Abstract
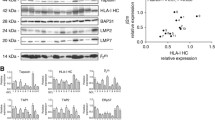
Defects of major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I antigen-processing machinery (APM) components have been shown to contribute to immune escape of malignant cells. We investigated the expression of APM components in astrocytomas without detectable defects in HLA class I antigen expression and correlated it with grade of malignancy. Quantitative immunohistochemical analysis of astrocytomas revealed reduced expression of the cytosolic proteasome subunit low molecular weight protein 2 (LMP2), the endoplasmatic reticulum (ER) transporter associated with antigen processing-1 (TAP1), and the ER chaperone β2-microglobulin (β2m) in astrocytoma cells when compared to astrocytes from nonpathological brain. Among human WHO grade II–IV astrocytomas, downregulation of LMP2, TAP1 and β2m correlated with grade of malignancy. Furthermore, astrocytoma cell lines (n = 12) expressed all APM components analyzed at levels comparable to dendritic cells (DC), which were used for comparative purposes. However, upregulation of β2m after stimulation with inflammatory cytokines was significantly lower in astrocytoma cell lines than in control cells. Our results support the hypothesis that coordinated downregulation or impaired upregulation of certain HLA class I APM components may serve as a mechanism for astrocytoma cells to evade the host’s immune response, even if HLA class I antigen surface expression is not altered.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bandoh N, Ogino T, Cho HS, Hur SY, Shen J, Wang X, Kato S, Miyokawa N, Harabuchi Y, Ferrone S (2005) Development and characterization of human constitutive proteasome and immunoproteasome subunit-specific monoclonal antibodies. Tissue Antigens 66:185–194
Bouvier M (2003) Accessory proteins and the assembly of human class I MHC molecules: a molecular and structural perspective. Mol Immunol 39:697–706
Brat DJ, Castellano-Sanchez AA, Hunter SB, Pecot M, Cohen C, Hammond EH, Devi SN, Kaur B, Van Meir EG (2004) Pseudopalisades in glioblastoma are hypoxic, express extracellular matrix proteases, and are formed by an actively migrating cell population. Cancer Res 64:920–927
Colonna M, Navarro F, Bellon T, Llano M, Garcia P, Samaridis J, Angman L, Cella M, Lopez-Botet M (1997) A common inhibitory receptor for major histocompatibility complex class I molecules on human lymphoid and myelomonocytic cells. J Exp Med 186:1809–1818
Cromme FV, van Bommel PF, Walboomers JM, Gallee MP, Stern PL, Kenemans P, Helmerhorst TJ, Stukart MJ, Meijer CJ (1994) Differences in MHC and TAP-1 expression in cervical cancer lymph node metastases as compared with the primary tumours. Br J Cancer 69:1176–1181
Dissemond J, Busch M, Kothen T, Mors J, Weimann TK, Lindeke A, Goos M, Wagner SN (2004) Differential downregulation of endoplasmic reticulum-residing chaperones calnexin and calreticulin in human metastatic melanoma. Cancer Lett 203:225–231
Dunn GP, Bruce AT, Ikeda H, Old LJ, Schreiber RD (2002) Cancer immunoediting: from immunosurveillance to tumor escape. Nat Immunol 3:991–998
Facoetti A, Nano R, Zelini P, Morbini P, Benericetti E, Ceroni M, Campoli M, Ferrone S (2005) Human leukocyte antigen and antigen processing machinery component defects in astrocytic tumors. Clin Cancer Res 11:8304–8311
Ferrone S, Marincola FM (1995) Loss of HLA class I antigens by melanoma cells: molecular mechanisms, functional significance and clinical relevance. Immunol Today 16:487–494
Friese MA, Platten M, Lutz SZ, Naumann U, Aulwurm S, Bischof F, Buhring HJ, Dichgans J, Rammensee HG, Steinle A et al (2003) MICA/NKG2D-mediated immunogene therapy of experimental gliomas. Cancer Res 63:8996–9006
Germain RN, Margulies DH (1993) The biochemistry and cell biology of antigen processing and presentation. Annu Rev Immunol 11:403–450
Giorda E, Sibilio L, Martayan A, Moretti S, Venturo I, Mottolese M, Ferrara GB, Cappellacci S, Eibenschutz L, Catricala C, Grammatico P, Giacomini P (2003) The antigen processing machinery of class I human leukocyte antigens: linked patterns of gene expression in neoplastic cells. Cancer Res 63:4119–4127
