Abstract
The Atlantic meridional overturning circulation (AMOC) is projected to weaken in the coming century due to anthropogenic climate change. Various studies have considered AMOC weakening and collapse, with less research focusing on the processes and timescales of the recovery phase. This study uses a coupled climate model to explore the roles of salinity and temperature in AMOC recovery after a weakening. The North Atlantic and Arctic region was hosed with freshwater for 200 years. The mean Atlantic salinity increased strongly during recovery, and remained elevated for ~ 600 years post hosing. The behaviour of the AMOC was well reconstructed by applying “rotated geostrophy” to meridional density gradient profiles between 50°N and 30°S. This makes it possible to determine the role of overturning, gyre, and surface fluxes in the North and South Atlantic. Changes at 50°N dominate the weakening and early recovery. The magnitude of the overshoot to high AMOC transports in the recovery phase was related to density changes in the South Atlantic.
Similar content being viewed by others
1 Introduction
1.1 The AMOC and its stability
The Atlantic meridional overturning circulation (AMOC) is an oceanic system of currents carrying warm buoyant waters to high northern latitudes, balanced by a cool deep return flow. Climate projections suggest that the AMOC strength will decline due to anthropogenic climate change. The IPCC report stated best estimate reductions of 11–34% for the RCP2.6 and RCP8.5 scenarios, respectively, running up to 2100 (Collins et al. 2013). However the degree of resilience to short term forcing remains unclear. A potential driver of AMOC weakening is the melting of the Greenland ice sheet. By 2100 annual average temperatures over Greenland could increase by 3 °C due to greenhouse gas increases—sufficient to give a gradual effective elimination of the sheet ice (Gregory et al. 2004). It has been suggested that a temperature increase of 1.6 °C may be sufficient (Robinson et al. 2012). Should the entire ice sheet melt, it would release profound quantities of freshwater into the North Atlantic Ocean, impacting regional buoyancy over a period of 1000 years or more, (Gregory et al. 2004). A model study (Jungclaus et al. 2006) which reassessed previous IPCC simulations (Schmittner et al. 2005) with the addition of a freshwater source from Greenland ice melt found AMOC reductions of 35% and 42%, for conservative and high melting estimates respectively, compared to 30% without Greenland melting. Further freshwater may be supplied by the melting of Arctic sea ice (Sevellec et al. 2017). The focus of this study is the mechanistic nature of AMOC weakening and recovery, and how these two processes differ from one another.
Freshwater hosing experiments seek to explore the impact of the North Atlantic being freshened by ice melt. Kleinen et al. (2009) found that the ocean responded dynamically to the input of freshwater (hosing) in the HadCM3 climate model. Hosing weakens the AMOC, reducing the northward advection of heat and salt. However, a fresh buoyant cap forms at the air–sea boundary, beneath which the subsurface waters become isolated from surface fluxes and so remain warm and salty as they travel north. This leads to density anomalies that can cause instability in the water column.
In hosing simulations that continue for a substantial time with no additional hosing after the AMOC has weakened, the AMOC often recovers and sometimes with an overshoot, (Vellinga et al. 2002; Stouffer et al. 2006; Cao et al. 2016). This may be due to the gradual warming of subsurface waters at low- and middle-latitudes (Stouffer and Manabe 1999) along with increased northward salinity advection (Thorpe et al. 2001; Bitz et al. 2007). In low-resolution (FAMOUS) simulations, the AMOC has been shown to begin recovery soon after the hosing ends (Smith and Gregory 2009), with similar rates of recovery seen in simulations where the AMOC had weakened to different extents. Smith and Gregory (2009) found no evidence of irreversible weakening in the AMOC. Two of the simulations ended with AMOC strengths greater than that of the control run, as had been previously reported (Stouffer et al. 2006). This was attributed to double-up resulting from ‘compensating’ deep-water formation in the GIN Seas continuing whilst the Atlantic deep-water formation recovered (Smith and Gregory 2009).
1.2 Changing salinity of the Atlantic Ocean
It has been suggested that the principle diagnostic for controlling AMOC strength is the mean Atlantic salinity. Changes in Atlantic salinity have been found to play an important role in weakening and recovery of the AMOC due to its impact on water density (Jackson 2013). It has also been shown that the strength of overturning scales with the meridional density gradient (Stommel 1961; Cimatoribus et al. 2014) and that it may be possible to estimate the Atlantic stream function by a comparison of density profiles in the North and South of the Atlantic (Sijp et al. 2012; Butler et al. 2016). Changes to the North–South Atlantic density gradient have been found to be able to collapse the overturning (Cimatoribus et al. 2014).
