Abstract
Background
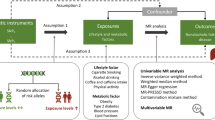
Vitamin D deficiency is associated with glycemic dysregulation in many observational studies. However, the causality between them has not been fully established, especially in Asian origin. We used bidirectional Mendelian randomization (MR) analysis to explore the causal relationship between 25-hydroxyvitamin D [25(OH)D] and glycemic status and indices.
Methods
Participants were included from a survey in East China from 2014 to 2016 (10,338 and 10,655 participants having diabetes and vitamin D-related genotyping information). We calculated weighted genetic risk scores (GRS) as the instrumental variables for 25(OH)D concentration and diabetes based on related single nucleotide polymorphisms. Diagnosis of type 2 diabetes and prediabetes was based on American Diabetes Association criteria.
Results
The MR-derived odds ratios of genetically determined 25(OH)D for risk of type 2 diabetes (1565/10655) and prediabetes (3915/10655) was 0.985 (95% CI 0.940, 1.032) and 0.982 (95% CI 0.948, 1.016), respectively. The MR-derived estimates for fasting plasma glucose and HbA1c were also not significant. Moreover, the MR-derived regression coefficients of genetically determined diabetes and prediabetes for 25(OH)D was 0.448 (95% CI − 0.395, 1.291) and 1.303 (95% CI − 1.210, 3.816).
Conclusions
Our results support the conclusion that there is no causal association between vitamin D and type 2 diabetes and prediabetes using a bidirectional MR approach in a Chinese population.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ogurtsova K, da Rocha Fernandes JD, Huang Y, Linnenkamp U, Guariguata L, Cho NH, Cavan D, Shaw JE, Makaroff LE (2017) IDF Diabetes Atlas: global estimates for the prevalence of diabetes for 2015 and 2040. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 128:40–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diabres.2017.03.024
Wang L, Gao P, Zhang M, Huang Z, Zhang D, Deng Q, Li Y, Zhao Z, Qin X, Jin D, Zhou M, Tang X, Hu Y, Wang L (2017) Prevalence and ethnic pattern of diabetes and prediabetes in China in 2013. JAMA 317(24):2515–2523. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2017.7596
Palacios C, Gonzalez L (2014) Is vitamin D deficiency a major global public health problem? J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 144(Pt A):138–145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsbmb.2013.11.003
Hossein-nezhad A, Holick MF (2013) Vitamin D for health: a global perspective. Mayo Clin Proc 88(7):720–755. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mayocp.2013.05.011
Wang N, Han B, Li Q, Chen Y, Chen Y, Xia F, Lin D, Jensen MD, Lu Y (2015) Vitamin D is associated with testosterone and hypogonadism in Chinese men: results from a cross-sectional SPECT-China study. Reprod Biol Endocrinol 13:74. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12958-015-0068-2
Wang N, Zhai H, Zhu C, Li Q, Han B, Chen Y, Zhu C, Chen Y, Xia F, Lin D, Lu Y (2016) Combined association of vitamin D and Sex hormone binding globulin with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in men and postmenopausal women: a cross-sectional study. Med (Baltim) 95(4):e2621. https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000002621
Forouhi NG, Ye Z, Rickard AP, Khaw KT, Luben R, Langenberg C, Wareham NJ (2012) Circulating 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentration and the risk of type 2 diabetes: results from the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer (EPIC)-Norfolk cohort and updated meta-analysis of prospective studies. Diabetologia 55(8):2173–2182. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00125-012-2544-y
Knekt P, Laaksonen M, Mattila C, Harkanen T, Marniemi J, Heliovaara M, Rissanen H, Montonen J, Reunanen A (2008) Serum vitamin D and subsequent occurrence of type 2 diabetes. Epidemiology 19(5):666–671. https://doi.org/10.1097/EDE.0b013e318176b8ad
Lips P, Eekhoff M, van Schoor N, Oosterwerff M, de Jongh R, Krul-Poel Y, Simsek S (2017) Vitamin D and type 2 diabetes. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 173:280–285. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsbmb.2016.11.021
