Abstract
We analyzed the functional outcome and self-evaluation of the voice of patients with T1 glottic carcinoma treated with endoscopic laser surgery and radiotherapy. We performed an objective voice evaluation, as well as a physical, emotional and functional well being assessment of 19 patients treated with laser surgery and 18 patients treated with radiotherapy. Voice quality is affected both by surgery and radiotherapy. Voice parameters only show differences in the maximum phonation time between both treatments. Results in the Voice Handicap Index show that radiotherapy has less effect on patient voice quality perception. There is a reduced impact on the patient’s perception of voice quality after radiotherapy, despite there being no significant differences in vocal quality between radiotherapy and laser cordectomy.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Surgery and radiotherapy offer the same results in the treatment of early glottic carcinoma, with a cure rate of approximately 90% [1].
The introduction of endoscopic CO2 laser surgery in early glottic carcinoma (epidermoid carcinoma confined to the true vocal cords with normal mobility) has added controversy to the standard treatment choice. Laser surgery is quicker, which reduces cost considerably. However many institutions prefer to use radiotherapy in the belief that the voice will be better preserved after treatment [2]. Although the principal objective of oncology treatment is the complete eradication of the illness, normal voice preservation is another important consideration in the treatment choice of early glottic carcinoma. For this reason, post-treatment voice quality is a relevant factor to take into account when evaluating the results.
Quantitative acoustic measurements are more regularly studied. These are obtained from tools that digitize and analyze the voice being investigated and quantify the characteristics that deviate from normality, understanding normality to mean when the voice is uniform in both amplitude and tone periodicity. The addition of noise to the voice signal is also a defect that affects voice quality, and this is the third acoustic characteristic that is studied using spectrography.
Another of the factors to take into account is the auditive perception that is generated in the listener and is evaluated by ways of perceived voice quality, making use of semi-objective scales such as the GRBAS scale, as described by Hirano [3]. It is recommended that these measurements are made by two experts, although the parameters have shown sufficient reliability (inter- and intra-observer reproducibility) when used in a clinical setting [4].
Although all these measurements are important parameters in defining voice quality, they fail to provide information on the patient’s perceived voice quality. For this there is a method available that permits the patient to describe the sensations their voice gives: the Voice Handicap Index [5]. It is a questionnaire that reviews situations grouped into three areas (functional, physiological and emotional) and gives an idea of the subjective impact that a vocal problem produces in a specific individual.
In this study, we present the objective and subjective analysis of voice quality following treatment of an early epidermoid glottic carcinoma. Results from the objective evaluation of the voice, along with the self-evaluation of voice quality quantified using the Voice Handicap Index of a group of patients treated with endoscopic laser surgery are compared with patients treated with radiotherapy.
Materials and methods
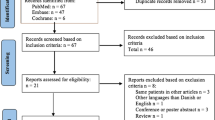
Voice analysis and quality of life studies of 19 patients treated with laser surgery and 18 with radiotherapy, suffering from early glottic carcinoma, were evaluated. Lesions were classified according to the American Joint Committee on Cancer [6].
In patients who received radiotherapy as the primary treatment, this was performed using a 6 mv linear accelerator to bilateral ports and one in front, with field sizes ranging from 5 × 5 to 6 × 6 cm. Wedges were used to establish dose homogeneity.
In the case of patients treated with surgery, the treatment consisted of direct laryngoscopy for the complete resection (partial transmuscular cordectomy) of the lesion with CO2 laser. Objective voice analysis and voice quality studies, performed by both patients and examiners by means of an examination protocol including: perceptual analysis of dysphonia, acoustic analysis, aerodynamic efficiency and patient perception, were applied to both groups. In all patients, this protocol was undertaken at least 6 months after completing treatment.
Perceptual analysis of dysphonia (GRBAS)
Perceptual analysis of dysphonia was performed using the GRBAS scale [3]. Two experienced professionals evaluated the recorded voice samples simultaneously, classifying each sample from 0 to 3 (0 = normal, 1 = mild, 2 = moderate, 3 = severe). The severity of hoarseness is quantified under the parameter G (grade), which represents overall voice quality. B (breathiness): audible impression of turbulent air leakage through an insufficient glottic closure, which may include short aphonic moments (unvoiced segments). R (roughness or harshness): audible impression of irregular glottic pulses, abnormal fluctuations in F 0, separately perceived acoustic impulses (as in vocal fry), includes diplophonia and register breaks. A (asthenicity): impression of weakness in the spontaneous phonation, hypokinetic or hypofunctional voice. S (strain, vocal tension): auditive impression of excessive force or tension associated with spontaneous phonation.
