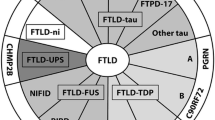
Abstract
Frontotemporal lobar degeneration is the term used to describe the non-Alzheimer clinical syndromes of frontotemporal dementia, semantic dementia and progressive non-fluent aphasia, regardless of the underlying neuropathological features. Considerable progress has been made in recent years in our understanding of the aetiology of this disorder, notably the identification of mutations in tau and progranulin genes, both on chromosome 17q21. Mutations in tau appear to affect the ability of tau to bind microtubules and/or increase this protein’s ability to form fibrils. In contrast, progranulin mutations cause haploinsufficiency leading to TDP-43 accumulation. These genes collectively account for 10–20% of FTLD. However, it is clear that much remains to be discovered before our knowledge of this heterogeneous condition is complete.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amtul Z, Lewis PA, Piper S, Crook R, Baker M, Findlay K, Singleton A, Hogg M, Younkin L, Younkin SG, Hardy J, Hutton M, Boeve BF, Tang-Wai D, Golde TE (2002) A presenilin 1 mutation associated with familial frontotemporal dementia inhibits gamma-secretase cleavage of APP and notch. Neurobiol Dis 9:269–273
Arai T, Nonaka T, Hasegawa M, Akiyama H, Yoshida M, Hashizume Y, Tsuchiya K, Oda T, Ikeda K (2003) Neuronal and glial inclusions in frontotemporal dementia with or without motor neuron disease are immunopositive for p62. Neurosci Lett 342:41–44
Armstrong RA, Kerty E, Skullerud K, Cairns NJ (2006) Neuropathological changes in ten cases of neuronal intermediate filament inclusion disease (NIFID): a study using alpha-internexin immunohistochemistry and principal components analysis (PCA). J Neural Transm 113:1207–1215
Baker CA, Martin D, Manuelidis L (2002) Microglia from Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease-infected brains are infectious and show specific mRNA activation profiles. J Virol 76:10905–10913
Baker M, Mackenzie IR, Pickering-Brown SM, Gass J, Rademakers R, Lindholm C, Snowden J, Adamson J, Sadovnick AD, Rollinson S, Cannon A, Dwosh E, Neary D, Melquist S, Richardson A, Dickson D, Berger Z, Eriksen J, Robinson T, Zehr C, Dickey CA, Crook R, McGowan E, Mann D, Boeve B, Feldman H, Hutton M (2006) Mutations in progranulin cause tau-negative frontotemporal dementia linked to chromosome 17. Nature 442:916–919
Behrens MI, Mukherjee O, Tu PH, Liscic RM, Grinberg LT, Carter D, Paulsmeyer K, Taylor-Reinwald L, Gitcho M, Norton JB, Chakraverty S, Goate AM, Morris JC, Cairns NJ (2007) Neuropathologic heterogeneity in HDDD1: a familial frontotemporal lobar degeneration with ubiquitin-positive inclusions and progranulin mutation. Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord 21:1–7
Benussi L, Binetti G, Sina E, Gigola L, Bettecken T, Meitinger T, Ghidoni R (2007) A novel deletion in progranulin gene is associated with FTDP-17 and CBS. Neurobiol Aging (in press)
Benussi L, Signorini S, Ghidoni R, Alberici A et al (2004) Identification of genetic loci associated with familial frontotemporal dementia. Neurobiol Aging 25:4–149
Bhandari V, Palfree RG, Bateman A (1992) Isolation and sequence of the granulin precursor cDNA from human bone marrow reveals tandem cysteine-rich granulin domains. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89:1715–1719