Seida JC, Mitri J, Colmers IN, Majumdar SR, Davidson MB, Edwards AL, Hanley DA, Pittas AG, Tjosvold L, Johnson JA (2014) Clinical review: effect of vitamin D3 supplementation on improving glucose homeostasis and preventing diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 99(10):3551–3560. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2014-2136
Afzal S, Brondum-Jacobsen P, Bojesen SE, Nordestgaard BG (2014) Vitamin D concentration, obesity, and risk of diabetes: a mendelian randomisation study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 2(4):298–306. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2213-8587(13)70200-6
Ye Z, Sharp SJ, Burgess S, Scott RA, Imamura F, InterAct C, Langenberg C, Wareham NJ, Forouhi NG (2015) Association between circulating 25-hydroxyvitamin D and incident type 2 diabetes: a mendelian randomisation study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 3(1):35–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2213-8587(14)70184-6
Scragg R, Sowers M, Bell C, Third National H, Nutrition Examination S (2004) Serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D, diabetes, and ethnicity in the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Diabetes Care 27(12):2813–2818
Hypponen E, Power C (2006) Vitamin D status and glucose homeostasis in the 1958 British birth cohort: the role of obesity. Diabetes Care 29(10):2244–2246. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc06-0946
Smith GD, Ebrahim S (2003) ‘Mendelian randomization’: can genetic epidemiology contribute to understanding environmental determinants of disease? Int J Epidemiol 32(1):1–22
Didelez V, Sheehan N (2007) Mendelian randomization as an instrumental variable approach to causal inference. Stat Methods Med Res 16(4):309–330. https://doi.org/10.1177/0962280206077743
Wang N, Wang X, Han B, Li Q, Chen Y, Zhu C, Chen Y, Xia F, Cang Z, Zhu C, Lu M, Meng Y, Chen C, Lin D, Wang B, Jensen MD, Lu Y (2015) Is exposure to famine in childhood and economic development in adulthood associated with diabetes? J Clin Endocrinol Metab 100(12):4514–4523. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2015-2750
Wang N, Chen Y, Ning Z, Li Q, Han B, Zhu C, Chen Y, Xia F, Jiang B, Wang B, Wang X, Jensen MD, Lu Y (2016) Exposure to famine in early life and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in adulthood. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 101(5):2218–2225. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2016-1076
Wang N, Wang X, Li Q, Han B, Chen Y, Zhu C, Chen Y, Lin D, Wang B, Jensen MD, Lu Y (2017) The famine exposure in early life and metabolic syndrome in adulthood. Clin Nutr 36(1):253–259. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clnu.2015.11.010
Xu Y, Wang L, He J, Bi Y, Li M, Wang T, Wang L, Jiang Y, Dai M, Lu J, Xu M, Li Y, Hu N, Li J, Mi S, Chen CS, Li G, Mu Y, Zhao J, Kong L, Chen J, Lai S, Wang W, Zhao W, Ning G, China Noncommunicable Disease Surveillance G (2013) Prevalence and control of diabetes in Chinese adults. JAMA 310(9):948–959. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2013.168118
Cho YS, Lee JY, Park KS, Nho CW (2012) Genetics of type 2 diabetes in East Asian populations. Curr Diab Rep 12(6):686–696. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11892-012-0326-z
Xu M, Huang Y, Xie L, Peng K, Ding L, Lin L, Wang P, Hao M, Chen Y, Sun Y, Qi L, Wang W, Ning G, Bi Y (2016) Diabetes and risk of arterial stiffness: a Mendelian randomization analysis. Diabetes 65(6):1731–1740. https://doi.org/10.2337/db15-1533
Li SS, Gao LH, Zhang XY, He JW, Fu WZ, Liu YJ, Hu YQ, Zhang ZL (2016) Genetically low vitamin D levels, bone mineral density, and bone metabolism markers: a Mendelian randomisation study. Sci Rep 6:33202. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep33202
