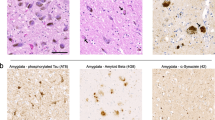
Abstract
Lewy bodies, the histologic hallmark of Parkinson’s disease (PD), are detected in the brains of about 10% of clinically normal people over the age of 60 years. When Lewy bodies are found in normal individuals, the process is sometimes referred to as incidental Lewy body disease (iLBD). The distribution of Lewy bodies in iLBD is similar to the distribution in PD, but neuronal populations vulnerable to Lewy bodies do not show significant neuronal loss in iLBD. It remains unknown if Lewy bodies in this setting represent pre-symptomatic PD or an age-related change unrelated to PD. To address this question we identified cases of iLBD and used a marker for dopaminergic and noradrenergic neurons, tyrosine hydroxylase (TH), to determine if there were changes similar to those found in PD. TH immunoreactivity in the striatum and the epicardial nerve fibers was decreased in iLBD compared to normal controls, but not to the same extent as in PD. The findings suggest that iLBD is preclinical PD and that the lack of symptoms is due to subthreshold pathology.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbott RD, Petrovitch H, White LR, Masaki KH, Tanner CM, Curb JD, Grandinetti A, Blanchette PL, Popper JS, Ross GW (2001) Frequency of bowel movements and the future risk of Parkinson’s disease. Neurology 57:456–462
Abbott RD, Ross GW, Petrovitch H, Tanner CM, Davis DG, Masaki KH, Launer LJ, Curb JD, White LR (2007) Bowel movement frequency in late-life and incidental Lewy bodies. Mov Disord [Epub ahead of print]
Beach TG, Tago H, Nagai T, Kimura H, McGeer PL, McGeer EG (1987) Perfusion-fixation of the human brain for immunohistochemistry: comparison with immersion-fixation. J Neurosci Methods 19:183–192
Beach TG, Walker DG, Sue LI, Newell A, Adler CC, Joyce JN (2004) Substantia nigra Marinesco bodies are associated with decreased striatal expression of dopaminergic markers. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 63:329–337
Beach TG, Adler CH, Sue LI, Peirce JB, Bachalakuri J, Dalsing-Hernandez JE, Lue LF, Caviness JN, Connor DJ, Sabbagh MN, Walker DG (2008) Reduced striatal tyrosine hydroxylase in incidental Lewy body disease. Acta Neuropathol [Epub ahead of print]
Bennett DA, Schneider JA, Arvanitakis Z, Kelly JF, Aggarwal NT, Shah RC, Wilson RS (2006) Neuropathology of older persons without cognitive impairment from two community-based studies. Neurology 66:1837–1844
Berendse HW, Booij J, Francot CM, Bergmans PL, Hijman R, Stoof JC, Wolters EC (2001) Subclinical dopaminergic dysfunction in asymptomatic Parkinson’s disease patients’ relatives with a decreased sense of smell. Ann Neurol 50:34–41
Bloch A, Probst A, Bissig H, Adams H, Tolnay M (2006) Alpha-synuclein pathology of the spinal and peripheral autonomic nervous system in neurologically unimpaired elderly subjects. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 32:284–295
Boeve BF, Dickson DW, Olson EJ, Shepard JW, Silber MH, Ferman TJ, Ahlskog JE, Benarroch EE (2007) Insights into REM sleep behavior disorder pathophysiology in brainstem-predominant Lewy body disease. Sleep Med 8:60–64
Booij J, Bergmans P, Winogrodzka A, Speelman JD, Wolters EC (2001) Imaging of dopamine transporters with [123I]FP-CIT SPECT does not suggest a significant effect of age on the symptomatic threshold of disease in Parkinson’s disease. Synapse 39:101–108
Booij J, Speelman JD, Horstink MW, Wolters EC (2001) The clinical benefit of imaging striatal dopamine transporters with [123I]FP-CIT SPET in differentiating patients with presynaptic parkinsonism from those with other forms of parkinsonism. Eur J Nucl Med 28:266–272
Braak H, Del Tredici K, Rub U, de Vos RA, Jansen Steur EN, Braak E (2003) Staging of brain pathology related to sporadic Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 24:197–211