Bigio EH, Johnson NA, Rademaker AW, Fung BB, Mesulam MM, Siddique N, Dellefave L, Caliendo J, Freeman S, Siddique T (2004) Neuronal ubiquitinated intranuclear inclusions in familial and non-familial frontotemporal dementia of the motor neuron disease type associated with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 63:801–811
Bird TD, Wijsman EM, Nochlin D, Leehey M, Sumi SM, Payami H, Poorkaj P, Nemens E, Rafkind M, Schellenberg GD (1997) Chromosome 17 and hereditary dementia: linkage studies in three non-Alzheimer families and kindreds with late-onset FAD. Neurology 48:949–954
Boeve BF, Baker M, Dickson DW, Parisi JE, Giannini C, Josephs KA, Hutton M, Pickering-Brown SM, Rademakers R, Tang-Wai D, Jack CR Jr, Kantarci K, Shiung MM, Golde T, Smith GE, Geda YE, Knopman DS, Petersen RC (2006) Frontotemporal dementia and parkinsonism associated with the IVS1 + 1G->A mutation in progranulin: a clinicopathologic study. Brain 129:3103–3114
Bronner IF, Rizzu P, Seelaar H, van Mil SE, Anar B, Azmani A, Kaat LD, Rosso S, Heutink P, van Swieten JC (2007) Progranulin mutations in Dutch familial frontotemporal lobar degeneration. Eur J Hum Genet 15(3):369–374
Bronner IF, Rizzu P, Seelaar H, van Mil SE, Anar B, Azmani A, Kaat LD, Rosso S, Heutink P, van Swieten JC (2007) Progranulin mutations in Dutch familial frontotemporal lobar degeneration. Eur J Hum Genet 15:369–374
Brown J, Ashworth A, Gydesen S, Sorensen A, Rossor M, Hardy J, Collinge J (1995) Familial non-specific dementia maps to chromosome 3. Hum Mol Genet 4:1625–1628
Brun A (1994) Clinical and neuropathological criteria for frontotemporal dementia. The Lund and Manchester Groups. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 57:416–418
Cairns NJ, Zhukareva V, Uryu K, Zhang B, Bigio E, Mackenzie IR, Gearing M, Duyckaerts C, Yokoo H, Nakazato Y, Jaros E, Perry RH, Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ (2004) Alpha-internexin is present in the pathological inclusions of neuronal intermediate filament inclusion disease. Am J Pathol 164:2153–2161
Cannon A, Baker M, Boeve B, Josephs K, Knopman D, Petersen R, Parisi J, Dickison D, Adamson J, Snowden J, Neary D, Mann D, Hutton M, Pickering-Brown SM (2006) CHMP2B mutations are not a common cause of frontotemporal lobar degeneration. Neurosci Lett 398:83–84
Cruts M, Gijselinck I, van der Zee J, Engelborghs S, Wils H, Pirici D, Rademakers R, Vandenberghe R, Dermaut B, Martin JJ, van Duijn C, Peeters K, Sciot R, Santens P, De Pooter T, Mattheijssens M, Van den Broeck M, Cuijt I, Vennekens K, De Deyn PP, Kumar-Singh S, Van Broeckhoven C (2006) Null mutations in progranulin cause ubiquitin-positive frontotemporal dementia linked to chromosome 17q21. Nature 442:920–924
Cruts M, Rademakers R, Gijselinck I, van der Zee J, Dermaut B, de Pooter T, de Rijk P, Del-Favero J, van Broeckhoven C (2005) Genomic architecture of human 17q21 linked to frontotemporal dementia uncovers a highly homologous family of low-copy repeats in the tau region. Hum Mol Genet 14:1753–1762
D’Souza I, Poorkaj P, Hong M, Nochlin D, Lee VM, Bird TD, Schellenberg GD (1999) Missense and silent tau gene mutations cause frontotemporal dementia with parkinsonism-chromosome 17 type, by affecting multiple alternative RNA splicing regulatory elements. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:5598–5603
D’Souza I, Schellenberg GD (2000) Determinants of 4-repeat tau expression. Coordination between enhancing and inhibitory splicing sequences for exon 10 inclusion. J Biol Chem 275:17700–17709