To understand the role of salinity in the Atlantic, we need to consider the freshwater transports at the southern limit of the basin. When the northward freshwater transport by overturning, Fov, at 30°S is positive the AMOC is net exporting salinity. Under this condition, if the strength of the AMOC is reduced it leads to a build up of salinity. This increases Atlantic density, which in turn drives an increase in the AMOC. Positive Fov therefore results in a negative feedback to a perturbation in the strength of the AMOC. However, when the Fov is negative the AMOC is importing salinity. A reduction in the strength of the AMOC results in a decrease in the salinity of the Atlantic, reducing Atlantic density. This in turn further reduces the strength of the AMOC, giving a positive feedback (Rahmstorf 1996). Simulations modelling AMOC collapse (Hawkins et al. 2011) have found a negative value for Fov during the collapse, with positive values on either side. It has been suggested that negative Fov indicates the presence of a bistable regime (de Vries and Weber 2005; Hawkins et al. 2011), though this is inconclusive with other studies suggesting a need to find the freshwater divergence over the basin (Dijkstra 2007; Huisman et al. 2010; Liu and Liu 2013, 2014). The use of Fov as an indicator of freshwater transport into the basin may be undermined if there large changes in the salinity transport by either gyre activity (Jackson 2013) or the Antarctic bottom water (AABW), as each of these can lead to a mismatch between the overtutning transport and the salinity feedback.
While Fov originates in bistability studies, as a diagnostic it is underpinned by the idea that the dominant feedback on AMOC transport is captured by the basin scale transport of freshwater at 30°S. We therefore intend to explore whether this diagnostic can be used to understand the weakening and recovery pathways in the essentially mono-stable simulations presented here.
Observations and reanalysis suggest that the Atlantic currently has negative Fov at 30°S (Weijer et al. 1999; Hawkins et al 2011; Bryden 2011; Garzoli et al. 2013). The observed values indicate a positive salinity advective feedback, meaning that freshwater perturbations may be amplified potentially enhancing any weakening (Garzoli et al. 2013). However, Fov cannot always be assumed to scale with the total freshwater transport, as a significant contribution can also be made by the freshwater transport by gyre activity, Faz. Fov has been found to reduce and become negative with increasing Faz, (de Vries and Weber 2005; Huisman et al. 2010; Cimatoribus et al. 2012, 2014; Jackson 2013). Changes in Fov can also be compensated for by changes in Faz, reducing the impact on the total freshwater transport (Jackson 2013).
1.3 Aims
While previous studies have identified processes related to AMOC weakening, recovery and overshoot, questions remain concerning the extent of mechanical symmetry between weakening and recovery phases, and how well these processes can be defined using the frameworks described in Sect. 1.2. In this study, we use both approaches to examine the decline and recovery phases. We use an ensemble of freshwater hosing simulations in a low-resolution coupled climate model to robustly distinguish between driving mechanisms and chaotic variability, and to determine the ability of the two frameworks to capture the driving mechanisms. We find that meridional density gradients explain the detailed temporal structure of the AMOC during both phases (Sect. 4), and that we are therefore able to reduce the problem to a density analysis of the North and South Atlantic (Sect. 5).
2 Methods
2.1 Model description
We used the Fast Met Office/UK Universities Simulator (FAMOUS), (Smith et al. 2008; Smith 2012). FAMOUS is a low-resolution ocean–atmosphere general circulation model. It is a computationally cheaper version of the higher resolution HadCM3, (Gordon et al. 2000), using mostly the same code, which has been tuned to produce similar climate results. FAMOUS has an ocean resolution of 3.75° longitude by 2.5° latitude, with 20 vertical levels. The horizontal atmospheric resolution is 7.5° longitude by 5° latitude, with 11 vertical levels. The atmosphere and ocean were coupled once per simulated day, consisting of 24 atmospheric time steps and 2 ocean time steps. Higher resolution models may have significant feedbacks that are absent from FAMOUS, such as altered net advection through the Bering Strait where a reduction of the freshwater flux may impact the response of the AMOC to freshwater forcing (de Boer and Nof 2004; Hu et al. 2012; Liu et al. 2013, 2017). However the relationship between Atlantic meridional density gradient and AMOC strength has been shown to be robust in an eddy-permitting model (Butler et al. 2016) indicating that our analysis approach is applicable to such models.