Acoustic and spectrographic analysis
The acoustic analysis was performed using Doctor Speech V3 software for Windows 95. The acoustic signal was recorded using the Voice Assessment application. The computer used was a Pentium II at 100 MHz and with 16 Mb of RAM and a Sound Blaster 16 sound card. The sampling frequency was 44,100 Hz and a high frequency range microphone was used. The microphone was located 10 cm from the patient’s mouth while they emitted the “e” sound at comfortable intensity and pitch levels in a soundproof chamber. The computer captured 3 s of sound. Once the signal was digitized, the computer calculated the following acoustic parameters: fundamental frequency (F 0), jitter or frequency variation (%), shimmer or amplitude variation (%) and NNE or normalized noise energy, which measures the degree of noise produced by turbulent air escaping through the glottis during vocal emission.
Using the same digitized voice sample, a narrow band spectrogram was generated (45 Hz) using the Speech Analysis application. The spectrograms obtained were grouped into four types according to the Yanagihara criteria [7].
Aerodynamic efficiency analysis
This consisted in measuring the maximum phonation time (TMF) for the “a” vocal after instructing the patient to sustain this vocal for the longest time possible at a comfortable pitch and intensity. The patients were asked to repeat the test at least three times and the highest value was retained.
Patient self-perception analysis (Voice Handicap Index)
The patients completed the “Voice Handicap Index” via a self-evaluation form comprising 30 questions covering three domains [5]: functional, physical and emotional, translated from the original work in English by one of the authors. Each question was assigned a score of 0–4 (from least disability to most). In each item, the maximum score was 40 points and we classified them as mild disability (less than 20), moderate (21–30) and severe (more that 30). Adding the three scores together, the maximum possible was 120, and we classified the vocal disability as mild (less than 30), moderate (31–60), severe (61–90) and very severe (91–120).
Statistical analysis
The data obtained was gathered in the statistical database SPSS 12.0. The statistical analysis used was the Student’s t test in order to compare averages and the Chi-squared test for comparing proportions. The statistical differences were considered significant when P was lower than 0.05.
Results
In the patient group treated with CO2 laser, the ages were in the range 44–86 years, with an average age of 64 and a mean follow-up of 30 months (12–48). In the patient group treated with radiotherapy, the ages were in the range 55–81 years, with an average age of 67 and a mean follow-up of 43 months (6–81). All patients in both groups were males.
In both groups, all lesions corresponded to stage I of the TNM classification. In the group of 19 patients treated with surgery, all the lesions were qualified as T1a and in the case of the 18 radiotherapy patients, 13 were classified as T1a and 5 as T1b. No metastases in the neck, or distant, were detected. At the time of the study, all patients were free from illness.
In the group of patients treated with radiotherapy, the nominal total dose was 6,525 cGy, with 225 cGy daily doses for a total of 29 days. Of the PTV volume, 100% received minimum doses of approximately 5,700 cGy, a maximum dose of approximately 6,720 cGy and an average dose of 6,520 cGy.
Aerodynamic efficiency and spectrographic analysis
In Table 1, the maximum phonation times are presented for the “a” vocal along with the quantitative voice analysis of the vocal “e” obtained in the groups treated with laser and with radiotherapy. There was no significant difference between the parameters: fundamental frequency, (F 0), jitter, shimmer and NNE on comparing both groups. However, there were significant differences in the maximum phonation time.
In spectrographic terms, the 19 voice samples of patients treated with laser were classified as Grade I 4 (21%), Grade II 5 (25%), Grade III 7 (37%) and Grade IV 3 (15%). In the group of patients treated with radiotherapy, the 18 voice samples were classified as Grade I 1 (5%), Grade II 7 (39%), Grade III 5 (28%) and Grade IV 5 (28%). On comparing the spectrograms obtained in both groups, there were no statistically significant differences (P = 0.401).
Perceptual dysphonia analysis (GRBAS)
Table 2 shows the results obtained using GRBAS scale on patients treated with CO2 laser surgery. Mild dysphonia was found in 31.5% of the cases, moderate dysphonia in 37% and severe dysphonias in the remaining 31.5%. Table 3 shows the GRABS results of the patients treated with radiotherapy. Normal voices were observed in 11%, mild dysphonias in 44.4%, moderate dysphonia in 27.8% and severe dysphonia in 16.7% of the cases. On comparing the results obtained in the G domain of the GRABS scale, which corresponds with the degree of dysphonia, no significant difference was found between each group (P = 0.309).