D’Souza I, Schellenberg GD (2002) tau Exon 10 expression involves a bipartite intron 10 regulatory sequence and weak 5’ and 3’ splice sites. J Biol Chem 277:26587–26599
Daniel R, Daniels E, He Z, Bateman A (2003) Progranulin (acrogranin/PC cell-derived growth factor/granulin-epithelin precursor) is expressed in the placenta, epidermis, microvasculature, and brain during murine development. Dev Dyn 227:593–599
Daniel R, He Z, Carmichael KP, Halper J, Bateman A (2000) Cellular localization of gene expression for progranulin. J Histochem Cytochem 48:999–1009
Dayanandan R, Van Slegtenhorst M, Mack TG, Ko L, Yen SH, Leroy K, Brion JP, Anderton BH, Hutton M, Lovestone S (1999) Mutations in tau reduce its microtubule binding properties in intact cells and affect its phosphorylation. FEBS Lett 446:228–232
Disset A, Michot C, Harris A, Buratti E, Claustres M, Tuffery-Giraud S (2005) A T3 allele in the CFTR gene exacerbates exon 9 skipping in vas deferens and epididymal cell lines and is associated with Congenital Bilateral Absence of Vas Deferens (CBAVD). Hum Mutat 25:72–81
Froelich S, Basun H, Forsell C, Lilius L, Axelman K, Andreadis A, Lannfelt L (1997) Mapping of a disease locus for familial rapidly progressive frontotemporal dementia to chromosome 17q12–21. Am J Med Genet 74:380–385
Gass J, Cannon A, Mackenzie IR, Boeve B, Baker M, Adamson J, Crook R, Melquist S, Kuntz K, Petersen R, Josephs K, Pickering-Brown SM, Graff-Radford N, Uitti R, Dickson D, Wzsolek Z, Gonzalez J, Beach TG, Bigio E, Johnson N, Weintraub S, Mesulam M, White CL 3rd, Woodruff B, Caselli R, Hsiung GY, Feldman H, Knopman D, Hutton M, Rademakers R (2006) Mutations in progranulin are a major cause of ubiquitin-positive frontotemporal lobar degeneration. Hum Mol Genet 15:2988–3001
Ghetti B, Murrell JR, Zolo P, Spillantini MG, Goedert M (2000) Progress in hereditary tauopathies: a mutation in the Tau gene (G389R) causes a Pick disease-like syndrome. Ann N Y Acad Sci 920:52–62
Goedert M, Spillantini MG, Jakes R, Rutherford D, Crowther RA (1989) Multiple isoforms of human microtubule-associated protein tau: sequences and localization in neurofibrillary tangles of Alzheimer’s disease. Neuron 3:519–526
Goedert M, Spillantini MG, Potier MC, Ulrich J, Crowther RA (1989) Cloning and sequencing of the cDNA encoding an isoform of microtubule-associated protein tau containing four tandem repeats: differential expression of tau protein mRNAs in human brain. Embo J 8:393–399
Grover A, Houlden H, Baker M, Adamson J, Lewis J, Prihar G, Pickering-Brown S, Duff K, Hutton M (1999) 5’ splice site mutations in tau associated with the inherited dementia FTDP-17 affect a stem-loop structure that regulates alternative splicing of exon 10. J Biol Chem 274:15134–15143
Hasegawa M, Smith MJ, Goedert M (1998) Tau proteins with FTDP-17 mutations have a reduced ability to promote microtubule assembly. FEBS Lett 437:207–210
He Z, Bateman A (2003) Progranulin (granulin-epithelin precursor, PC-cell-derived growth factor, acrogranin) mediates tissue repair and tumorigenesis. J Mol Med 81:600–612
He Z, Ong CH, Halper J, Bateman A (2003) Progranulin is a mediator of the wound response. Nat Med 9:225–229
Hong M, Zhukareva V, Vogelsberg-Ragaglia V, Wszolek Z, Reed L, Miller BI, Geschwind DH, Bird TD, McKeel D, Goate A, Morris JC, Wilhelmsen KC, Schellenberg GD, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM (1998) Mutation-specific functional impairments in distinct tau isoforms of hereditary FTDP-17. Science 282:1914–1917
