Abstract
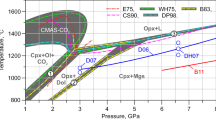
The carbonation reaction CaMg(CO3)2 (dolomite)+2SiO2 (coesite)=CaMgSi2O6 (diopside)+2 CO2 (vapor) has been determined experimentally between 3.5 and 6 GPa in a multiple-anvil, solid-media apparatus. This reaction, a candidate for carbonation of eclogites (garnet+clinopyroxene) in the Earth’s mantle, lies at higher pressure for a given temperature than do the carbonation reactions for peridotites (olivine+orthopyroxene±clinopyroxene). A depth interval may exist within the Earth’s mantle under either ‘normal’ or ‘subduction’ thermal regimes where carbonated peridotite could coexist with carbonate-free, CO2-bearing eclogite.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 25 May 1994/Accepted: 13 June 1995
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Luth, R. Experimental determination of the reaction dolomite + 2 coesite = diopside + 2 CO2 to 6 GPa. Contrib Mineral Petrol 122, 152–158 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004100050118
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004100050118