Groettrup M, Soza A, Kuckelkorn U, Kloetzel PM (1996) Peptide antigen production by the proteasome: complexity provides efficiency. Immunol Today 17:429–435
Hill A, Ploegh H (1995) Getting the inside out: the transporter associated with antigen processing (TAP) and the presentation of viral antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92:341–343
Höftberger R, Aboul-Enein F, Brueck W, Lucchinetti C, Rodriguez M, Schmidbauer M, Jellinger K, Lassmann H (2004) Expression of major histocompatibility complex class I molecules on the different cell types in multiple sclerosis lesions. Brain Pathol 14:43–50
Kaklamanis L, Leek R, Koukourakis M, Gatter KC, Harris AL (1995) Loss of transporter in antigen processing 1 transport protein and major histocompatibility complex class I molecules in metastatic versus primary breast cancer. Cancer Res 55:5191–5194
Karre K, Ljunggren HG, Piontek G, Kiessling R (1986) Selective rejection of H-2-deficient lymphoma variants suggests alternative immune defence strategy. Nature 319:675–678
Kleihues P, Cavenee W (2000) Pathology and genetics of tumours of the nervous system. IARC Press, Lyon
Kloetzel PM (2004) The proteasome and MHC class I antigen processing. Biochim Biophys Acta 1695:225–233
Kloetzel PM, Ossendorp F (2004) Proteasome and peptidase function in MHC-class-I-mediated antigen presentation. Curr Opin Immunol 16:76–81
Korkolopoulou P, Kaklamanis L, Pezzella F, Harris AL, Gatter KC (1996) Loss of antigen-presenting molecules (MHC class I and TAP-1) in lung cancer. Br J Cancer 73:148–153
Lampson LA, Fisher CA, Whelan JP (1983) Striking paucity of HLA-A, B, C and beta 2-microglobulin on human neuroblastoma cell lines. J Immunol 130:2471–2478
Lanier LL (2005) NK cell recognition. Annu Rev Immunol 23:225–274
Lanier LL (2000) Turning on natural killer cells. J Exp Med 191:1259–1262
Lopez-Albaitero A, Nayak JV, Ogino T, Machandia A, Gooding W, DeLeo AB, Ferrone S, Ferris RL (2006) Role of antigen-processing machinery in the in vitro resistance of squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck cells to recognition by CTL. J Immunol 176:3402–3409
Momburg F, Tan P (2002) Tapasin—the keystone of the loading complex optimizing peptide binding by MHC class I molecules in the endoplasmic reticulum. Mol Immunol 39:217–233
Ogino T, Bandoh N, Hayashi T, Miyokawa N, Harabuchi Y, Ferrone S (2003) Association of tapasin and HLA class I antigen down-regulation in primary maxillary sinus squamous cell carcinoma lesions with reduced survival of patients. Clin Cancer Res 9:4043–4051
Ogino T, Wang X, Ferrone S (2003) Modified flow cytometry and cell-ELISA methodology to detect HLA class I antigen processing machinery components in cytoplasm and endoplasmic reticulum. J Immunol Methods 278:33–44
Ogino T, Wang X, Kato S, Miyokawa N, Harabuchi Y, Ferrone S (2003) Endoplasmic reticulum chaperone-specific monoclonal antibodies for flow cytometry and immunohistochemical staining. Tissue Antigens 62:385–393
Paulsson KM, Wang P (2004) Quality control of MHC class I maturation. FASEB J 18:31–38
Perosa F, Luccarelli G, Prete M, Favoino E, Ferrone S, Dammacco F (2003) Beta 2-microglobulin-free HLA class I heavy chain epitope mimicry by monoclonal antibody HC-10-specific peptide. J Immunol 171:1918–1926
Prins RM, Liau LM (2003) Immunology and immunotherapy in neurosurgical disease. Neurosurgery 53:144–152; discussion 152–143
Romero JM, Jimenez P, Cabrera T, Cozar JM, Pedrinaci S, Tallada M, Garrido F, Ruiz-Cabello F (2005) Coordinated downregulation of the antigen presentation machinery and HLA class I/beta2-microglobulin complex is responsible for HLA-ABC loss in bladder cancer. Int J Cancer 113:605–610
Schreiner B, Mitsdoerffer M, Kieseier BC, Chen L, Hartung HP, Weller M, Wiendl H (2004) Interferon-beta enhances monocyte and dendritic cell expression of B7-H1 (PD-L1), a strong inhibitor of autologous T-cell activation: relevance for the immune modulatory effect in multiple sclerosis. J Neuroimmunol 155:172–182
