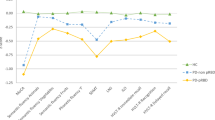
Abstract
High-oligomeric and low-total-α-synuclein cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) levels have been found in Parkinson’s disease (PD), but with inconsistent or limited data, particularly on their clinical and structural correlates in earliest (premotor) or latest (dementia) PD stages. We determined CSF oligomeric- and total-α-synuclein in 77 subjects: 23 with idiopathic REM-sleep behaviour disorder (iRBD, a condition likely to include a remarkable proportion of subjects in the premotor stage of PD) and 41 with PD [21 non-demented (PDND) + 20 demented (PDD)], intended to reflect the premotor–motor–dementia PD continuum, along with 13 healthy controls. The study protocol also included the Unified PD Rating Scale motor-section (UPDRS-III), mini mental state examination (MMSE), neuropsychological cognitive testing, 3T brain MRI for cortical-thickness analyses, CSF τ and CSF Aβ. CSF oligomeric-α-synuclein was higher in PDND than iRBD and in PDD than iRBD and controls, and correlated with UPDRS-III, MMSE, semantic fluency and visuo-perceptive scores across the proposed premotor–motor–dementia PD continuum (iRBD + PDND + PDD). CSF total-α-synuclein positively correlated with age, CSF Aβ, and, particularly, CSF τ, tending towards lower levels in PD (but not iRBD) vs. controls only when controlling for CSF τ. Low CSF total-α-synuclein was associated with dysfunction in phonetic-fluency (a frontal-lobe function) in PD and with frontal cortical thinning in iRBD and PDND independently of CSF τ. Conversely, the associations of high (instead of low) CSF total-α-synuclein with posterior-cortical neuropsychological deficits in PD and with posterior cortical thinning in PDD were driven by high CSF τ. These findings suggest that CSF oligomeric- and total-α-synuclein have different clinical, neuropsychological and MRI correlates across the proposed premotor–motor–dementia PD continuum. CSF total-α-synuclein correlations with CSF τ and Aβ support the hypothesis of an interaction among these proteins in PD, with CSF τ probably influencing the presence of high (instead of low) CSF total-α-synuclein and its correlates mostly in the setting of PD-related dementia.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mollenhauer B (2014) Quantification of α-synuclein in cerebrospinal fluid: how ideal is this biomarker for Parkinson’s disease? Parkinsonism Relat Disord 20(Suppl 1):S76–S79
Magdalinou N, Lees AJ, Zetterberg H (2014) Cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers in parkinsonian conditions: an update and future directions. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 85:1065–1075
Tolosa E, Gaig C, Santamaría J, Compta Y (2009) Diagnosis and the premotor phase of Parkinson disease. Neurology 72:S12–S20
Braak H, Del Tredici K, Rüb U, de Vos RA, Jansen Steur EN, Braak E (2003) Staging of brain pathology related to sporadic Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 24:197–211
Hely MA, Reid WG, Adena MA, Halliday GM, Morris JG (2008) The Sydney multicenter study of Parkinson’s disease: the inevitability of dementia at 20 years. Mov Disord 23:837–844
Braak H, Rüb U, Jansen Steur EN, Del Tredici K, de Vos RA (2005) Cognitive status correlates with neuropathologic stage in Parkinson disease. Neurology 64:1404–1410
Hong Z, Shi M, Chung KA, Quinn JF, Peskind ER, Galasko D, Jankovic J, Zabetian CP, Leverenz JB, Baird G, Montine TJ, Hancock AM, Hwang H, Pan C, Bradner J, Kang UJ, Jensen PH, Zhang J (2010) DJ-1 and alpha-synuclein in human cerebrospinal fluid as biomarkers of Parkinson’s disease. Brain 133:713–726
Tokuda T, Qureshi MM, Ardah MT, Varghese S, Shehab SA, Kasai T, Ishigami N, Tamaoka A, Nakagawa M, El-Agnaf OM (2010) Detection of elevated levels of α-synuclein oligomers in CSF from patients with Parkinson disease. Neurology 75:1766–1772