Patients self-perception analysis (Voice Handicap Index)
Table 4 shows the averages obtained from the “Voice Handicap Index” questionnaire in the functional, physical and emotional scales, as well as the scores obtained in both groups. Upon completing the comparison between the two groups, the statistical difference is significant, in favor of the radiotherapy patients in the functional and emotional ratings as well as the global scores. No significant differences were found in the physical scales.
Discussion
Early glottic carcinoma can be treated using endoscopic surgery, radiotherapy or partial open surgery. Lesions limited to the vocal fold are normally treated with endoscopic surgery or partial open surgery, with local control results of between 80 and 90% [8]. In choosing one treatment or another, one should contemplate the cure rate, larynx preservation rate, post-treatment voice quality, morbidity and treatment cost [9].
In recent years, endoscopic CO2 laser surgery has made headway compared to radiotherapy, based on its good oncology results and reduced morbidity. CO2 laser treatment in early glottic carcinoma has greatly improved voice quality compared to that obtained following cordectomy via laryngofissure. as documented by some authors such as Keilmann et al. [10]. However in other published studies, such as Schindler [11], this improvement is not as evident. One of the advantages of laser surgery is its low cost when compared to radiotherapy, as well as the additional benefit of being able to opt for radiotherapy at a later stage to treat a relapse or second primary malignancy. In many institutions, these tumours are treated with external radiotherapy because of the supposedly better functional and quality of life results obtained compared to patients treated with surgery [12].
Various studies have been published comparing voice quality after both treatments [13–15]. In some studies, voice quality is similar, while other authors maintain that the voice is better after radiotherapy than after laser surgery [16–18]. However, there are fewer published works that include patient opinions with regard to the impact the illness and the treatment has had on their quality of life [19–21].
In our work, no significant differences in fundamental frequency (F 0), jitter, shimmer and NNE were found between the two groups. There were, however, significant differences in maximum phonation time, favoring the patients treated with CO2 laser cordectomy. Other authors do not find significant differences in the maximum phonation time between the groups [22–24]. In the study by Tamura et al. [13] the fundamental frequency is higher for patients treated with CO2 laser surgery, which suggests that this surgery has a greater impact on the vocal fold function than radiotherapy. Krengli et al. [18] found statistically significant differences in the vocal acoustic parameters and fundamental frequency, favoring radiotherapy patients.
In terms of the spectrograms obtained in both groups, no statistically significant differences were found. According to our results, 48% of patients treated with laser, and 44% of radiotherapy patients have an aesthetically acceptable voice (type I and II dysphonia).
There were no significant differences found between the two groups on comparing the scores obtained using the G parameter of the GRABS scale, which corresponds to the degree of dysphonia. Other studies such as Loughran et al. [20] failed to find statistically significant differences on comparing GRABS between patients treated with each technique. In our work, there is an elevated percentage of patients treated with CO2 laser (84%) who obtained low scores in the breathy voice domain (B), which shows that apart from individual healing patterns, or treatment-induced secondary glottic defects, post-cordectomy phonetic compensating mechanisms are important in determining new voice quality. According to Sittel et al. [25], glottic phonation voice quality is better than that obtained by the non-glottic phonation. Although one could believe that these patients had benefited from voice therapy, there are contradictory opinions on this [26].
While acoustic, physiological and perceptual measurements are important parameters in assessing vocal function, they do not provide information about the patient’s perception of their own voice quality. Given that voice quality, because of its potential impact on quality of life, can be an important factor in the choice of treatment, it is important to include this information when evaluating results. Not only should dysphonia as a by-product of laryngeal physiology be considered, but also the effects on patient quality of life must be considered as well.
In our study, in order to quantify patient opinion as to the impact caused by treatment, the Voice Handicap Index has been employed. This is an instrument developed to help the professional in deciding the therapy, taking into account the patient’s subjective sensations with respect to their problem. It is a post-treatment global result evaluation method, from the point of view of the patient’s perceived global well being (physical, mental and social). Although it is a subjective evaluation based on the patient’s own perception, it can provide valuable data as to the reasons why patients with similar dysphonia characteristics can have different handicap severity indices [27]. VHI allows investigators to obtain information regarding the patient’s subjective perception as well as providing the physician with important information pre and post treatment. Given that the preservation of adequate phonation is an important consideration in early glottic carcinoma treatment selection and given equal oncologic results between the two treatments, the VHI proves to be a very important tool in the therapeutic decision-making process.
In our study, low scores were obtained for both groups in the three scales, functional, physical and emotional. This could imply reduced impact in the quality of life of patients treated either with laser surgery or radiotherapy. The statistically significant differences are in favor of radiotherapy patients in the functional and emotional scales, as well as the global scores. Although acoustic and perceptual voice analysis in both groups showed no significant differences, the radiotherapy group scored less in the VHI than the surgical group.