Seliger B, Atkins D, Bock M, Ritz U, Ferrone S, Huber C, Storkel S (2003) Characterization of human lymphocyte antigen class I antigen-processing machinery defects in renal cell carcinoma lesions with special emphasis on transporter-associated with antigen-processing down-regulation. Clin Cancer Res 9:1721–1727
Seliger B, Lichtenfels R, Kellner R (2003) Detection of renal cell carcinoma-associated markers via proteome- and other 'ome'-based analyses. Brief Funct Genomic Proteomic 2:194–212
Seliger B, Maeurer MJ, Ferrone S (2000) Antigen-processing machinery breakdown and tumor growth. Immunol Today 21:455–464
Seliger B, Wollscheid U, Momburg F, Blankenstein T, Huber C (2000) Coordinate downregulation of multiple MHC class I antigen processing genes in chemical-induced murine tumor cell lines of distinct origin. Tissue Antigens 56:327–336
Sernee MF, Ploegh HL, Schust DJ (1998) Why certain antibodies cross-react with HLA-A and HLA-G: epitope mapping of two common MHC class I reagents. Mol Immunol 35:177–188
Stam NJ, Spits H, Ploegh HL (1986) Monoclonal antibodies raised against denatured HLA-B locus heavy chains permit biochemical characterization of certain HLA-C locus products. J Immunol 137:2299–2306
Stevanovic S (2002) Identification of tumour-associated T-cell epitopes for vaccine development. Nat Rev Cancer 2:514–520
Surawicz TS, Davis F, Freels S, Laws ER Jr, Menck HR (1998) Brain tumor survival: results from the National Cancer Data Base. J Neurooncol 40:151–160
van Hall T, Wolpert EZ, van Veelen P, Laban S, van der Veer M, Roseboom M, Bres S, Grufman P, de Ru A, Meiring H, de Jong A, Franken K, Teixeira A, Valentijn R, Drijfhout JW, Koning F, Camps M, Ossendorp F, Karre K, Ljunggren HG, Melief CJ, Offringa R (2006) Selective cytotoxic T-lymphocyte targeting of tumor immune escape variants. Nat Med 12:417–424
Walker PR, Calzascia T, Dietrich PY (2002) All in the head: obstacles for immune rejection of brain tumours. Immunology 107:28–38
Wang X, Campoli M, Cho HS, Ogino T, Bandoh N, Shen J, Hur SY, Kageshita T, Ferrone S (2005) A method to generate antigen-specific mAb capable of staining formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissue sections. J Immunol Methods 299:139–151
Weber F, Meinl E, Aloisi F, Nevinny-Stickel C, Albert E, Wekerle H, Hohlfeld R (1994) Human astrocytes are only partially competent antigen presenting cells. Possible implications for lesion development in multiple sclerosis. Brain 117(1):59–69
Weller M, Fontana A (1995) The failure of current immunotherapy for malignant glioma. Tumor-derived TGF-beta, T-cell apoptosis, and the immune privilege of the brain. Brain Res Brain Res Rev 21:128–151
Whiteside TL, Stanson J, Shurin MR, Ferrone S (2004) Antigen-processing machinery in human dendritic cells: up-regulation by maturation and down-regulation by tumor cells. J Immunol 173:1526–1534
Wiendl H, Mitsdoerffer M, Hofmeister V, Wischhusen J, Bornemann A, Meyermann R, Weiss EH, Melms A, Weller M (2002) A functional role of HLA-G expression in human gliomas: an alternative strategy of immune escape. J Immunol 168:4772–4780
Wischhusen J, Friese MA, Mittelbronn M, Meyermann R, Weller M (2005) HLA-E protects glioma cells from NKG2D-mediated immune responses in vitro: implications for immune escape in vivo. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 64:523–528
Wischhusen J, Jung G, Radovanovic I, Beier C, Steinbach JP, Rimner A, Huang H, Schulz JB, Ohgaki H, Aguzzi A, et al (2002) Identification of CD70-mediated apoptosis of immune effector cells as a novel immune escape pathway of human glioblastoma. Cancer Res 62:2592–2599
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mehling, M., Simon, P., Mittelbronn, M. et al. WHO grade associated downregulation of MHC class I antigen-processing machinery components in human astrocytomas: does it reflect a potential immune escape mechanism?. Acta Neuropathol 114, 111–119 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-007-0231-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-007-0231-8