomalacia and the regulation of phosphate homeostasis. Bone 27:333–338
Kumar R, Haugen JD, Wieben ED, Londowski JM, Cai Q (1995) Inhibitors of renal epithelial phosphate transport in tumor-induced osteomalacia and uremia. Proc Assoc Am Physicians 107:296–305
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–685
Larsson T, Marsell R, Schipani E, Ohlsson C, Ljunggren O, Tenenhouse HS, Juppner H, Jonsson KB (2004) Transgenic mice expressing fibroblast growth factor 23 under the control of the alpha1(I) collagen promoter exhibit growth retardation, osteomalacia, and disturbed phosphate homeostasis. Endocrinology 145:3087–3094
Levi M, Kempson SA, Lotscher M, Biber J, Murer H (1996) Molecular regulation of renal phosphate transport. J Membr Biol 154:1–9
Lotscher M, Kaissling B, Biber J, Murer H, Kempson SA, Levi M (1996) Regulation of rat renal Na/Pi-cotransporter by parathyroid hormone: immunohistochemistry. Kidney Int 49:1010–1011
Magagnin S, Werner A, Markovich D, Sorribas V, Stange G, Biber J, Murer H (1993) Expression cloning of human and rat renal cortex Na/Pi cotransport. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:5979–5983
Murer H (1992) Homer Smith award. Cellular mechanisms in proximal tubular Pi reabsorption: some answers and more questions. J Am Soc Nephrol 2:1649–1665
Murer H, Biber J (1995) Molecular mechanisms in renal phosphate reabsorption. Nephrol Dial Transplant 10:1501–1504
Murer H, Biber J (1994) Renal sodium-phosphate cotransport. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 3:504–510
Murer H, Biber J (1993) Structural identification of brush border membrane transport systems—towards an understanding of regulatory mechanisms. Clin Invest 71:852–854
Murer H, Evers C, Stoll R, Kinne R (1977) The effect of parathyroid hormone (PTH) and dietary phosphate on the sodium-dependent phosphate transport system located in the rat renal brush border membrane. Curr Probl Clin Biochem 8:455–462
Murer H, Hernando N, Forster I, Biber J (2001) Molecular aspects in the regulation of renal inorganic phosphate reabsorption: the type IIa sodium/inorganic phosphate co-transporter as the key player. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 10:555–561
Murer H, Hernando N, Forster L, Biber J (2001) Molecular mechanisms in proximal tubular and small intestinal phosphate reabsorption (plenary lecture). Mol Membr Biol 18:3–11
Murer H, Kohler K, Lambert G, Stange G, Biber J, Forster I (2002) The renal type IIa Na/Pi cotransporter: structure-function relationships. Cell Biochem Biophys 36:215–220
Murer H, Lotscher M, Kaissling B, Levi M, Kempson SA, Biber J (1996) Renal brush border membrane Na/Pi-cotransport: molecular aspects in PTH-dependent and dietary regulation. Kidney Int 49:1769–1773
Pfister MF, Hilfiker H, Forgo J, Lederer E, Biber J, Murer H (1998) Cellular mechanisms involved in the acute adaptation of OK cell Na/Pi-cotransport to high- or low-Pi medium. Pflugers Arch 435:713–719
Pfister MF, Ruf I, Stange G, Ziegler U, Lederer E, Biber J, Murer H (1998) Parathyroid hormone leads to the lysosomal degradation of the renal type II Na/Pi cotransporter. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:1909–1914
Puschett JB, Fernandez PC, Boyle IT, Gray RW, Omdahl JL, DeLuca HF (1972) The acute renal tubular effects of 1,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 141:379–384
Puschett JB, Kuhrman MS (1978) Renal tubular effects of 1,25-dihydroxy vitamin D3: interactions with vasopressin and parathyroid hormone in the vitamin D-depleted rat. J Lab Clin Med 92:895–903
Radanovic T, Wagner CA, Murer H, Biber J (2005) Regulation of intestinal phosphate transport. I. Segmental expression and adaptation to low-P(i) diet of the type IIb Na(+)–P(i) cotransporter in mouse small intestine. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 288:G496–G500
Riminucci M, Collins MT, Fedarko NS, Cherman N, Corsi A, White KE, Waguespack S, Gupta A, Hannon T, Econs MJ, Bianco P, Gehron Robey P (2003) FGF-23 in fibrous dysplasia of bone and its relationship to renal phosphate wasting. J Clin Invest 112:683–692