Braak H, de Vos RA, Bohl J, Del Tredici K (2006) Gastric alpha-synuclein immunoreactive inclusions in Meissner’s and Auerbach’s plexuses in cases staged for Parkinson’s disease-related brain pathology. Neurosci Lett 396:67–72
Braak H, Sastre M, Bohl JR, de Vos RA, Del Tredici K (2007) Parkinson’s disease: lesions in dorsal horn layer I, involvement of parasympathetic and sympathetic pre- and postganglionic neurons. Acta Neuropathol 113:421–429
Brooks DJ, Frey KA, Marek KL, Oakes D, Paty D, Prentice R, Shults CW, Stoessl AJ (2003) Assessment of neuroimaging techniques as biomarkers of the progression of Parkinson’s disease. Exp Neurol 184(Suppl 1):S68–S79
DelleDonne A, Tsuboi Y, Uchikado H, Ahmed Z, Mash DC, Dickson DW (2006) Tyrosine hydroxylase expression in the nigrostriatal pathway in Lewy body disease with and without dementia. Mov Disord 21(Suppl 15):S553
Del Tredici K, Rub U, De Vos RA, Bohl JR, Braak H (2002) Where does Parkinson disease pathology begin in the brain? J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 61:413–426
Foltynie T, Matthews FE, Ishihara L, Brayne C (2006) The frequency and validity of self-reported diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease in the UK elderly: MRC CFAS cohort. BMC Neurol 6:29
Forno LS (1969) Concentric hyalin intraneuronal inclusions of Lewy type in the brains of elderly persons (50 incidental cases): relationship to parkinsonism. J Am Geriatr Soc 17:557–575
Fujishiro H, Frigerio R, Burnett M, Klos KJ, Josephs JA, DelleDonne A, Parisi JE, Ahlskog JE, Dickson DW (2008) Cardiac sympathetic denervation correlates with clinical and pathologic stages of Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 23 (in press)
Fumimura Y, Ikemura M, Saito Y, Sengoku R, Kanemaru K, Sawabe M, Arai T, Ito G, Iwatsubo T, Fukayama M, Mizusawa H, Murayama S (2007) Analysis of the adrenal gland is useful for evaluating pathology of the peripheral autonomic nervous system in Lewy body disease. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 66:354–362
Gibb WR, Lees AJ (1988) The relevance of the Lewy body to the pathogenesis of idiopathic Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 51:745–752
Gibb WR, Lees AJ (1989) The significance of the Lewy body in the diagnosis of idiopathic Parkinson’s disease. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 15:27–44
Guttman M, Burkholder J, Kish SJ, Hussey D, Wilson A, DaSilva J, Houle S (1997) [11C]RTI-32 PET studies of the dopamine transporter in early dopa-naive Parkinson’s disease: implications for the symptomatic threshold. Neurology 48:1578–1583
Hamada K, Hirayama M, Watanabe H, Kobayashi R, Ito H, Ieda T, Koike Y, Sobue G (2003) Onset age and severity of motor impairment are associated with reduction of myocardial 123I-MIBG uptake in Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 74:423–426
Hattori T (1993) Conceptual history of the nigrostriatal dopamine system. Neurosci Res 16:239–262
Hawkes CH, Shephard BC, Daniel SE (1997) Olfactory dysfunction in Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 62:436–446
Hilker R, Schweitzer K, Coburger S, Ghaemi M, Weisenbach S, Jacobs AH, Rudolf J, Herholz K, Heiss WD (2005) Nonlinear progression of Parkinson disease as determined by serial positron emission tomographic imaging of striatal fluorodopa F 18 activity. Arch Neurol 62:378–382
Hughes AJ, Daniel SE, Kilford L, Lees AJ (1992) Accuracy of clinical diagnosis of idiopathic Parkinson’s disease: a clinico-pathological study of 100 cases. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 55:181–184
Hughes AJ, Daniel SE, Blankson S, Lees AJ (1993) A clinicopathologic study of 100 cases of Parkinson’s disease. Arch Neurol 50:140–148
Jellinger KA (2004) Lewy body-related alpha-synucleinopathy in the aged human brain. J Neural Transm 111:1219–1235
Kawano H, Okada R, Yano K (2003) Histological study on the distribution of autonomic nerves in the human heart. Heart Vessels 18:32–39