Mollenhauer B, Locascio JJ, Schulz-Schaeffer W, Sixel-Döring F, Trenkwalder C, Schlossmacher MG (2011) α-Synuclein and tau concentrations in cerebrospinal fluid of patients presenting with parkinsonism: a cohort study. Lancet Neurol 10:230–240
Parnetti L, Chiasserini D, Bellomo G, Giannandrea D, De Carlo C, Qureshi MM, Ardah MT, Varghese S, Bonanni L, Borroni B, Tambasco N, Eusebi P, Rossi A, Onofrj M, Padovani A, Calabresi P, El-Agnaf O (2011) Cerebrospinal fluid Tau/α-synuclein ratio in Parkinson’s disease and degenerative dementias. Mov Disord 26:1428–1435
Kang JH, Irwin DJ, Chen-Plotkin AS, Parkinson’s Progression Markers Initiative et al (2013) Association of cerebrospinal fluid β-amyloid 1-42, T-tau, P-tau181, and α-synuclein levels with clinical features of drug-naive patients with early Parkinson disease. JAMA Neurol 70:1277–1287
van Dijk KD, Bidinosti M, Weiss A, Raijmakers P, Berendse HW, van de Berg WD (2014) Reduced α-synuclein levels in cerebrospinal fluid in Parkinson’s disease are unrelated to clinical and imaging measures of disease severity. Eur J Neurol 21:388–394
Ohrfelt A, Grognet P, Andreasen N, Wallin A, Vanmechelen E, Blennow K, Zetterberg H (2009) Cerebrospinal fluid alpha-synuclein in neurodegenerative disorders-a marker of synapse loss? Neurosci Lett 450:332–335
Park MJ, Cheon SM, Bae HR, Kim SH, Kim JW (2011) Elevated levels of α-synuclein oligomer in the cerebrospinal fluid of drug-naïve patients with Parkinson’s disease. J Clin Neurol 7:215–222
Aerts MB, Esselink RA, Abdo WF, Bloem BR, Verbeek MM (2012) CSF α-synuclein does not differentiate between parkinsonian disorders. Neurobiol Aging 33:430.e1–430.e3
Slaets S, Vanmechelen E, Le Bastard N, Decraemer H, Vandijck M, Martin JJ, De Deyn PP, Engelborghs S (2014) Increased CSF α-synuclein levels in Alzheimer’s disease: correlation with tau levels. Alzheimers Dement. doi:10.1016/j.jalz.2013.10.004
Winner B, Jappelli R, Maji SK, Desplats PA, Boyer L, Aigner S, Hetzer C, Loher T, Vilar M, Campioni S, Tzitzilonis C, Soragni A, Jessberger S, Mira H, Consiglio A, Pham E, Masliah E, Gage FH, Riek R (2011) In vivo demonstration that alpha-synuclein oligomers are toxic. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108:4194–4199
Parnetti L, Chiasserini D, Persichetti E, Eusebi P, Varghese S, Qureshi MM, Dardis A, Deganuto M, De Carlo C, Castrioto A, Balducci C, Paciotti S, Tambasco N, Bembi B, Bonanni L, Onofrj M, Rossi A, Beccari T, El-Agnaf O, Calabresi P (2014) Cerebrospinal fluid lysosomal enzymes and α-synuclein in Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 29(8):1019–1027
Hoehn MM, Yahr MD (1967) Parkinsonism: onset, progression and mortality. Neurology 17:427–442
Williams-Gray CH, Foltynie T, Brayne CEG, Brayne CE, Robbins TW, Barker RA (2007) Evolution of cognitive dysfunction in an incident Parkinson’s disease cohort. Brain 130:1787–1798
Weintraub D, Doshi J, Koka D, Davatzikos C, Siderowf AD, Duda JE, Wolk DA, Moberg PJ, Xie SX, Clark CM (2011) Neurodegeneration across stages of cognitive decline in Parkinson disease. Arch Neurol 68:1562–1568
Iranzo A, Tolosa E, Gelpi E, Molinuevo JL, Valldeoriola F, Serradell M, Sanchez-Valle R, Vilaseca I, Lomeña F, Vilas D, Lladó A, Gaig C, Santamaria J (2013) Neurodegenerative disease status and post-mortem pathology in idiopathic rapid-eye-movement sleep behaviour disorder: an observational cohort study. Lancet Neurol 12:443–453
Hughes AJ, Daniel SE, Kilford L, Lees AJ (1992) Accuracy of clinical diagnosis of idiopathic Parkinson’s disease: a clinico-pathological study of 100 cases. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 55:181–184
Emre M, Aarsland D, Brown R, Burn DJ, Duyckaerts C, Mizuno Y, Broe GA, Cummings J, Dickson DW, Gauthier S, Goldman J, Goetz C, Korczyn A, Lees A, Levy R, Litvan I, McKeith I, Olanow W, Poewe W, Quinn N, Sampaio C, Tolosa E, Dubois B (2007) Clinical diagnostic criteria for dementia associated with Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 22:1689–1707