Hosler BA, Siddique T, Sapp PC, Sailor W, Huang MC, Hossain A, Daube JR, Nance M, Fan C, Kaplan J, Hung WY, McKenna-Yasek D, Haines JL, Pericak-Vance MA, Horvitz HR, Brown RH Jr (2000) Linkage of familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis with frontotemporal dementia to chromosome 9q21–q22. JAMA 284:1664–1669
Houlden H, Baker M, Adamson J, Grover A, Waring S, Dickson D, Lynch T, Boeve B, Petersen RC, Pickering-Brown S, Owen F, Neary D, Craufurd D, Snowden J, Mann D, Hutton M (1999) Frequency of tau mutations in three series of non-Alzheimer’s degenerative dementia. Ann Neurol 46:243–248
Hutton M, Lendon CL, Rizzu P, Baker M, Froelich S, Houlden H, Pickering-Brown S, Chakraverty S, Isaacs A, Grover A, Hackett J, Adamson J, Lincoln S, Dickson D, Davies P, Petersen RC, Stevens M, de Graaff E, Wauters E, van Baren J, Hillebr M, Joosse M, Kwon JM, Nowotny P, Che LK, Norton J, Morris JC, Reed LA, Trojanowski J, Basun H, Lannfelt L, Neystat M, Fahn S, Dark F, Tannenberg T, Dodd PR, Hayward N, Kwok JB, Schofield PR, Andreadis A, Snowden J, Craufurd D, Neary D, Owen F, Oostra BA, Hardy J, Goate A, van Swieten J, Mann D, Lynch T, Heutink P (1998) Association of missense and 5’-splice-site mutations in tau with the inherited dementia FTDP-17. Nature 393:702–705
Ikeda M, Ishikawa T, Tanabe H (2004) Epidemiology of frontotemporal lobar degeneration. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord 17:265–268
Jiang Z, Cote J, Kwon JM, Goate AM, Wu JY (2000) Aberrant splicing of tau pre-mRNA caused by intronic mutations associated with the inherited dementia frontotemporal dementia with parkinsonism linked to chromosome 17. Mol Cell Biol 20:4036–4048
Johnston C, Jiang W, Chu T, Levine B (2001) Identification of genes involved in the host response to neurovirulent alphavirus infection. J Virol 75:10431–10445
Josephs KA, Holton JL, Rossor MN, Godbolt AK, Ozawa T, Strand K, Khan N, Al-Sarraj S, Revesz T (2004) Frontotemporal lobar degeneration and ubiquitin immunohistochemistry. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 30:369–373
Kertesz A, Kawarai T, Rogaeva E, St George-Hyslop P, Poorkaj P, Bird TD, Munoz DG (2000) Familial frontotemporal dementia with ubiquitin-positive, tau-negative inclusions. Neurology 54:818–827
Knopman DS, Mastri AR, Frey WH 2nd, Sung JH, Rustan T (1990) Dementia lacking distinctive histologic features: a common non-Alzheimer degenerative dementia. Neurology 40:251–256
Le Ber I, van der Zee J, Hannequin D, Gijselinck I, Campion D, Puel M, Laquerriere A, De Pooter T, Camuzat A, Van den Broeck M, Dubois B, Sellal F, Lacomblez L, Vercelletto M, Thomas-Anterion C, Michel BF, Golfier V, Didic M, Salachas F, Duyckaerts C, Cruts M, Verpillat P, Van Broeckhoven C, Brice A (2007) Progranulin null mutations in both sporadic and familial frontotemporal dementia. Hum Mutat
Lee G, Neve RL, Kosik KS (1989) The microtubule binding domain of tau protein. Neuron 2:1615–1624
Lendon CL, Lynch T, Norton J, McKeel DW Jr., Busfield F, Craddock N, Chakraverty S, Gopalakrishnan G, Shears SD, Grimmett W, Wilhelmsen KC, Hansen L, Morris JC, Goate AM (1998) Hereditary dysphasic disinhibition dementia: a frontotemporal dementia linked to 17q21–22. Neurology 50:1546–1555
