Abstract
Purpose
Anabolic steroid (AS) misuse is widespread amongst recreational bodybuilders; however, their effects on the cardiovascular system are uncertain. Our aim was to document the impact of AS use on cardiac structure, function and the presence of focal fibrosis using the gold standard cardiovascular magnetic resonance imaging (CMR).
Methods
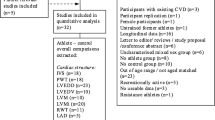
A cross-sectional cohort design was utilised with 21 strength-trained participants who underwent CMR imaging of the heart and speckle-tracking echocardiography. Thirteen participants (30 ± 5 years) taking AS for at least 2 years and currently on a “using”-cycle were compared with age and training-matched controls (n = 8; 29 ± 6 years) who self-reported never having taken AS (NAS).
Results
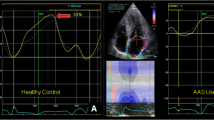
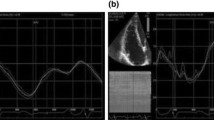
AS users had higher absolute left ventricular (LV) mass (220 ± 45 g) compared to NAS (163 ± 27 g; p < 0.05) but this difference was removed when indexed to fat-free mass. AS had a reduced right ventricular (RV) ejection fraction (AS 51 ± 4 % vs. NAS 59 ± 5 %; p < 0.05) and a significantly lower left ventricular E’:A’ myocardial tissue velocity ratio [AS 0.99(0.54) vs. NAS 1.78(0.46) p < 0.05] predominantly due to greater tissue velocities with atrial contraction. Peak LV longitudinal strain was lower in AS users (AS −14.2 ± 2.7 % vs. NAS −16.6 ± 1.9 %; p < 0.05). There was no evidence of focal fibrosis in any participant.
Conclusions
AS use was associated with significant LV hypertrophy, albeit in-line with greater fat-free mass, reduced LV strain, diastolic function, and reduced RV ejection fraction in male bodybuilders. There was, however, no evidence of focal fibrosis in any AS user.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AS:
-
Anabolic steroids
- BMI:
-
Body mass index
- CMR:
-
Cardiovascular magnetic resonance
- HLA:
-
horizontal long axis
- LGE:
-
Late gadolinium enhancement
- LV:
-
Left ventricle
- RV:
-
Right ventricle
- ε:
-
Myocardial strain
References
Angell P, Chester N, Green D, Somauroo J, Whyte G, George K (2012a) Anabolic steroids and cardiovascular risk. Sports Med 42(2):119–134
Angell P, Chester N, Green DJ, Shah R, Somauroo J, Whyte G, George K (2012b) Anabolic steroid use and longitudinal, radial and circumferential cardiac motion. Med Sci Sports Exerc 44:583–590
Assomull RG, Prasad SK, Lyne J, Smith G, Burman ED, Khan M, Sheppard MN, Poole-Wilson PA, Pennell DJ (2006) Cardiovascular magnetic resonance, fibrosis, and prognosis in dilated cardiomyopathy. J Am Coll Cardiol 48(10):1977–1985. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2006.07.049
Baggish AL, Weiner RB, Kanayama G, Hudson JI, Picard MH, Hutter AM Jr, Pope HG Jr (2010) Long-term anabolic-androgenic steroid use is associated with left ventricular dysfunction. Circ Heart Fail 3(4):472–476. doi:10.1161/CIRCHEARTFAILURE.109.931063
Batterham A, George K, Whyte G, Sharma S, McKenna W (1999) Scaling cardiac structural data by body dimensions: a review of theory, practice, and problems. Int J Sports Med 20:495–502
Bigi MA, Aslani A (2009) Short QT interval: a novel predictor of androgen abuse in strength trained athletes. Ann Noninvasive Electrocardiol 14(1):35–39. doi:10.1111/j.1542-474X.2008.00271.x