Cuellar-Partida AG, Williams KM, Yazar S, Guggenheim JA, Hewitt AW, Williams C, Wang JJ, Kho PF, Saw SM, Cheng CY, Wong TY, Aung T, Young TL, Tideman JWL, Jonas JB, Consortium for Refractive E, Myopia, Mitchell P, Wojciechowski R, Stambolian D, Hysi P, Hammond CJ, Mackey DA, Lucas RM, MacGregor S (2017) Genetically low vitamin D concentrations and myopic refractive error: a Mendelian randomization study. Int J Epidemiol 46(6):1882–1890. https://doi.org/10.1093/ije/dyx068
Vimaleswaran KS, Berry DJ, Lu C, Tikkanen E, Pilz S, Hiraki LT, Cooper JD, Dastani Z, Li R, Houston DK, Wood AR, Michaelsson K, Vandenput L, Zgaga L, Yerges-Armstrong LM, McCarthy MI, Dupuis J, Kaakinen M, Kleber ME, Jameson K, Arden N, Raitakari O, Viikari J, Lohman KK, Ferrucci L, Melhus H, Ingelsson E, Byberg L, Lind L, Lorentzon M, Salomaa V, Campbell H, Dunlop M, Mitchell BD, Herzig KH, Pouta A, Hartikainen AL, Genetic Investigation of Anthropometric Traits GC, Streeten EA, Theodoratou E, Jula A, Wareham NJ, Ohlsson C, Frayling TM, Kritchevsky SB, Spector TD, Richards JB, Lehtimaki T, Ouwehand WH, Kraft P, Cooper C, Marz W, Power C, Loos RJ, Wang TJ, Jarvelin MR, Whittaker JC, Hingorani AD, Hypponen E (2013) Causal relationship between obesity and vitamin D status: bi-directional Mendelian randomization analysis of multiple cohorts. PLoS Med 10(2):e1001383. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.1001383
Lawlor DA, Harbord RM, Sterne JA, Timpson N, Davey Smith G (2008) Mendelian randomization: using genes as instruments for making causal inferences in epidemiology. Stat Med 27(8):1133–1163. https://doi.org/10.1002/sim.3034
Fall T, Hagg S, Magi R, Ploner A, Fischer K, Horikoshi M, Sarin AP, Thorleifsson G, Ladenvall C, Kals M, Kuningas M, Draisma HH, Ried JS, van Zuydam NR, Huikari V, Mangino M, Sonestedt E, Benyamin B, Nelson CP, Rivera NV, Kristiansson K, Shen HY, Havulinna AS, Dehghan A, Donnelly LA, Kaakinen M, Nuotio ML, Robertson N, de Bruijn RF, Ikram MA, Amin N, Balmforth AJ, Braund PS, Doney AS, Doring A, Elliott P, Esko T, Franco OH, Gretarsdottir S, Hartikainen AL, Heikkila K, Herzig KH, Holm H, Hottenga JJ, Hypponen E, Illig T, Isaacs A, Isomaa B, Karssen LC, Kettunen J, Koenig W, Kuulasmaa K, Laatikainen T, Laitinen J, Lindgren C, Lyssenko V, Laara E, Rayner NW, Mannisto S, Pouta A, Rathmann W, Rivadeneira F, Ruokonen A, Savolainen MJ, Sijbrands EJ, Small KS, Smit JH, Steinthorsdottir V, Syvanen AC, Taanila A, Tobin MD, Uitterlinden AG, Willems SM, Willemsen G, Witteman J, Perola M, Evans A, Ferrieres J, Virtamo J, Kee F, Tregouet DA, Arveiler D, Amouyel P, Ferrario MM, Brambilla P, Hall AS, Heath AC, Madden PA, Martin NG, Montgomery GW, Whitfield JB, Jula A, Knekt P, Oostra B, van Duijn CM, Penninx BW, Smith GD, Kaprio J, Samani NJ, Gieger C, Peters A, Wichmann HE, Boomsma DI, de Geus EJ, Tuomi T, Power C, Hammond CJ, Spector TD, Lind L, Orho-Melander M, Palmer CN, Morris AD, Groop L, Jarvelin MR, Salomaa V, Vartiainen E, Hofman A, Ripatti S, Metspalu A, Thorsteinsdottir U, Stefansson K, Pedersen NL, McCarthy MI, Ingelsson E, Prokopenko I, European Network for G, Genomic Epidemiology c (2013) The role of adiposity in cardiometabolic traits: a Mendelian randomization analysis. PLoS Med 10(6):e1001474. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.1001474
Vimaleswaran KS, Cavadino A, Berry DJ, LifeLines Cohort Study i, Jorde R, Dieffenbach AK, Lu C, Alves AC, Heerspink HJ, Tikkanen E, Eriksson J, Wong A, Mangino M, Jablonski KA, Nolte IM, Houston DK, Ahluwalia TS, van der Most PJ, Pasko D, Zgaga L, Thiering E, Vitart V, Fraser RM, Huffman JE, de Boer RA, Schottker B, Saum KU, McCarthy MI, Dupuis J, Herzig KH, Sebert S, Pouta A, Laitinen J, Kleber ME, Navis G, Lorentzon M, Jameson K, Arden N, Cooper JA, Acharya J, Hardy R, Raitakari O, Ripatti S, Billings LK, Lahti J, Osmond C, Penninx BW, Rejnmark L, Lohman KK, Paternoster L, Stolk RP, Hernandez DG, Byberg L, Hagstrom E, Melhus H, Ingelsson E, Mellstrom D, Ljunggren O, Tzoulaki I, McLachlan S, Theodoratou E, Tiesler CM, Jula A, Navarro P, Wright AF, Polasek O, International Consortium for Blood P, Cohorts for H, Aging Research in Genomic Epidemiology c, Global Blood Pressure Genetics c, Caroline H, Wilson JF, Rudan