Loughran et al. [20] performed a study where they compared the results between both therapies in terms of the Voice Handicap Index as well as two other questionnaires aimed at evaluating the patient’s subjective voice quality (Vocal Performance Questionnaire, VPQ, and Voice Symptom Score, VoiSS). In this work, no significant differences were discovered between radiotherapy and CO2 laser surgery patients in any of the questionnaires, except for the emotional sub-scale inVoiSS.
However, in other studies the average global score in the Voice Handicap Index questionnaire is lower for patients treated with endoscopic laser resection than in patients treated with radiotherapy. Peeters et al. [21] compared the results of both the Voice Handicap Index and a quality of life questionnaire (COOP/WOONCA) following both treatments. In their results, they found statistically significant differences in favor of laser surgery for the VHI and none in the quality of life results. They found higher scores for global VHI results in 40% of patients treated using surgery, and 58% for those treated with radiotherapy. Their conclusions reveal that the treatment for T1 glottic carcinoma frequently generates vocal problems in day-to-day life, influencing negatively certain social activities. This data contradicts the results of our study where VHI scores of both groups were low and the differences found favored the radiotherapy patient group. Recently, Cohen et al. [28] published a meta-analysis in order to classify the quality of life related to voice in patients with TI glottic carcinomas treated with radiotherapy compared with CO2 laser resection. Six studies with a total of 208 patients treated with surgery and 91 with radiotherapy had similar scores for VHI, from which they concluded that both treatments result in comparable vocal handicap levels for patients with T1 glottic carcinomas [28].
In other works such as that by Stoeckli [19], which value long-term results with regard to quality of life (QOL) of early glottic carcinoma patients, no differences were found between the two treatments and they conclude that both therapies provide good results in terms of quality of life. They show in addition, differences in the relative scores for questions such as swallowing, xerostomy and dental problems, favoring patients treated surgically, and show no differences with regard to perceived voice quality. These results could be related to the fact that xerostomy, edema, mucositis and fibrosis increase the sensation of handicap to such an extent that these effects on patient quality of life could be greater than those coming from the dysphonia itself in laser surgery patients.
Few are the patients that have a so-called “normal” voice upon completing radiotherapy, above all taking into account that the larynx of these patients has undergone a surgical procedure in order to get a biopsy, has been intensely exposed to tobacco smoke and belongs generally to aged patients. All these factors negatively affect voice quality [29]. Despite this, the results of our work reveal that radiotherapy treatment for T1 glottic carcinoma generates lower repercussions in the subjective perception of residual dysphonia, as much in functional as in emotional aspects, when compared with CO2 laser surgery. The scores obtained in the VHI were low in the three domains for both groups, from which we can infer a scarce impact on the quality of life for laser surgery and radiotherapy for this type of patient.
Conclusions
Both CO2 laser resection and external radiotherapy as treatment for T1 vocal carcinoma offer similar objective measurement results (acoustic and spectrographic analysis) and subjective measurement results (GRABS scoring). However, in our series, the self-evaluation of the quality of voice, quantified by the VHI, shows a lower impact for radiotherapy patients.
References
Jepsen M, Gurushanthaiah D, Roy N, Smith ME, Gray S, Davis K (2003) Voice, speech, and swallowing outcomes in laser treated laryngeal cancer. Laryngoscope 113:923–928
Delsupehe KG, Zink I, Lejaegere M, Bastian RW (1999) Voice quality after narrow-margin laser cordectomy compared with laryngeal irradiation. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 121:528–533
Hirano M (1981) Clinical examination of voice. Springer, New York, pp 81–84
Núñez Batalla F, Corte Santos P, Sequeiros Santiago G, Señaris González B, Suárez Nieto C (2004) Evaluación perceptual de la disfonía: Correlación con los parámetros acústicos y fiabilidad. Acta Otorrinolaringol Esp 55:195–197
Jacobson BH, Jonson A, Grywalski C (1997) The Voice Handicap Index (VHI): development and validation. Am J Speech Lang Pathol 6:66–70
American Joint Committee on Cancer: manual for staging of cancer, 3rd edn (1988) In: Beahrs OH, Henson DE, Hutter RVP, Myers MH (eds). Lippincott, Philadelphia, pp 39–44
Yanagihara N (1967) Significance of harmonic changes and noise components in hoarseness. J Speech Hear Res 10:531–541