D’Andrea A, Caso P, Salerno G, Scarafile R, De Corato G, Mita C, Di Salvo G, Severino S, Cuomo S, Liccardo B, Esposito N, Calabro R (2007) Left ventricular early myocardial dysfunction after chronic misuse of anabolic androgenic steroids: a Doppler myocardial and strain imaging analysis. Br J Sports Med 41(3):149–155. doi:10.1136/bjsm.2006.030171
D’Ascenzo S, Millimaggi D, Di Massimo C, Saccani-Jotti G, Botre F, Carta G, Tozzi-Ciancarelli MG, Pavan A, Dolo V (2007) Detrimental effects of anabolic steroids on human endothelial cells. Toxicol Lett 169(2):129–136. doi:10.1016/j.toxlet.2006.12.008
Ferrando AA, Tipton KD, Doyle D, Phillips SM, Cortiella J, Wolfe RR (1998) Testosterone injection stimulates net protein synthesis but not tissue amino acid transport. Am J Physiol 275(5 Pt 1):E864–E871
Fineschi V, Riezzo I, Centini F, Silingardi E, Licata M, Beduschi G, Karch SB (2007) Sudden cardiac death during anabolic steroid abuse: morphologic and toxicologic findings in two fatal cases of bodybuilders. Int J Legal Med 121(1):48–53
Hundley WG, Bluemke DA, Finn JP, Flamm SD, Fogel MA, Friedrich MG, Ho VB, Jerosch-Herold M, Kramer CM, Manning WJ, Patel M, Pohost GM, Stillman AE, White RD, Woodard PK (2010) ACCF/ACR/AHA/NASCI/SCMR 2010 expert consensus document on cardiovascular magnetic resonance: a report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation Task Force on Expert Consensus Documents. J Am Coll Cardiol 55(23):2614–2662. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2009.11.011
Jellis C, Martin J, Narula J, Marwick TH (2010) Assessment of nonischemic myocardial fibrosis. J Am Coll Cardiol 56(2):89–97
Kasikcioglu E, Oflaz H, Umman B, Bugra Z (2009) Androgenic anabolic steroids also impair right ventricular function. Int J Cardiol 134(1):123–125. doi:10.1016/j.ijcard.2007.12.027
Kühl HP, Hanrath P, Franke A (2003) M-mode echocardiography overestimates left ventricular mass in patients with normal left ventricular shape: a comparative study using three-dimensional echocardiography. Eur J Echocardiogr 4(4):313
Luke JL, Farb A, Virmani R, Sample RH (1990) Sudden cardiac death during exercise in a weight lifter using anabolic androgenic steroids: pathological and toxicological findings. J Forensic Sci 35(6):1441–1447
Lunghetti S, Zaca V, Maffei S, Carrera A, Gaddi R, Diciolla F, Maccherini M, Chiavarelli M, Mondillo S, Favilli R (2009) Cardiogenic shock complicating myocardial infarction in a doped athlete. Acute Card Care 11(4):250–251. doi:10.1080/17482940902842564
Maior AS, Menezes P, Pedrosa RC, Carvalho DP, Soares PP, Nascimento JHM (2010) Abnormal cardiac repolarization in anabolic androgenic steroid users carrying out submaximal exercise testing. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 37(12):1129–1133
Maior A, Carvalho A, Marques-Neto S, Menezes P, Soares P, Nascimento J (2012) Cardiac autonomic dysfunction in anabolic steroid users. Scand J Med Sci Sports. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0838.2011.01436.x
McGill HC, Anselmo VC, Buchanan JM, Sheridan PJ (1980) The heart is a target organ for androgen. Science 207(4432):775
Missouris CG, Forbat SM, Singer DR, Markandu ND, Underwood R, MacGregor GA (1996) Echocardiography overestimates left ventricular mass: a comparative study with magnetic resonance imaging in patients with hypertension. J Hypertens 14(8):1005–1010
O’Hanlon R, Grasso A, Roughton M, Moon JC, Clark S, Wage R, Webb J, Kulkarni M, Dawson D, Sulaibeekh L (2010) Prognostic significance of myocardial fibrosis in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. J Am Coll Cardiol 56(11):867–874