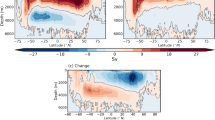
FAMOUS representation of the AMOC compares well with a variety of higher resolution fully coupled climate models (Boulton et al. 2014). Comparison with observational data is difficult due to the short observational record. However, the mean transports at 26°N in the Atlantic given by FAMOUS and those estimated by the RAPID/MOCHA/WBTS array over the years 2004–2012 (McCarthy et al. 2015), both give ~ 17.5 Sv. In the control runs, which used a pre-industrial climate with constant forcings, FAMOUS was found to have interannual variability of ~ 2 Sv. FAMOUS has broadly realistic sea surface salinity and temperature values, Fig. 1. The surface salinity values vary more strongly, with a wider range of values, in FAMOUS than in observations. In the Northern Hemisphere FAMOUS has a high latitude cold bias in winter, making it 5 °C cooler than observations. This leads to excessive North Atlantic sea ice and likely contributes to the strength of the AMOC. The control stream function and zonal mean salinity are given in the top panels of Fig. 2.
2.2 Freshwater hosing scenarios
The freshwater forcing, F, was achieved by applying an additional fresh water flux to the ice calving parameter, in units of kg m−2 s−1. This was calculated as:
where H is the hosing rate in Sv, ρfw a constant for the density of freshwater, here taken to be 1000 kg m−3, and A is the hosing area in m2.
Simulations were hosed with 0.2 or 0.5 Sv of freshwater. This was applied evenly over the surface from 50°N in the Atlantic to the Bering Strait. The freshwater input was balanced by volume compensation, throughout the entire ocean, effectively subtracting salt out of the surface of the hosing region and adding it back in equally over all ocean boxes to conserve the global reservoir. This was chosen in preference to surface compensation, where the freshwater input is balanced by returning the salinity to the surface boxes only. Surface compensation impacts global density stratification and has been shown to result in a bistable AMOC in FAMOUS, while the volume compensation used here results in an essentially mono-stable AMOC (Jackson et al. 2017).
‘Top hat’ experiments were used, where the full hosing value was imposed from the first time step. Hosing was applied constantly for 200 years, and then stopped. The simulations were then run on for a further 400 years to observe the recovery process. Ten simulations were run with each of 0, 0.2 and 0.5 Sv of freshwater forcing, each of the 10 runs being initialised from a different point along an equilibrium state simulation. Unless otherwise specified, the results presented will be the ensemble mean for each hosing rate.
2.3 Salinity budget and transports
As there is no advection through the Bering Strait in FAMOUS, we take the Atlantic basin as having two open boundaries, at 30°S and at the air–sea surface. The salinity budget of the Atlantic is the change in salinity (S, in PSU), over time (t, in s), throughout a volume (V, in m3):
where FS is the northward salinity flux at 30°S which can be described using the freshwater transports Fov, Faz, and a small term for the diffusion, Fd. Surf is the net salinity input due to precipitation, evaporation, river runoff, ice melt, and hosing. Additionally there is a residual component, Res, which includes small terms such as the Mediterranean outflow, Gent-McWilliams scheme, and the Robert-Asselin filter (Smith et al. 2008).
The freshwater flux into the Atlantic basin by overturning, Fov, at ~ 30°S is calculated using the mean zonal salinity and velocity through a zonal section. Fov may be calculated using the equation:
where So is a reference salinity, used to remove the barotropic contribution, \(\stackrel{-}{V}\left(z\right)\) is the zonally integrated meridional velocity, and \(\langle S\left(z\right)\rangle\) is the zonally averaged salinity (Jackson 2013).
The Faz is related to the strength of the zonal salinity and velocity gradients. This may be expressed as (Cimatoribus et al. 2012):
where \(v^{\prime}=~v - \langle v \rangle\), and \(S^{\prime}=~S - \langle S \rangle.\)
3 Ocean response to imposition and removal of freshwater forcing
3.1 Asymmetric overturning adjustments during weakening and recovery
The majority of the weakening of the stream function occurred within the first 80 years of hosing, Fig. 3. The North Atlantic stream function responded quickly to the removal of hosing before overshooting the initial value, giving clear asymmetry over the 200 years before and after hosing is removed. After 200 years unhosed the stream functions in all simulations recovered to near control values.
These changes indicate wider readjustments between the relative influences of different water masses. The hosing reduces the NADW transport, and a reverse circulation consisting of an enhanced AABW transport develops, Fig. 2. Once hosing is removed the AABW rapidly reduces in latitudinal extent, with the centre of the recovering AMOC between 20°N and 30°N, at a depth of < 1000 m. As the AMOC gains in strength its centre migrates deeper and northward. Four hundred years after hosing was removed the AMOC has slightly higher maximum values than the initial state, by ~ 3 Sv, with a greater region showing high values.
