Abstract
Objective
This study aimed to determine the prevalence and clinical features of Parkinson’s disease (PD)/PD dementia (PD/PDD) or dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB) in idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus (iNPH).
Methods
Patients with iNPH who were admitted to the Department of Neurology, Juntendo University School of Medicine over the past 10 years have been retrospectively analyzed. The diagnosis of iNPH and concomitant PD/PDD or DLB was established using diagnostic criteria. Motor symptoms were assessed by the Movement Disorder Society-sponsored revision of the Unified Parkinson’s Disease Rating Scale (MDS-UPDRS) III. 123I-ioflupane single-photon emission computed tomography (DaT-SPECT) and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) real-time quaking-induced conversion (RT-QuIC)-based assay were performed for alpha synuclein aggregation.
Results
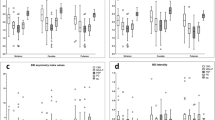
Overall, 79 patients met the criteria for iNPH, of which 34 developed iNPH without accompanying disorders (iNPHa; 43%), 23 developed iNPH with comorbid PD/PDD (iNPHc + PD/PDD; 29.1%), and 8 developed iNPH with comorbid DLB (iNPHc + DLB; 10.1%). Significant differences in facial expansion and upper-limb parkinsonism were observed with a comorbidity of either PD/PDD or DLB. The specific binding ratio (SBR) of DaTscan was reduced in iNPHa (p = 0.02), but it reduced further with comorbid PD/PDD (p < 0.01) or DLB (p < 0.01). RT-QuIC was positive for all 13 comorbid PD/PDD and negative for all 19 iNPHa.
Conclusion
These results highlight that synucleinopathies coexist with iNPH. These can be differentiated by performing DaTscan and RT-QuIC, which can affect its clinical features.

Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Summary data will be shared by qualified researchers.
Code availability
Not applicable.
Availability of data and material
We will inform you individually if you wish.
References
Edwards RJ, Dombrowski SM, Luciano MG, Pople IK (2004) Chronic hydrocephalus in adults. Brain Pathol 14:325–336
Stolze H, Kuhtz-Buschbeck JP, Drucke H, Johnk K, Illert M, Deuschl G (2001) Comparative analysis of the gait disorder of normal pressure hydrocephalus and Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 70:289–297
Fasano A, Espay AJ, Tang-Wai DF, Wikkelsö C, Krauss JK (2020) Gaps, controversies, and proposed roadmap for research in normal pressure hydrocephalus. Mov Disord 35:1945–1954
Reitz C, Brayne C, Mayeux R (2011) Epidemiology of Alzheimer disease. Nat Rev Neurol 7:137–152
Mathew R, Pavithran S, Byju P (2018) Neuropsychiatric manifestations of cognitively advanced idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus. Dement Geriatr Cogn Dis Extra 8:467–475
Ogino A, Kazui H, Miyoshi N, Hashimoto M, Ohkawa S, Tokunaga H, Ikejiri Y, Takeda M (2006) Cognitive impairment in patients with idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord 21:113–119
Oliveira MF, Oliveira JR, Rotta JM, Pinto FC (2014) Psychiatric symptoms are present in most of the patients with idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus. Arq Neuropsiquiatr 72:435–438
Chen Z, Liu C, Zhang J, Relkin N, Xing Y, Li Y (2017) Cerebrospinal fluid Abeta42, t-tau, and p-tau levels in the differential diagnosis of idiopathic normal-pressure hydrocephalus: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Fluids Barriers CNS 14:13