Fahn S, Elton RL, Members of the UPDRS Development Committee Unified Parkinson’s disease rating scale (1987) Unified Parkinson’s disease rating scale. In: Fahn S, Marsden CD, Calne DB, Lieberman A (eds) Recent developments in Parkinson’s disease. McMillan Health Care Information, Florham Park, p 153
Folstein MF, Folstein SE, McHugh PR (1975) ‘‘Mini-Mental state.’’ A practical method for grading the cognitive state of patients for the clinician. J Psychiatr Res 12:189–198
Compta Y, Martí MJ, Ibarretxe-Bilbao N, Junqué C, Valldeoriola F, Muñoz E, Ezquerra M, Ríos J, Tolosa E (2009) Cerebrospinal tau, phospho-tau, and beta-amyloid and neuropsychological functions in Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 24:2203–2210
Lezak MD, Howieson DB, Loring DW (2004) Neuropsychological assessment, 4th edn. Oxford University Press Inc., New York
Peña-Casanova J, Gramunt-Fombuena N, Quiñones-Ubeda S, Sánchez-Benavides G, Aguilar M, Badenes D, Molinuevo JL, Robles A, Barquero, Payno M, Antúnez C, Martínez-Parra C, Frank-García A, Fernández M, Alfonso V, Sol JM, Blesa R, NEURONORMA Study Team (2009) Spanish multicenter normative studies (NEURONORMA project): norms for the Rey-Osterrieth complex figure (copy and memory), and free and cued selective reminding test. Arch Clin Neuropsychol 24:371–393
Peña-Casanova J, Quiñones-Ubeda S, Gramunt-Fombuena N, Aguilar M, Casas L, Molinuevo JL, Robles A, Rodríguez D, Barquero, Antúnez C, Martínez-Parra C, Frank-García A, Fernández M, Molano A, Alfonso V, Sol JM, Blesa R, NEURONORMA Study Team (2009) Spanish multicenter normative studies (NEURONORMA Project): norms for boston naming test and token test. Arch Clin Neuropsychol 24:343–354
Peña-Casanova J, Quiñones-Ubeda S, Gramunt-Fombuena N, Quintana-Aparicio M, Aguilar M, Badenes D, Cerulla N, Molinuevo JL, Ruiz E, Robles A, Barquero, Antúnez C, Martínez-Parra C, Frank-García A, Fernández M, Alfonso V, Sol JM, Blesa R, NEURONORMA Study Team (2009) Spanish Multicenter normative Studies (NEURONORMA Project): Norms for verbal fluency tests. Arch Clin Neuropsychol 24:395–411
Peña-Casanova J, Quintana-Aparicio M, Quiñones-Ubeda S, Aguilar M, Molinuevo JL, Serradell M, Robles A, Barquero, Villanueva C, Antúnez C, Martínez-Parra C, Frank-García A, Aguilar MD, Fernández M, Alfonso V, Sol JM, Blesa R, NEURONORMA Study Team (2009) Spanish Multicenter normative Studies (NEURONORMA Project): norms for the visual object and space perception battery-abbreviated, and judgment of line orientation. Arch Clin Neuropsychol 24:355–370
Dale AM, Fischl B, Sereno MI (1999) Cortical surface-based analysis. I. segmentation and surface reconstruction. Neuroimage 9:179–194
Fischl B, Dale AM (2000) Measuring the thickness of the human cerebral cortex from magnetic resonance images. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:11050–11055
Perneger TV (1998) What’s wrong with Bonferroni adjustments. Br Med J 316:1236–1238
Hansson O, Hall S, Ohrfelt A, Zetterberg H, Blennow K, Minthon L, Nägga K, Londos E, Varghese S, Majbour NK, Al-Hayani A, El-Agnaf OM (2014) Levels of cerebrospinal fluid α-synuclein oligomers are increased in Parkinson’s disease with dementia and dementia with Lewy bodies compared to Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Res Ther 6:25
Wennström M, Suroya Y, Hall S, Nilsson C, Minthon L, Boström F, Hansson O, Nielsen HM (2008) Low CSF levels of both α-synuclein and the α-synuclein cleaving enzyme neurosin in patients with synucleinopathy. PLoS ONE 8:e53250
Apaydin H, Ahlskog JE, Parisi JE, Boeve BF, Dickson DW (2002) Parkinson disease neuropathology: later-developing dementia and loss of the levodopa response. Arch Neurol 59:102–112
Compta Y, Parkkinen L, O’Sullivan SS, Vandrovcova J, Holton JL, Collins C, Lashley T, Kallis C, Williams DR, de Silva R, Lees AJ, Revesz T (2011) Lewy- and Alzheimer-type pathologies in Parkinson’s disease dementia: which is moreimportant? Brain 134:1493–1505