3.2 Salinity and heat changes in the Atlantic basin
In this section we test the hypothesis that the asymmetry in weakening and recovery phases can be explained in terms of the mean Atlantic salinity and heat. This would be consistent with the idea that AMOC stability is determined by freshwater fluxes at the southern boundary of the Atlantic.
The mean salinity of the region between 30°S in the Atlantic and the Bering Strait was calculated for all of the hosing simulations. The mean salinity initially decreased due to the hosing. Increasing hosing does not linearly reduce salinity due to the impact of transports and feedbacks, Fig. 4a. In the 0.2 Sv runs these feedbacks lead to the salinity returning to initial values during hosing, with partial recovery in the 0.5 Sv ensemble. When the hosing was removed the mean salinity sharply increased, then began to level off after ~ 50 years. After another ~ 150 years the salinity reached a peak before returning to control values. Regardless of forcing rate this took ~ 600 years, being controlled by ocean overturning fluxes (not shown).
a Ensemble mean salinity from 30°S to the Bering Strait for 600-year simulations, with 0.2 and 0.5 Sv of freshwater forcing through the first 200 years. b Stream function versus basin mean salinity for the 0.2 and 0.5 Sv ensembles, from 30°S to the Bering Strait. Reference years marked in black. Legend applies to both plots
Figure 4b demonstrates the absence of a simple relationship between the mean Atlantic salinity and the strength of the Atlantic stream function. Salinity and the stream function are initially well correlated (for the first 80 and 40 years for the 0.2 and 0.5 Sv ensembles, respectively), however the mean Atlantic salinity starts to increase before hosing ends while the AMOC continues to weaken. At the start of the recovery phase there was a quick increase in the value of the mean salinity before any substantial response in the strength of the stream function. This will partly be the direct impact of the removal of hosing, before the other salinity fluxes have had time to respond. The 0.5 Sv ensemble had maximum mean salinity values during the overshoot, before slowly reducing as the basin readjusts towards the control state.
The temperature of the basin also varied significantly over the course of the simulation, showing less asymmetry in the response through hosing and recovery. During the hosing phase the mean temperature of the Atlantic and Arctic region increased, Fig. 5. When the hosing was removed, temperature was slower to return to the initial values. The developed temperature anomaly continued to dissipate through the overshoot and later stage of recovery. The impact this had on the densities for the 0.5 Sv ensemble will be explored further in Sect. 5.
a Ensemble mean temperature from 30°S to the Bering Strait for 10 600-year simulations with 0.5 or 0.2 Sv freshwater forcing through the first 200 years. b Stream function versus basin mean temperature for the 0.2 and 0.5 Sv ensemble groups. End of hosing marked in black. Legend applies to both plots
4 Understanding AMOC behaviour with meridional density differences
4.1 Reconstructing stream function from density profiles
We want to find a mechanistic explanation for the asymmetric response of the AMOC. A promising approach to this problem is to explore the role of salinity and temperature by reconstructing the stream function from meridional density profiles. Butler et al. (2016) used a scaling relationship that links the Atlantic overturning to the twice vertically-integrated meridional density gradient, which they described as geostrophy, rotated by 90°. We can logically see that meridional pressure gradients can impact meridional overturning, as changes in the meridional pressure gradient will induce changes in zonal flow, impacting zonal pressure gradients, and thereby driving changes in meridional flow. Butler et al. (2016) obtained the strongest correlations by using density gradients at the western boundary. Here, we will use zonal means because of their connection with meridional heat and salinity transport.
4.2 Extent of reconstructive skill in hosing scenarios
The full width of the Atlantic was used to reconstruct the ensemble mean stream function, Fig. 6. This gave a good approximation to the form of the stream function profiles calculated from the velocities, both spatially and temporally. We have taken our southern section at 30°S to describe the densities within the southern limit of the Atlantic Basin. The northern section is at 50°N, in order to both capture the subpolar densities and retain sufficient depth to include deep ocean processes. The scaling factor applied to the reconstruction was chosen to match the magnitude of the pre-hosing state to the control AMOC, and does not fully capture the magnitude of AMOC weakening.
In order to consider how well the variability was captured we will compare the time series for single simulations as calculated from the velocities and from meridional densities, Fig. 7. The reconstructions demonstrate both the features of weakening and recovery and the background decadal variability of the control run. Again, due to the constant scaling factor used, the full extent of weakening in the hosed runs is not seen in the reconstructions.