Leverenz JB, Yu CE, Montine TJ, Steinbart E, Bekris LM, Zabetian C, Kwong LK, Lee VM, Schellenberg GD, Bird TD (2007) A novel progranulin mutation associated with variable clinical presentation and tau, TDP43 and alpha-synuclein pathology. Brain 130:1360–1374
Lipton AM, White CL 3rd, Bigio EH (2004) Frontotemporal lobar degeneration with motor neuron disease-type inclusions predominates in 76 cases of frontotemporal degeneration. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 108:379–385
Mackenzie IA, Feldman H (2003) The relationship between extramotor ubiquitin-immunoreactive neuronal inclusions and dementia in motor neuron disease. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 105:98–102
Mackenzie IR, Baker M, Pickering-Brown S, Hsiung GY, Lindholm C, Dwosh E, Gass J, Cannon A, Rademakers R, Hutton M, Feldman HH (2006) The neuropathology of frontotemporal lobar degeneration caused by mutations in the progranulin gene. Brain 129:3081–3090
Mackenzie IR, Baker M, West G, Woulfe J, Qadi N, Gass J, Cannon A, Adamson J, Feldman H, Lindholm C, Melquist S, Pettman R, Sadovnick AD, Dwosh E, Whiteheart SW, Hutton M, Pickering-Brown SM (2006) A family with tau-negative frontotemporal dementia and neuronal intranuclear inclusions linked to chromosome 17. Brain 129:853–867
Mackenzie IR, Shi J, Shaw CL, Duplessis D, Neary D, Snowden JS, Mann DM (2006) Dementia lacking distinctive histology (DLDH) revisited. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 112:551–559
Malaspina A, Kaushik N, de Belleroche J (2001) Differential expression of 14 genes in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis spinal cord detected using gridded cDNA arrays. J Neurochem 77:132–145
Mann DM (1998) Dementia of frontal type and dementias with subcortical gliosis. Brain Pathol 8:325–338
Mann DM, McDonagh AM, Snowden J, Neary D, Pickering-Brown SM (2000) Molecular classification of the dementias. Lancet 355:626
Masellis M, Momeni P, Meschino W, Heffner R Jr., Elder J, Sato C, Liang Y, St George-Hyslop P, Hardy J, Bilbao J, Black S, Rogaeva E (2006) Novel splicing mutation in the progranulin gene causing familial corticobasal syndrome. Brain 129:3115–3123
Mercado PA, Ayala YM, Romano M, Buratti E, Baralle FE (2005) Depletion of TDP 43 overrides the need for exonic and intronic splicing enhancers in the human apoA-II gene. Nucleic Acids Res 33:6000–6010
Mesulam M, Johnson N, Krefft TA, Gass JM, Cannon AD, Adamson JL, Bigio EH, Weintraub S, Dickson DW, Hutton ML, Graff-Radford NR (2007) Progranulin mutations in primary progressive aphasia: the PPA1 and PPA3 families. Arch Neurol 64:43–47
Momeni P, Cairns NJ, Perry RH, Bigio EH, Gearing M, Singleton AB, Hardy J (2006) Mutation analysis of patients with neuronal intermediate filament inclusion disease (NIFID). Neurobiol Aging 27:778.e1–778.e6
Morita M, Al-Chalabi A, Andersen PM, Hosler B, Sapp P, Englund E, Mitchell JE, Habgood JJ, de Belleroche J, Xi J, Jongjaroenprasert W, Horvitz HR, Gunnarsson LG, Brown RH Jr (2006) A locus on chromosome 9p confers susceptibility to ALS and frontotemporal dementia. Neurology 66:839–844
Mukherjee O, Pastor P, Cairns NJ, Chakraverty S, Kauwe JS, Shears S, Behrens MI, Budde J, Hinrichs AL, Norton J, Levitch D, Taylor-Reinwald L, Gitcho M, Tu PH, Tenenholz Grinberg L, Liscic RM, Armendariz J, Morris JC, Goate AM (2006) HDDD2 is a familial frontotemporal lobar degeneration with ubiquitin-positive, tau-negative inclusions caused by a missense mutation in the signal peptide of progranulin. Ann Neurol 60:314–322