Hamilton R, Patel S, Lee EB, Jackson EM, Lopinto J, Arnold SE, Clark CM, Basil A, Shaw LM, Xie SX, Grady MS, Trojanowski JQ (2010) Lack of shunt response in suspected idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus with Alzheimer disease pathology. Ann Neurol 68:535–540
Kang K, Jeon JS, Kim T, Choi D, Ko PW, Hwang SK, Lee HW (2016) Asymmetric and upper body parkinsonism in patients with idiopathic normal-pressure hydrocephalus. J Clin Neurol 12:452–459
Odagiri H, Baba T, Nishio Y, Iizuka O, Narita W, Matsuda M, Mori E (2015) Clinical characteristics of idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus with Lewy body diseases. J Neurol Sci 359:309–311
Del Bigio MR (1993) Neuropathological changes caused by hydrocephalus. Acta Neuropathol 85:573–585
Mostile G, Portaro G, Certo F, Luca A, Manna R, Terranova R, Altieri R, Nicoletti A, Barbagallo GMV, Zappia M (2021) iNPH with parkinsonism: response to lumbar CSF drainage and ventriculoperitoneal shunting. J Neurol 268:1254–1265
Pozzi NG, Brumberg J, Todisco M, Minafra B, Zangaglia R, Bossert I, Trifirò G, Ceravolo R, Vitali P, Isaias IU, Fasano A, Pacchetti C (2021) Striatal dopamine deficit and motor impairment in idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus. Mov Disord 36:124–132
Relkin N, Marmarou A, Klinge P, Bergsneider M, Black PM (2005) Diagnosing idiopathic normal-pressure hydrocephalus. Neurosurgery 57:S4-16
Mori E, Ishikawa M, Kato T, Kazui H, Miyake H, Miyajima M, Nakajima M, Hashimoto M, Kuriyama N, Tokuda T, Ishii K, Kaijima M, Hirata Y, Saito M, Arai H (2012) Guidelines for management of idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus: second edition. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 52:775–809
Humpel C (2011) Identifying and validating biomarkers for Alzheimer’s disease. Trends Biotechnol 29:26–32
Postuma RB, Berg D, Stern M, Poewe W, Olanow CW, Oertel W, Obeso J, Marek K, Litvan I, Lang AE, Halliday G, Goetz CG, Gasser T, Dubois B, Chan P, Bloem BR, Adler CH, Deuschl G (2015) MDS clinical diagnostic criteria for Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 30:1591–1601
McKeith IG, Boeve BF, Dickson DW, Halliday G, Taylor JP, Weintraub D, Aarsland D, Galvin J, Attems J, Ballard CG, Bayston A, Beach TG, Blanc F, Bohnen N, Bonanni L, Bras J, Brundin P, Burn D, Chen-Plotkin A, Duda JE, El-Agnaf O, Feldman H, Ferman TJ, Ffytche D, Fujishiro H, Galasko D, Goldman JG, Gomperts SN, Graff-Radford NR, Honig LS, Iranzo A, Kantarci K, Kaufer D, Kukull W, Lee VMY, Leverenz JB, Lewis S, Lippa C, Lunde A, Masellis M, Masliah E, McLean P, Mollenhauer B, Montine TJ, Moreno E, Mori E, Murray M, O’Brien JT, Orimo S, Postuma RB, Ramaswamy S, Ross OA, Salmon DP, Singleton A, Taylor A, Thomas A, Tiraboschi P, Toledo JB, Trojanowski JQ, Tsuang D, Walker Z, Yamada M, Kosaka K (2017) Diagnosis and management of dementia with Lewy bodies: Fourth consensus report of the DLB Consortium. Neurology 89:88–100
Emre M, Aarsland D, Brown R, Burn DJ, Duyckaerts C, Mizuno Y, Broe GA, Cummings J, Dickson DW, Gauthier S, Goldman J, Goetz C, Korczyn A, Lees A, Levy R, Litvan I, McKeith I, Olanow W, Poewe W, Quinn N, Sampaio C, Tolosa E, Dubois B (2007) Clinical diagnostic criteria for dementia associated with Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 22:1689–1707
Takanashi M, Funayama M, Matsuura E, Yoshino H, Li Y, Tsuyama S, Takashima H, Nishioka K, Hattori N (2018) Isolated nigral degeneration without pathological protein aggregation in autopsied brains with LRRK2 p.R1441H homozygous and heterozygous mutations. Acta Neuropathol Commun 6:105