Rizzoli R, Fleisch H, Bonjour JP (1977) Role of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 on intestinal phosphate absorption in rats with a normal vitamin D supply. J Clin Invest 60:639–647
Rowe PS, de Zoysa PA, Dong R, Wang HR, White KE, Econs MJ, Oudet CL (2000) MEPE, a new gene expressed in bone marrow and tumors causing osteomalacia. Genomics 67:54–68
Rowe PS, Kumagai Y, Gutierrez G, Garrett IR, Blacher R, Rosen D, Cundy J, Navvab S, Chen D, Drezner MK, Quarles LD, Mundy GR (2004) MEPE has the properties of an osteoblastic phosphatonin and minhibin. Bone 34:303–319
Schiavi SC, Kumar R (2004) The phosphatonin pathway: new insights in phosphate homeostasis. Kidney Int 65:1–14
Segawa H, Kaneko I, Yamanaka S, Ito M, Kuwahata M, Inoue Y, Kato S, Miyamoto K (2004) Intestinal Na–P(i) cotransporter adaptation to dietary P(i) content in vitamin D receptor null mice. Am J Physiol Ren Physiol 287:F39–F47
Shimada T, Urakawa I, Yamazaki Y, Hasegawa H, Hino R, Yoneya T, Takeuchi Y, Fujita T, Fukumoto S, Yamashita T (2004) FGF-23 transgenic mice demonstrate hypophosphatemic rickets with reduced expression of sodium phosphate cotransporter type IIa. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 314:409–414
Sitara D, Razzaque MS, Hesse M, Yoganathan S, Taguchi T, Erben RG, H JA-P, Lanske B (2004) Homozygous ablation of fibroblast growth factor-23 results in hyperphosphatemia and impaired skeletogenesis, and reverses hypophosphatemia in Phex-deficient mice. Matrix Biol 23:421–432
Stauber A, Radanovic T, Stange G, Murer H, Wagner CA, Biber J (2005) Regulation of intestinal phosphate transport. II. Metabolic acidosis stimulates Na(+)-dependent phosphate absorption and expression of the Na(+)–P(i) cotransporter NaPi-IIb in small intestine. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 288:G501–G506
Steele TH, Engle JE, Tanaka Y, Lorenc RS, Dudgeon KL, DeLuca HF (1975) Phosphatemic action of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3. Am J Physiol 229:489–495
Stoll R, Kinne R, Murer H (1979) Effect of dietary phosphate intake on phosphate transport by isolated rat renal brush-border vesicles. Biochem J 180:465–470
Tanaka Y, Deluca HF (1973) The control of 25-hydroxyvitamin D metabolism by inorganic phosphorus. Arch Biochem Biophys 154:566–574
Towbin H, Staehelin T, Gordon J (1992) Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications, 1979. Biotechnology 24:145–149
Traebert M, Roth J, Biber J, Murer H, Kaissling B (2000) Internalization of proximal tubular type II Na–P(i) cotransporter by PTH: immunogold electron microscopy. Am J Physiol Ren Physiol 278:F148–F154
Verri T, Markovich D, Perego C, Norbis F, Stange G, Sorribas V, Biber J, Murer H (1995) Cloning of a rabbit renal Na–Pi cotransporter, which is regulated by dietary phosphate. Am J Physiol 268:F626–F633
Werner A, Kempson SA, Biber J, Murer H (1994) Increase of Na/Pi-cotransport encoding mRNA in response to low Pi diet in rat kidney cortex. J Biol Chem 269:6637–6639
Werner A, Moore ML, Mantei N, Biber J, Semenza G, Murer H (1991) Cloning and expression of cDNA for a Na/Pi cotransport system of kidney cortex. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:9608–9612
Werner A, Murer H, Kinne RK (1994) Cloning and expression of a renal Na–Pi cotransport system from flounder. Am J Physiol 267:F311–F317
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank Stacy Sommer for assistance in the animal experiments. These studies were supported by NIH grant DK 65830 to R. Kumar, the Swiss National Science Foundation (31-65397.01) to H. Murer, and the sixth European Frame Work EuReGene Project (005085) to C. A. Wagner and H. Murer. Theresa J. Berndt and Bernhard Bielesz contributed equally to this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Berndt, T.J., Bielesz, B., Craig, T.A. et al. Secreted frizzled-related protein-4 reduces sodium–phosphate co-transporter abundance and activity in proximal tubule cells. Pflugers Arch - Eur J Physiol 451, 579–587 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-005-1495-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-005-1495-2