Nacharaju P, Lewis J, Easson C, Yen S, Hackett J, Hutton M, Yen SH (1999) Accelerated filament formation from tau protein with specific FTDP-17 missense mutations. FEBS Lett 447:195–199
Neary D, Snowden JS, Gustafson L, Passant U, Stuss D, Black S, Freedman M, Kertesz A, Robert PH, Albert M, Boone K, Miller BL, Cummings J, Benson DF (1998) Frontotemporal lobar degeneration: a consensus on clinical diagnostic criteria. Neurology 51:1546–1554
Neary D, Snowden JS, Mann DM (2000) Classification and description of frontotemporal dementias. Ann N Y Acad Sci 920:46–51
Neary D, Snowden JS, Northen B, Goulding P (1988) Dementia of frontal lobe type. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 51:353–361
Neumann M, Mackenzie IR, Cairns NJ, Boyer PJ, Markesbery WR, Smith CD, Taylor JP, Kretzschmar HA, Kimonis VE, Forman MS (2007) TDP-43 in the ubiquitin pathology of frontotemporal dementia with VCP gene mutations. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 66:152–157
Neumann M, Sampathu DM, Kwong LK, Truax AC, Micsenyi MC, Chou TT, Bruce J, Schuck T, Grossman M, Clark CM, McCluskey LF, Miller BL, Masliah E, Mackenzie IR, Feldman H, Feiden W, Kretzschmar HA, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM (2006) Ubiquitinated TDP-43 in frontotemporal lobar degeneration and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Science 314:130–133
Ohmi K, Greenberg DS, Rajavel KS, Ryazantsev S, Li HH, Neufeld EF (2003) Activated microglia in cortex of mouse models of mucopolysaccharidoses I and IIIB. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:1902–1907
Pickering-Brown S, Baker M, Yen SH, Liu WK, Hasegawa M, Cairns N, Lantos PL, Rossor M, Iwatsubo T, Davies Y, Allsop D, Furlong R, Owen F, Hardy J, Mann D, Hutton M (2000) Pick’s disease is associated with mutations in the tau gene. Ann Neurol 48:859–867
Pickering-Brown SM, Baker M, Gass J, Boeve BF, Loy CT, Brooks WS, Mackenzie IR, Martins RN, Kwok JB, Halliday GM, Kril J, Schofield PR, Mann DM, Hutton M (2006) Mutations in progranulin explain atypical phenotypes with variants in MAPT. Brain 129:3124–3126
Pickering-Brown SM, Baker M, Nonaka T, Ikeda K, Sharma S, Mackenzie J, Simpson SA, Moore JW, Snowden JS, de Silva R, Revesz T, Hasegawa M, Hutton M, Mann DM (2004) Frontotemporal dementia with Pick-type histology associated with Q336R mutation in the tau gene. Brain 127:1415–1426
Pickering-Brown SM, Richardson AM, Snowden JS, McDonagh AM, Burns A, Braude W, Baker M, Liu WK, Yen SH, Hardy J, Hutton M, Davies Y, Allsop D, Craufurd D, Neary D, Mann DM (2002) Inherited frontotemporal dementia in nine British families associated with intronic mutations in the tau gene. Brain 125:732–751
Poorkaj P, Bird TD, Wijsman E, Nemens E, Garruto RM, Anderson L, Andreadis A, Wiederholt WC, Raskind M, Schellenberg GD (1998) Tau is a candidate gene for chromosome 17 frontotemporal dementia. Ann Neurol 43:815–825
Rademakers R, Cruts M, Dermaut B, Sleegers K, Rosso SM, Van den Broeck M, Backhovens H, van Swieten J, van Duijn CM, Van Broeckhoven C (2002) Tau negative frontal lobe dementia at 17q21: significant finemapping of the candidate region to a 4.8 cM interval. Mol Psychiatry 7:1064–1074
Rizzini C, Goedert M, Hodges JR, Smith MJ, Jakes R, Hills R, Xuereb JH, Crowther RA, Spillantini MG (2000) Tau gene mutation K257T causes a tauopathy similar to Pick’s disease. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 59:990–1001