Smith JC, Johnson JT, Myers EN (2002) Management and outcome of early glottic carcinoma. Otolaryngolog Head Neck Surg 126:356–364
Smith J, Jonson J, Cognetti D, Landsittel D, Gooding W, Cano E, Myers EN (2003) Quality of life, functional outcome, and costs of early glottic cancer. Laryngoscope 113:68–76
Keilmann A, Bergler W, Artzt M, Hormann K (1996) Vocal function following laser and conventional surgery of small malignant vocal fold tumours. J Laryngol Otol 110(12):1138–1141
Schindler A, Palonta F, Preti G, Ottaviani F, Schindler O, Cavalot Al (2004) Voice quality after carbon dioxide laser and conventional surgery for T1A glottic carcinoma. J Voice 18(4):545–550
Gallo A, Vincentiis M, Manciocco V, Simonelli M, Fiorella ML, Shah JP (2002) CO2 laser cordectomy for early-stage glottic carcinoma: a long-term follow-up of 156 cases. Laryngoscope 112:370–374
Tamura E, Kitahara S, Obura M, Cono N (2003) Voice quality after laser surgery or radiotherapy for T1a glottic carcinoma. Laryngoscope 113:910–914
Piazza C, Cantarella G, Balzanelli C, Nicolai P (2003) Vocal outcome after endoscopic cordectomies for Tis and T1 glottic carcinoma. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 112:174–179
Wedman J, Heimdal J, Elstad I, Olofsson J (2002) Voice results in patients with T1a glottic cancer treated by radiotherapy or endoscopic measures. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 259:547–550
Pellitteri PK, Kennedy TL, Vrabec DP, Beiler D, Hellstrom M (1991) Radiotherapy: the mainstay in the treatment of early glottic carcinoma. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 117:297–301
Verdonck-de Leeuw IM, Keus RB, Hilgers FJ, Koopmans-van Beinum FJ, Greven AJ, De Jong JM, Vreeburg G, Bartelink H (1999) Consequences of voice impairment in daily life for patients following radiotherapy for early glottic cancer: voice quality, vocal function, and vocal performance. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 44:1071–1078
Krengli M, Policarpo M, Manfreda I, Aluffi P, Gambaro G, Panella M, Pia F (2004) Voice quality alter treatment for T1a glottic carcinoma- radiotherapy versus laser cordectomy. Acta Oncol 43(3):284–289
Stoeckli SJ, Guidicelli M, Schneider A, Huber A, Schmid S (2001) Quality of life after treatment for early laryngeal carcinoma. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 258:96–99
Loughran S, Calder N, MacGregor FB, Carding F, Mackenzie K (2003) Quality of life and voice following endoscopic resection or radiotherapy for early glottic cancer. Clin Otolaryngol 30(11):42–47
Peeters AJ, van Gogh CD, Goor KM, Verdonck-de Leeuw IM, Langendijk JA, Mahieu HF (2004) Health status and voice outcome after treatment for T1a glottic carcinoma. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 261(10):534–540
Hirano M, Hirade Y, Kawasaki H (1985) Vocal function following carbon dioxide laser surgery for glottic carcinoma. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 94:232–235
Mc Guirt WF, Blalock D, Kaufman JA (1994) Comparative voice result after resection or irradiation of T1 vocal cord carcinoma. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 120:951–955
Cragle SP, Brandenburg JH (1993) Laser cordectomy or radiotherapy: cure rates, communication and cost. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 108:648–654
Sittel C, Eckel H, Eschenburg C (1998) Phonatory results after laser surgery for glottic carcinoma. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 119:418–424
Bertino G, Bellomo A, Ferrero F, Ferlito A (2001) Acoustic analysis of voice quality with or without false vocal fold displacement after cordectomy. J Voice 15:131–140
Murry T, Rosen CA (2000) Outcome measurements and quality of life in voice disorders. In: Rosen CA, Murry T (eds) The otolaryngologic clinics of North America: voice disorders and phonosurgery I, vol 33. Saunders, Philadelphia, pp 905–16
Cohen SM, Garrett CG, Dupont WD, Ossoff RH, Courey MS (2006) Voice-related quality of life in T1 glottic cancer: irradiation versus endoscopic excision. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 115:581–586
Verdonck IM, Hilgers F, Keus R, Koopmans F, Greven A, Jong J, Vreeburg G, Bartelink H (1999) Multidimensional assessment of voice characteristics after radioterapy for early glottic cancer. Laryngoscope 109:24–48
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
Open Access This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Noncommercial License ( https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/2.0 ), which permits any noncommercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and source are credited.
About this article
Cite this article
Núñez Batalla, F., Caminero Cueva, M.J., Señaris González, B. et al. Voice quality after endoscopic laser surgery and radiotherapy for early glottic cancer: objective measurements emphasizing the Voice Handicap Index. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 265, 543–548 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-007-0512-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-007-0512-9