Masliah E, Rockenstein E, Veinbergs I, Sagara Y, Mallory M, Hashimoto M, Mucke L (2001) Beta-amyloid peptides enhance alpha-synuclein accumulation and neuronal deficits in a transgenic mouse model linking Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:12245–12250
Guo JL, Covell DJ, Daniels JP, Iba M, Stieber A, Zhang B, Riddle DM, Kwong LK, Xu Y, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM (2013) Distinct α-synuclein strains differentially promote tau inclusions in neurons. Cell 154:103–117
Compta Y, Ibarretxe-Bilbao N, Pereira JB, Junqué C, Bargalló N, Tolosa E, Valldeoriola F, Muñoz E, Camara A, Buongiorno M, Martí MJ (2012) Grey matter volume correlates of cerebrospinal markers of Alzheimer-pathology in Parkinson’s disease and related dementia. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 18:941–947
Stewart T, Liu C, Ginghina C, Cain KC, Auinger P, Cholerton B, Shi M, Zhang J, Parkinson Study Group DATATOP Investigators (2014) Cerebrospinal fluid α-synuclein predicts cognitive decline in Parkinson disease progression in the DATATOP cohort. Am J Pathol 184:966–975
Litvan I, Goldman JG, Tröster AI, Schmand BA, Weintraub D, Petersen RC, Mollenhauer B, Adler CH, Marder K, Williams-Gray CH, Aarsland D, Kulisevsky J, Rodriguez-Oroz MC, Burn DJ, Barker RA, Emre M (2012) Diagnostic criteria for mild cognitive impairment in Parkinson’s disease: movement disorder society task force guidelines. Mov Disord 27:349–356
Wang Y, Shi M, Chung KA, Zabetian CP, Leverenz JB, Berg D, Srulijes K, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM, Siderowf AD, Hurtig H, Litvan I, Schiess MC, Peskind ER, Masuda M, Hasegawa M, Lin X, Lin X, Pan C, Galasko D, Goldstein DS, Jensen PH, Yang H, Cain KC, Zhang J (2012) Phosphorylated α-synuclein in Parkinson’s disease. Sci Trasnl Med 4:121ra20
Acknowledgments
The authors are most grateful to all the study participants, and acknowledge the help of Dr. M. Salazar, Dr. F. Basora, Dr. G. Sánchez-Etayo (Anesthesiology Service), Dr. F. Macule (Knee Surgery Unit), Mrs. A Martín, Mr. C. Garrido, Mr. M. Fabregat and Mr. S. Sotes (MRI Unit technicians). This study was funded through “Premio de la Federación Española de Parkinson [FEP] 2011” (PI041833; P. I.: Y. Compta) and “Fundació La Marató de TV-3” (N-2006-TV060510; P. I.: M.J. Marti).
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical standard
This study was approved by the Institution Ethics Committee and has therefore been performed in accordance with the ethical standards laid down in the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments. All participants gave their informed consent prior to their inclusion in the study. There are no details in this manuscript that might disclose the identity of the participants.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
415_2014_7560_MOESM1_ESM.jpg
Box plots of CSF total-α-synuclein in controls vs. PD (PDND + PDD) after excluding cases with CSFτ > 400 pg/mL [A], >300 pg/mL [B] and >250 pg/mL [C]. Mann–Whitney’s U test comparisons were non-significant (p > 0.05), but there was a trend towards more subjects with CSF total-α-synuclein below the median value of this CSF biomarker in PD vs. controls (Fisher’s exact test, p = 0.059) (JPEG 115 kb)
415_2014_7560_MOESM2_ESM.jpg
Significant negative correlations between CSF τ levels and cortical thickness (CTh) in the left pars opercularis, right middle frontal and middle temporal gyri, and the right cuneus, in PDD patients (co-varied for age). Results were obtained using Monte Carlo simulation with 10,000 iterations applied to CTh maps to provide cluster-wise correction for multiple comparisons (p threshold <0.05; 1.3) (JPEG 145 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Compta, Y., Valente, T., Saura, J. et al. Correlates of cerebrospinal fluid levels of oligomeric- and total-α-synuclein in premotor, motor and dementia stages of Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol 262, 294–306 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-014-7560-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-014-7560-z