Pennell D, Sechtem U, Higgins C, Manning W, Pohost G, Rademakers F, van Rossum A, Shaw L (2004) Clinical indications for cardiovascular magnetic resonance (CMR): Consensus Panel report. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson 6(4):727–765. doi:10.1081/jcmr-200038581
Pluim BM, Beyerbacht HP, Chin JC, Zwinderman A, Van der Laarse A, De Roos A, Vliegen HW, Van der Wall EE (1997) Comparison of echocardiography with magnetic resonance imaging in the assessment of the athlete’s heart. Eur Heart J 18(9):1505
Riebe D, Fernhall B, Thompson PD (1992) The blood pressure response to exercise in anabolic steroid users. Med Sci Sports Exerc 24(6):633–637
Sader MA, Griffiths KA, McCredie RJ, Handelsman DJ, Celermajer DS (2001) Androgenic anabolic steroids and arterial structure and function in male bodybuilders. J Am Coll Cardiol 37(1):224–230. doi:S0735-1097(00)01083-4
Simonetti OP, Kim RJ, Fieno DS, Hillenbrand HB, Wu E, Bundy JM, Finn JP, Judd RM (2001) An Improved MR imaging technique for the visualization of myocardial infarction1. Radiology 218(1):215
Stewart GA, Foster J, Cowan M, Rooney E, McDonagh T, Dargie HJ, Rodger RSC, Jardine AG (1999) Echocardiography overestimates left ventricular mass in hemodialysis patients relative to magnetic resonance imaging. Kidney Int 56(6):2248–2253
Urhausen A, Holpes R, Kindermann W (1989) One- and two-dimensional echocardiography in bodybuilders using anabolic steroids. Eur J Appl Physiol Occup Physiol 58(6):633–640
Weber KT, Brilla CG, Janicki JS (1993) Myocardioal fibrosis: functional significance and regulatory factors. Cardiovasc Res 27:341–348
Wilson M, O’Hanlon R, Prasad S, Deighan A, MacMillan P, Oxborough D, Godfrey R, Smith G, Maceira A, Sharma S, George K, Whyte G (2011) Diverse patterns of myocardial fibrosis in lifelong, veteran endurance athletes. J Appl Physiol 110:1622–1626. doi:10.1152/japplphysiol.01280.2010
Wysoczanski M, Rachko M, Bergmann SR (2008) Acute myocardial infarction in a young man using anabolic steroids. Angiology 59(3):376–378. doi:10.1177/0003319707304883
Zaugg M, Jamali NZ, Lucchinetti E, Xu W, Alam M, Shafiq SA, Siddiqui MAQ (2001) Anabolic androgenic steroids induce apoptotic cell death in adult rat ventricular myocytes. J Cell Physiol 187(1):90–95
Acknowledgments
Dr. Ismail is supported by the British Heart Foundation, Imperial College London and the National Institute for Health Research Cardiovascular Biomedical Research Unit at the Royal Brompton Hospital. We would like to thank the staff of the Royal Brompton CMR Unit, in particular, Ms. Susan Clark, Ms. Bethan Cowley and Ms. Claire McLeod for their contributions to data collection. The results from this work do not constitute endorsement by ACSM.
Conflict of interest
There are no conflicts of interest for any of the authors.
Ethical standards
The study was conducted in accordance with the principles set out by the declaration of Helsinki. All participants provided written informed consent and local ethics approval was obtained.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by David C. Poole.
Peter J. Angell, Tevfik F. Ismail, Sanjay Prasad and Keith George have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Angell, P.J., Ismail, T.F., Jabbour, A. et al. Ventricular structure, function, and focal fibrosis in anabolic steroid users: a CMR study. Eur J Appl Physiol 114, 921–928 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-014-2820-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-014-2820-2