Klos KJ, Ahlskog JE, Josephs KA, Apaydin H, Parisi JE, Boeve BF, DeLucia MW, Dickson DW (2006) Alpha-synuclein pathology in the spinal cords of neurologically asymptomatic aged individuals. Neurology 66:1100–1102
Knopman DS, Parisi JE, Salviati A, Floriach-Robert M, Boeve BF, Ivnik RJ, Smith GE, Dickson DW, Johnson KA, Petersen LE, McDonald WC, Braak H, Petersen RC (2003) Neuropathology of cognitively normal elderly. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 62:1087–1095
Mikolaenko I, Pletnikova O, Kawas CH, O’Brien R, Resnick SM, Crain B, Troncoso JC (2005) Alpha-synuclein lesions in normal aging, Parkinson disease, and Alzheimer disease: evidence from the Baltimore Longitudinal Study of Aging (BLSA). J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 64:156–162
Mitsui J, Saito Y, Momose T, Shimizu J, Arai N, Shibahara J, Ugawa Y, Kanazawa I, Tsuji S, Murayama S (2006) Pathology of the sympathetic nervous system corresponding to the decreased cardiac uptake in 123I-metaiodobenzylguanidine (MIBG) scintigraphy in a patient with Parkinson disease. J Neurol Sci 243:101–104
Miyamoto T, Miyamoto M, Inoue Y, Usui Y, Suzuki K, Hirata K (2006) Reduced cardiac 123I-MIBG scintigraphy in idiopathic REM sleep behavior disorder. Neurology 67:2236–2238
Orimo S, Ozawa E, Nakade S, Sugimoto T, Mizusawa H (1999) (123)I-metaiodobenzylguanidine myocardial scintigraphy in Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 67:189–194
Orimo S, Amino T, Itoh Y, Takahashi A, Kojo T, Uchihara T, Tsuchiya K, Mori F, Wakabayashi K, Takahashi H (2005) Cardiac sympathetic denervation precedes neuronal loss in the sympathetic ganglia in Lewy body disease. Acta Neuropathol 109:583–588
Orimo S, Takahashi A, Uchihara T, Mori F, Kakita A, Wakabayashi K, Takahashi H (2007) Degeneration of cardiac sympathetic nerve begins in the early disease process of Parkinson’s disease. Brain Pathol 17:24–30
Ross GW, Petrovitch H, Abbott RD, Nelson J, Markesbery W, Davis D, Hardman J, Launer L, Masaki K, Tanner CM, White LR (2004) Parkinsonian signs and substantia nigra neuron density in descendents elders without PD. Ann Neurol 56:532–539
Schenck CH, Bundlie SR, Mahowald MW (1996) Delayed emergence of a parkinsonian disorder in 38% of 29 older men initially diagnosed with idiopathic rapid eye movement sleep behaviour disorder. Neurology 46:388–393
Stiasny-Kolster K, Doerr Y, Moller JC, Hoffken H, Behr TM, Oertel WH, Mayer G (2005) Combination of ‘idiopathic’ REM sleep behaviour disorder and olfactory dysfunction as possible indicator for alpha-synucleinopathy demonstrated by dopamine transporter FP-CIT-SPECT. Brain 128:126–137
Wakabayashi K, Takahashi H (1997) The intermediolateral nucleus and Clarke’s column in Parkinson’s disease. Acta Neuropathol 94:287–289
Wakabayashi K, Takahashi H (1997) Neuropathology of autonomic nervous system in Parkinson’s disease. Eur Neurol 38(Suppl 2):2–7
Wakabayashi K, Takahashi H, Takeda S, Ohama E, Ikuta F (1988) Parkinson’s disease: the presence of Lewy bodies in Auerbach’s and Meissner’s plexuses. Acta Neuropathol 76:217–221
Acknowledgments
This study is supported by the Morris K. Udall Center for Excellence in Parkinson’s Disease Research at Mayo Clinic (NIH P50-NS40256-09). The authors acknowledge Michael Oelkers and Allison Kendall for their efforts in acquiring tissue for these studies through the Mayo Tissue Registry. The assistance of Virginia Phillips, Linda Rousseau and Monica Casey-Castanedes for histologic and immunohistochemistry studies is also greatly appreciated.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dickson, D.W., Fujishiro, H., DelleDonne, A. et al. Evidence that incidental Lewy body disease is pre-symptomatic Parkinson’s disease. Acta Neuropathol 115, 437–444 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-008-0345-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-008-0345-7