Comparison of reconstructed stream functions and that calculated from the velocities for control, 0.2 and 0.5 Sv individual runs. Note that different y-axes have been applied to make the comparison of variability and form clearer, while the full extent of weakening is not captured by the reconstruction
5 What dominates the density changes?
5.1 Relative role of the northern and southern densities
Having seen that the meridional density profiles at 30°S and 50°N can be used to reconstruct the strength of the stream function at 30°N, we now want to understand what induces these density changes. To simplify this question we break the influence down into that led by changes at 50°N and that due to changes at 30°S, Fig. 8. This was done by repeating the reconstruction calculation using the 0.2 and 0.5 Sv ensemble means, firstly for the impact from density changes at 50°N, by holding the density profile at 30°S constantly equal to its initial state value. Then holding the density at 50°N constant to find the stream function resulting from changes at 30°S alone. This showed that the AMOC strength was primarily determined by the changes in the densities in the north. Density changes in the south are well correlated to density changes in the North but smaller in amplitude, acting as a simple moderator of AMOC decline and initial recovery. The 0.2 and 0.5 Sv runs show different magnitudes of impact while responding similarly and on the same timescales. They both show northern values rapidly recover in the first 100 years after hosing, followed by a more gradual adjustment. The 0.5 Sv run has an overshoot that cannot be explained without determining why the densities at 30°S return to initial values on a longer timescale than densities at 50°N.
We have concluded that changes in overturning, with the exception of the overshoot, can be explained by changes in density at 50°N. To explain these density changes we have focused on the 0.5 Sv ensemble and determined the causes of convergence of heat and salinity over the northern and southern regions.
5.2 Understanding density changes with heat and salinity fluxes
The density changes at 50°N and 30°S can be understood by considering the changes in ocean transport and air-sea fluxes of heat and salinity. To do this we consider the ocean convergences (including overturning, gyre, and diffusion components) and surface fluxes over the boxes 45°N–55°N, and 32°S–22°S, Fig. 9. We chose these broader regions to avoid impacts from localised variability. The northern box was chosen to centre on 50°N, and the southern box was chosen as the southernmost 10° where the domain would be zonally contained within lateral continental boundaries. The residual term was taken as the rate of change of the variable minus the sum of the ocean convergences and the surface fluxes, calculated using decadal mean values. The heat residual term is small, however the salinity residual is non-negligible, due in part to the sub-grid scale eddy transports as represented by the Gent-McWilliams scheme (1990). In both the northern and southern boxes, there is some salinity reduction that cannot be attributed since it appears in the residual term.
Change in salinity and heat over boxes in the north (45°N–55°N) and south (32°S–22°S) of the Atlantic. Red: ocean convergence including overturning, gyre activity and diffusion, given as 10-year rolling means; blue: surface flux including hosing input, using decadal mean data; black: calculated rate of change of variable in box, given as 10-year rolling mean; dashed: the residual term calculated from the decadal data for the rate of change minus the sum of surface fluxes and ocean convergence. The shaded region gives ± 1 standard deviation and the black vertical line marks the end of hosing
At the start of hosing we see an initial freshening in the northern box, due to half of the box being within the hosing region. Then there is a strong increase in salinity convergence over the northern box, due to high salinity, reduced velocity, northward transports into the region. This acts to increase the density of the local water mass. The ocean heat convergence reduces during hosing, in line with the weakening of the AMOC. However, the heat content of this box increases significantly in the hosing phase. The region typically has a large heat flux to the atmosphere, as it imports warm lower latitude waters that release heat as they travel northward. The imposed freshwater forcing acts as a cap over the surface of the region, trapping warm saline waters underneath, greatly reducing the surface heat loss. In this model, the AMOC weakening is driven by the reduced density of the northern upper ocean resulting from freshening at the surface and warming from 200 to 2000 m (Fig. 10).
When hosing is switched off (year 200) the northern surface freshwater input decreases, Fig. 9. The ocean salinity convergence responds quickly (20 years), with reduced northward transport of salinity into the northern region. This represents the shutting down of the high salinity subsurface transport that was seen in Fig. 2. The recovering AMOC brings in high salinity anomalies that contribute to the overshoot. These anomalies developed at low latitude due to changes in atmospheric circulation patterns, notably the southward shift of the ITCZ, during weak AMOC (not shown), as has been previously reported (Wu et al. 2011; Jackson 2013; Bouttes et al. 2015). The heat of the northern box decreases over the first 50 years after hosing ends. During this time, the surface cap dissipates allowing for the surface flux to start to recover, as the strengthening AMOC exports some of the heat anomaly. The heat convergence then undergoes a fast transition, as the recovering AMOC again brings in waters warmed at lower latitudes. The high frequency structure of the overshoot is lead by these density fluctuations being transported into the downwelling region.