Matsuda H, Murata M, Mukai Y, Sako K, Ono H, Toyama H, Inui Y, Taki Y, Shimomura H, Nagayama H, Tateno A, Ono K, Murakami H, Kono A, Hirano S, Kuwabara S, Maikusa N, Ogawa M, Imabayashi E, Sato N, Takano H, Hatazawa J, Takahashi R (2018) Japanese multicenter database of healthy controls for [(123)I]FP-CIT SPECT. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 45:1405–1416
Fairfoul G, McGuire LI, Pal S, Ironside JW, Neumann J, Christie S, Joachim C, Esiri M, Evetts SG, Rolinski M, Baig F, Ruffmann C, Wade-Martins R, Hu MT, Parkkinen L, Green AJ (2016) Alpha-synuclein RT-QuIC in the CSF of patients with alpha-synucleinopathies. Ann Clin Transl Neurol 3:812–818
Magdalinou NK, Ling H, Smith JD, Schott JM, Watkins LD, Lees AJ (2013) Normal pressure hydrocephalus or progressive supranuclear palsy? A clinicopathological case series. J Neurol 260:1009–1013
Zeidler M, Dorman PJ, Ferguson IT, Bateman DE (1998) Parkinsonism associated with obstructive hydrocephalus due to idiopathic aqueductal stenosis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 64:657–659
Tashiro Y, Drake JM (1998) Reversibility of functionally injured neurotransmitter systems with shunt placement in hydrocephalic rats: implications for intellectual impairment in hydrocephalus. J Neurosurg 88:709–717
Komatsu J, Samuraki M, Nakajima K, Arai H, Arai H, Arai T, Asada T, Fujishiro H, Hanyu H, Iizuka O, Iseki E, Kashihara K, Kosaka K, Maruno H, Mizukami K, Mizuno Y, Mori E, Nakamura H, Nakano S, Nakashima K, Nishio Y, Orimo S, Takahashi A, Taki J, Tokuda T, Urakami K, Utsumi K, Wada K, Washimi Y, Yamashina S, Yamasaki J, Yoshita M, Yamada M (2018) (123)I-MIBG myocardial scintigraphy for the diagnosis of DLB: a multicentre 3-year follow-up study. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 89:1167–1173
Bongianni M, Ladogana A, Capaldi S, Klotz S, Baiardi S, Cagnin A, Perra D, Fiorini M, Poleggi A, Legname G, Cattaruzza T, Janes F, Tabaton M, Ghetti B, Monaco S, Kovacs GG, Parchi P, Pocchiari M, Zanusso G (2019) α-Synuclein RT-QuIC assay in cerebrospinal fluid of patients with dementia with Lewy bodies. Ann Clin Transl Neurol 6:2120–2126
Orimo S, Suzuki M, Inaba A, Mizusawa H (2012) 123I-MIBG myocardial scintigraphy for differentiating Parkinson’s disease from other neurodegenerative parkinsonism: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 18:494–500
Funding
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AS: collected data, conducted statistical analysis, and wrote the draft. YI: collected samples. Ayami Okuzumi conducted RT-QuIC. TH: edited the draft. TT: Initiated and organized the project and finalized the manuscript. NH: organized the project.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
Anri Sakurai, Taiji Tsunemi, Yuta Ishiguro, Ayami Okuzumi, Taku Hatano and Nobutaka Hattori have no conflict of interest to declare.
Ethics approval
This study protocol complied with the Declaration of Helsinki and was approved by the ethics committee of Juntendo University.
Consent to participate
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants.
Consent for publication
The participants have consented to the submission of this manuscript to the journal.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sakurai, A., Tsunemi, T., Ishiguro, Y. et al. Comorbid alpha synucleinopathies in idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus. J Neurol 269, 2022–2029 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-021-10778-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-021-10778-1