I, Salomaa V, Heinrich J, Campbell H, Price JF, Karlsson M, Lind L, Michaelsson K, Bandinelli S, Frayling TM, Hartman CA, Sorensen TI, Kritchevsky SB, Langdahl BL, Eriksson JG, Florez JC, Spector TD, Lehtimaki T, Kuh D, Humphries SE, Cooper C, Ohlsson C, Marz W, de Borst MH, Kumari M, Kivimaki M, Wang TJ, Power C, Brenner H, Grimnes G, van der Harst P, Snieder H, Hingorani AD, Pilz S, Whittaker JC, Jarvelin MR, Hypponen E (2014) Association of vitamin D status with arterial blood pressure and hypertension risk: a mendelian randomisation study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 2(9):719–729. https://doi.org/10.1016/s2213-8587(14)70113-5
de Boer IH, Tinker LF, Connelly S, Curb JD, Howard BV, Kestenbaum B, Larson JC, Manson JE, Margolis KL, Siscovick DS, Weiss NS, Women’s Health Initiative I (2008) Calcium plus vitamin D supplementation and the risk of incident diabetes in the Women’s Health Initiative. Diabetes Care 31(4):701–707. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc07-1829
Krul-Poel YH, Ter Wee MM, Lips P, Simsek S (2017) Management of endocrine disease: the effect of vitamin D supplementation on glycaemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Endocrinol 176(1):R1–R14. https://doi.org/10.1530/EJE-16-0391
Buijsse B, Boeing H, Hirche F, Weikert C, Schulze MB, Gottschald M, Kuhn T, Katzke VA, Teucher B, Dierkes J, Stangl GI, Kaaks R (2013) Plasma 25-hydroxyvitamin D and its genetic determinants in relation to incident type 2 diabetes: a prospective case-cohort study. Eur J Epidemiol 28(9):743–752. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10654-013-9844-5
Sheehan NA, Didelez V, Burton PR, Tobin MD (2008) Mendelian randomisation and causal inference in observational epidemiology. PLoS Med 5(8):e177. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.0050177
Rosen CJ, Adams JS, Bikle DD, Black DM, Demay MB, Manson JE, Murad MH, Kovacs CS (2012) The nonskeletal effects of vitamin D: an Endocrine Society scientific statement. Endocr Rev 33(3):456–492. https://doi.org/10.1210/er.2012-1000
Acknowledgements
YL and NW designed research; NW, CW, XC, HW, YC, CC and BH conducted research; NW and CW analyzed data; and NW, CW and YL wrote the paper. YL had primary responsibility for the final content. All authors read and approved the final manuscript. The authors thank Xiaojin Wang and Bingshun Wang from the Department of Biostatistics and Shanghai Jiaotong University School of Medicine for data processing. The authors thank Weiping Tu, Bin Li and Ling Hu for help in organize this investigation. The authors thank all team members and participants in the SPECT-China study.
Funding
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81570726, 81600609); Shanghai JiaoTong University School of Medicine (2014); Science and Technology Commission of Shanghai Municipality (16411971200, 16410723200); Commission of Health and Family Planning of Pudong District (PW2015D-5); the Fourth Round of Three-Year Public Health Action Plan of Shanghai by the Shanghai Municipal Commission of Health and Family Planning (15GWZK0202, 20164Y0079); Municipal Human Resources Development Program for Outstanding Young Talents in Medical and Health Sciences in Shanghai (2017YQ053); and Clinical Research Plan of SHDC (16CR3076B). The funders played no role in the design or conduct of the study, collection, management, analysis, or interpretation of data or in the preparation, review, or approval of the article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
No potential conflicts of interest relevant to this article are reported.
Additional information
The abstract of the paper has already been published in Diabetes 2018 Jul 67(Supplement 1): https://doi.org/10.2337/db18-1602-P.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, N., Wang, C., Chen, X. et al. Vitamin D, prediabetes and type 2 diabetes: bidirectional Mendelian randomization analysis. Eur J Nutr 59, 1379–1388 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-019-01990-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-019-01990-x