The southern box shows smaller amplitude net change during hosing. As the AMOC weakens, the South Atlantic changes from transporting heat northwards to bringing it southwards, in a more hemispherically symmetric manner. This means that instead of being a region of cool waters taking up atmospheric heat, the surface waters are able to warm the overlying atmosphere. On the removal of hosing, the ocean heat convergence responds significantly faster than the surface flux, leading to a cooling of the local ocean.
5.3 Role of overturning and gyre feedbacks
In order to identify the ocean mechanisms related to changes in the convergence of density we break the transports down into components of overturning, gyre activity, and diffusion. The distinction between these components at 50°N is less clear, due to the horizontal elements of the overturning transport in the sub-polar region, however we can still learn something from the apparent components. The northward salinity transports at 50°N, Fig. 11a, increased over the first 30 years of hosing, after which gyre transport began to weaken, while the overturning transport strengthened—due to high salinity values (Fig. 2). The two components therefore compensated for each other, suggesting a shift in the circulation structure and giving a steady total transport for much of the hosing phase. The overturning recovered quickly its initial values on the removal of forcing, while the gyre took longer, first exceeding initial values. This shows the low latitude high salinity anomalies being transported to the downwelling region by the gyre. This enhances the stream function recovery, with the gyre transports returning to near initial values during the stream function overshoot. A similar behaviour can be seen in the thermoclines at 50°N, which show a ‘double dip’ during recovery at around 1500 m deep, Fig. 12b. After a relatively fast initial recovery there seems to be a fluctuation during the overshoot, due to the downwelling of patches of warm water transported north from the sub-tropics by gyre activity, Fig. 11a.
Changes to the total salinity transport at 30°S were less pronounced, and yet as the boundary to the Atlantic basin, may still be significant to the basin state. The value of Fov at 30°S was positive in the control state (0.17 Sv, which is equivalent to a \(-6\times {10}^{6}\) kg s−1 salinity transport) and it remained so throughout hosing, having a minimum value of 0.1 Sv, Fig. 11b. This suggests that the AMOC control state may have been more stable in these simulations than in observation and reanalysis. The overturning did begin to import salinity into the basin at 30°S during the recovery phase, however this was compensated for by changes in gyre activity (increase in Faz)—and so did not indicate change in the total salinity imported into the Atlantic basin. The use of Fov as an indicator requires that the changes in other contributions to freshwater transport, such as Faz, are smaller at 30°S (Jackson 2013) which was not the case here. Weak AMOC coincided with times of reduced total northward freshwater transport at 30°S.
5.4 Influence of 30°S in AMOC overshoot
The changes in the southern density profile enhanced the strength of overturning. This was due to the warming caused by ocean heat convergence exceeding the atmospheric cooling, Fig. 9, net reducing local densities. The thermocline at 30°S deepens during hosing, Fig. 12a, due to reduced North Atlantic overturning leading to the Atlantic exporting less dense water. The thermocline later shoals as it drains. This occurs on a multi-centennial timescale, with some lag to changes in freshwater forcing. As the response time is longer further from the site of hosing, the density profile at 30°S still contributes to an enhanced AMOC once the northern signal showed a near return to control values, Fig. 8. This means that the densities of the South Atlantic provide a low frequency signal that gives the magnitude of the overshoot, with the higher frequency variability coming from the North Atlantic. This is in contrast with previous model studies’ explanation for overshoot behaviour. It has been reported that as the AMOC begins to recover, the salinity anomaly built up in the subtropical gyre is advected to higher latitudes (Wu et al. 2011; Jackson 2013, using CO2 and freshwater forcing, respectively) leading to higher density waters in the downwelling regions—briefly enhancing the AMOC (Bouttes et al. 2015).
6 Discussion
All hosed runs displayed asymmetry between weakening and recovery. The stream function at 30°N, 1500 meters deep, weakened quite smoothly over the 200 years of hosing. In the following 200 years it recovered, overshot and returned to near control values. The ensemble mean stream function strength for the 0.5 Sv simulations increased by 20 Sv over the course of 120 years.
Multiple studies have explored the climate impacts of an abrupt AMOC weakening (Vellinga and Wood 2002; Jackson et al. 2015) however less research has been done on the climate impact of abrupt recovery and overshoot. The findings of this study suggest that this could be an important topic for future research.