Rizzu P, van Mil SE, Anar B, Rosso SM, Kaat LD, Heutink P, van Swieten JC (2006) CHMP2B mutations are not a cause of dementia in Dutch patients with familial and sporadic frontotemporal dementia. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet 141:944–946
Rizzu P, Van Swieten JC, Joosse M, Hasegawa M, Stevens M, Tibben A, Niermeijer MF, Hillebrand M, Ravid R, Oostra BA, Goedert M, van Duijn CM, Heutink P (1999) High prevalence of mutations in the microtubule-associated protein tau in a population study of frontotemporal dementia in the Netherlands. Am J Hum Genet 64:414–421
Rollinson S, Snowden JS, Neary D, Morrison KE, Mann DM, Pickering-Brown SM (2007) TDP-43 gene analysis in frontotemporal lobar degeneration. Neurosci Lett 419(1):1–4
Rosso SM, Kamphorst W, de Graaf B, Willemsen R, Ravid R, Niermeijer MF, Spillantini MG, Heutink P, van Swieten JC (2001) Familial frontotemporal dementia with ubiquitin-positive inclusions is linked to chromosome 17q21–22. Brain 124:1948–1957
Schumacher A, Friedrich P, Diehl-Schmid J, Ibach B, Eisele T, Laws SM, Forstl H, Kurz A, Riemenschneider M (2006) No association of chromatin-modifying protein 2B with sporadic frontotemporal dementia. Neurobiol Aging
Schymick J, Yang Y, Andersen P, Vonsattel J, Greenway M, Momeni P, Elder J, Chio A, Restagno G, Robberecht W, Dahlberg C, Mukherjee O, Goate A, Graff-Radford N, Caselli R, Hutton M, Gass J, Cannon A, Rademakers R, Singleton A, Hardiman O, Rothstein J, Hardy J, Traynor B (2007) Progranulin mutations and ALS or ALS-FTD phenotypes. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry
Skibinski G, Parkinson NJ, Brown JM, Chakrabarti L, Lloyd SL, Hummerich H, Nielsen JE, Hodges JR, Spillantini MG, Thusgaard T, Brandner S, Brun A, Rossor MN, Gade A, Johannsen P, Sorensen SA, Gydesen S, Fisher EM, Collinge J (2005) Mutations in the endosomal ESCRTIII-complex subunit CHMP2B in frontotemporal dementia. Nat Genet 37:806–808
Snowden JS, Neary D, Mann DM (2002) Frontotemporal dementia. Br J Psychiatry 180:140–143
Snowden JS, Pickering-Brown SM, Mackenzie IR, Richardson AM, Varma A, Neary D, Mann DM (2006) Progranulin gene mutations associated with frontotemporal dementia and progressive non-fluent aphasia. Brain 129:3091–3102
Spillantini MG, Crowther RA, Kamphorst W, Heutink P, van Swieten JC (1998) Tau pathology in two Dutch families with mutations in the microtubule-binding region of tau. Am J Pathol 153:1359–1363
Spillantini MG, Murrell JR, Goedert M, Farlow MR, Klug A, Ghetti B (1998) Mutation in the tau gene in familial multiple system tauopathy with presenile dementia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:7737–7741
Spillantini MG, Van Swieten JC, Goedert M (2000) Tau gene mutations in frontotemporal dementia and parkinsonism linked to chromosome 17 (FTDP-17). Neurogenetics 2:193–205
Spina S, Murrell JR, Huey ED, Wassermann EM, Pietrini P, Baraibar MA, Barbeito AG, Troncoso JC, Vidal R, Ghetti B, Grafman J (2007) Clinicopathologic features of frontotemporal dementia with Progranulin sequence variation. Neurology 68(11):820–827
Stevens M, van Duijn CM, Kamphorst W, de Knijff P, Heutink P, van Gool WA, Scheltens P, Ravid R, Oostra BA, Niermeijer MF, van Swieten JC (1998) Familial aggregation in frontotemporal dementia. Neurology 50:1541–1545
Suzuki M, Nishiahara M (2002) Granulin precursor gene: a sex steroid-inducible gene involved in sexual differentiation of the rat brain. Mol Genet Metab 75:31–37
Suzuki M, Yonezawa T, Fujioka H, Matuamuro M, Nishihara M (2001) Induction of granulin precursor gene expression by estrogen treatment in neonatal rat hypothalamus. Neurosci Lett 297:199–202
Taniguchi S, McDonagh AM, Pickering-Brown SM, Umeda Y, Iwatsubo T, Hasegawa M, Mann DM (2004) The neuropathology of frontotemporal lobar degeneration with respect to the cytological and biochemical characteristics of tau protein. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 30:1–18
Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM (2002) The role of tau in Alzheimer’s disease. Med Clin North Am 86:615–627
van der Zee J, Le Ber I, Maurer-Stroh S, Engelborghs S, Gijselinck I, Camuzat A, Brouwers N, Vandenberghe R, Sleegers K, Hannequin D, Dermaut B, Schymkowitz J, Campion D, Santens P, Martin JJ, Lacomblez L, De Pooter T, Peeters K, Mattheijssens M, Vercelletto M, Van den Broeck M, Cruts M, De Deyn PP, Rousseau F, Brice A, Van Broeckhoven C (2007) Mutations other than null mutations producing a pathogenic loss of progranulin in frontotemporal dementia. Hum Mutat 28:416
van der Zee J, Rademakers R, Engelborghs S, Gijselinck I, Bogaerts V, Vandenberghe R, Santens P, Caekebeke J, De Pooter T, Peeters K, Lubke U, Van den Broeck M, Martin JJ, Cruts M, De Deyn PP, Van Broeckhoven C, Dermaut B (2006) A Belgian ancestral haplotype harbours a highly prevalent mutation for 17q21-linked tau-negative FTLD. Brain 129:841–852
Vance C, Al-Chalabi A, Ruddy D, Smith BN, Hu X, Sreedharan J, Siddique T, Schelhaas HJ, Kusters B, Troost D, Baas F, de Jong V, Shaw CE (2006) Familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis with frontotemporal dementia is linked to a locus on chromosome 9p13.2–21.3. Brain 129:868–876
Watts GD, Wymer J, Kovach MJ, Mehta SG, Mumm S, Darvish D, Pestronk A, Whyte MP, Kimonis VE (2004) Inclusion body myopathy associated with Paget disease of bone and frontotemporal dementia is caused by mutant valosin-containing protein. Nat Genet 36:377–381
Wilhelmsen KC, Forman MS, Rosen HJ, Alving LI, Goldman J, Feiger J, Lee JV, Segall SK, Kramer JH, Lomen-Hoerth C, Rankin KP, Johnson J, Feiler HS, Weiner MW, Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ, Miller BL (2004) 17q-linked frontotemporal dementia-amyotrophic lateral sclerosis without tau mutations with tau and alpha-synuclein inclusions. Arch Neurol 61:398–406
Wilhelmsen KC, Lynch T, Pavlou E, Higgins M, Nygaard TG (1994) Localization of disinhibition-dementia-parkinsonism-amyotrophy complex to 17q21–22. Am J Hum Genet 55:1159–1165
Zhu J, Nathan C, Jin W, Sim D, Ashcroft GS, Wahl SM, Lacomis L, Erdjument-Bromage H, Tempst P, Wright CD, Ding A (2002) Conversion of proepithelin to epithelins:roles of SLPI and elastase in host defense and wound repair. Cell 111:867–878
Zhukareva V, Vogelsberg-Ragaglia V, Van Deerlin VM, Bruce J, Shuck T, Grossman M, Clark CM, Arnold SE, Masliah E, Galasko D, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM (2001) Loss of brain tau defines novel sporadic and familial tauopathies with frontotemporal dementia. Ann Neurol 49:165–175
Acknowledgments
The work is supported by the MRC.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pickering-Brown, S.M. Progranulin and frontotemporal lobar degeneration. Acta Neuropathol 114, 39–47 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-007-0241-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-007-0241-6