The meridional density gradient was a better indicator of the stream function than the mean basin salinity. This indicates that the distribution of heat and salinity within the Atlantic, rather than the mean value, was the primary control. High latitude subsurface heat increase, resulting from suppression of ventilation, has been reported in previous freshwater forcing studies, (Mignot et al. 2007; Krebs and Timmermann 2007). This has been suggested to destabilise the water column and contribute to an abrupt AMOC recovery, once the forcing is removed allowing the isopycnal slopes to readjust, and heat to be released to the atmosphere. In this study the heat changes played a strong, destabilising, role throughout. A high salinity anomaly in the sub-tropical North Atlantic, accumulated during weak AMOC, being transported northwards as the AMOC recovers has been previously observed in models. The high-density water mass reaching downwelling regions has been used to explain strong recovery and overshoot, (Wu et al. 2011; Jackson 2013; Bouttes et al. 2015). The way in which models disperse this density anomaly defines the recovery process within each model (Sgubin et al. 2015). Our results indicate that the progress of the high-density water mass through the North Atlantic plays a crucial role in the recovery, and gives the high-frequency variability within the overshoot. However, the overshoot itself was caused by the longer timescale behaviour governing pycnocline depth in the South Atlantic.
In summary, the results of this study suggest a recovery process of the AMOC that is mechanistically different from the weakening process, influenced by the deepening of the South Atlantic thermocline. The initial stream function recovery in FAMOUS was related to the removal of hosing input, allowing North Atlantic surface heat and freshwater fluxes to recover. For the full recovery, the density needed to increase in the northern latitudes. The overshoot took its high frequency structure from the north Atlantic density transports, and its magnitude from density changes at 30°S.
References
Bitz CM, Chiang JCH, Cheng W, Barsugli JJ (2007) Rates of thermohaline recovery from freshwater pulses in modern, Last Glacial Maximum, and greenhouse warming climates. Geophys Res Lett 34:L07708. https://doi.org/10.1029/2006GL029237
Boulton CA, Allison LC, Lenton TM (2014) Early warning signals of Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation collapse in a fully coupled climate model. Nat Commun. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms6752
Bouttes N, Good P, Gregory JM, Lowe JA (2015) Non-linearity of ocean heat uptake during warming and cooling in the FAMOUS climate model. Geophys Res Lett 42:2409–2416
Bryden H (2011) South Atlantic overturning circulation at 24 S. J Mar Res 69(1):38–55(18)
Butler ED, Oliver KIC, Hirschi JJM, Mecking JV (2016) Reconstructing global overturning from meridional density gradients. Clim Dyn 46(7–8):2593–2610. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-015-2719-6
Cao L, Duan L, Bala G, Caldeira K (2016) Simulated long-term climate response to idealized solar geoengineering. Geophys Res Lett 43(5):2209–2217. https://doi.org/10.1002/2016GL068079
Cimatoribus AA, Drijfhout SS, den Toom M, Dijkstra HA (2012) Sensitivity of the Atlantic meridional overturning circulation to south Atlantic freshwater anomalies. Clim Dyn 39:2291–2306
Cimatoribus AA, Drijfhout SS, Dijkstra HA (2014) Meridional overturning circulation: stability and ocean feedbacks in a box model. Clim Dyn 42:311–328
Collins M, Knutti R, Arblaster J, Dufresne J-L, Fichefet T, Friedlingstein P, Gao X, Gutowski WJ, Johns T, Krinner G, Shongwe M, Tebaldi C, Weaver AJ, Wehner M (2013) Long-term climate change: projections, commitments and irreversibility. In: Climate change 2013: the physical science basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
de Boer AM, Nof D (2004) The exhaust valve of the North Atlantic. J Clim 17(3):417–422. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0442(2004)017%3C0417:TEVOTN%3E2.0.CO;2
de Vries P, Weber SL (2005) The Atlantic freshwater budget as a diagnostic for the existence of a stable shut down of the meridional overturning circulation. Geophys Res Lett 32:L09606
Dijkstra HA (2007) Characterization of the multiple equilibria regime in a global ocean model. Tellus 59A:695–705
Garzoli SL, Baringer MO, Dong S, Perez RC, Ya Q (2013) South Atlantic meridional fluxes. Deep Sea Res I 71:21–32
Gent PR, McWilliams JC (1990) Isopycnal mixing in ocean circulation models. J Phys Oceanogr 20(1):150–155
Gordon C, Cooper C, Senior CA, Banks H, Gregory JM, Johns TC, Mitchell JFB, Wood R (2000) The simulation of SST, sea ice extents and ocean heat transports in a version of the Hadley Centre coupled model without flux adjustments. Clim Dyn 16:147–168
Gregory JM, Huybrechts P, Raper SCB (2004) Threatened loss of the Greenland ice-sheet. Nature 428(April):2513–2513. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature02512
Hawkins E, Smith RS, Allison LC, Gregory JM, Woollings TJ, Pohlmann H, De Cuevas B (2011) Bistability of the Atlantic overturning circulation in a global climate model and links to ocean freshwater transport. Geophys Res Lett 38(10):1–6
Hu A, Meehl GA, Han W, Timmermann A, Otto-Bliesner B, Liu Z, Washington WM, Large W, Abe-Ouchi A, Kimoto M, Lambeck K, Wu B (2012) Role of the Bering Strait on the hysteresis of the ocean conveyor belt circulation and glacial climate stability. Proc Nat Acad Sci 109(17):6417–6422. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1116014109
Huisman SE, den Toom M, Dijkstra HA, Drijfhout SS (2010) An indicator of the multiple equilibria regime of the Atlantic meridional overturning circulation. J Phys Oceanogr 40:551–567
Jackson LC (2013) Shutdown and recovery of the AMOC in a coupled global climate model: the role of the advective feedback. Geophys Res Lett 40(6):1182–1188. https://doi.org/10.1002/grl.50289
Jackson LC, Kahana R, Graham T, Ringer MA, Woollings T, Mecking JV, Wood RA (2015) Global and European climate impacts of a slowdown of the AMOC in a high resolution GCM. Clim Dyn 45:3299–3316. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-015-2540-2
Jackson LC, Smith RS, Wood RA (2017) Ocean and atmosphere feedbacks affecting AMOC hysteresis in a GCM. Clim Dyn 49:173. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-016-3336-8
Jungclaus JH, Haak H, Esch M, Roeckner E, Marotzke J (2006) Will Greenland melting halt the thermohaline circulation? Geophys Res Lett 33(17):1–5. https://doi.org/10.1029/2006GL026815
Kleinen T, Osborn T, Briffa K (2009) Sensitivity of climate response to variations in freshwater hosing location. Ocean Dyn 59(3):509–521. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10236-009-0189-2
Krebs U, Timmermann A (2007) Fast advective recovery of the Atlantic meridional overturning circulation after a Heinrich event. Paleoceanography 22(1):1–9. https://doi.org/10.1029/2005PA001259
Liu W, Liu Z (2013) A diagnostic indicator of the stability of the Atlantic meridional overturning circulation in CCSM3. J Clim 26:1926–1938
Liu W, Liu Z (2014) A note on the stability indicator of the Atlantic Meridional overturning circulation. J Clim 27:969–975
Liu W, Liu Z, Hu A (2013) The stability of an evolving Atlantic meridional overturning circulation. Geophys Res Lett 40:1562–1568
Liu W, Xie S-P, Liu Z, Zhu J (2017) Overlooked possibility of a collapsed Atlantic Meridional overturning circulation in warming climate. Sci Adv 3:e1601666
McCarthy GD, Smeed DA, Johns WE, Frajka-Williams E, Moat BI, Rayner D, Baringer MO, Meinen CS, Collins J, Bryden HL (2015) Measuring the Atlantic Meridional overturning circulation at 26°N. Prog Oceanogr 130:91–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pocean.2014.10.006
Mignot J, Ganopolski A, Levermann A (2007) Atlantic subsurface temperatures: response to a shutdown of the overturning circulation and consequences for its recovery. J Clim 20(19):4884–4898. https://doi.org/10.1175/JCLI4280.1
Rahmstorf S (1996) On the freshwater forcing and transport of the Atlantic thermohaline circulation. Clim Dyn 12:799–811
Robinson A, Calov R, Ganopolski A (2012) Multistability and critical thresholds of the Greenland ice sheet. Nat Clim Change 2(6):429–432
Schmittner A, Latif M, Schneider B (2005) Model projections of the North Atlantic thermohaline circulation for the 21st century assessed by observations. Geophys Res Lett 32:L23710. https://doi.org/10.1029/2005GL024368
Sévellec F, Fedorov AV, Liu W (2017) Arctic sea-ice decline weakens the Atlantic Meridional overturning circulation. Nat Clim Change 7:604–610
Sgubin G, Swingedouw D, Drijfhout S, Hagemann S, Robertson E (2015) Multimodel analysis on the response of the AMOC under an increase of radiative forcing and its symmetrical reversal. Clim Dyn 45(5–6):1429–1450. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-014-2391-2
Sijp WP, England MH, Gregory JM (2012) Precise calculations of the existence of multiple AMOC equilibria in coupled climate models. Part I: equilibrium states. J Clim 25:282–298
Smith RS (2012) The FAMOUS climate model (versions XFXWB and XFHCC): description update to version XDBUA. Geosci Model Dev 5(1):269–276. https://doi.org/10.5194/gmd-5-269-2012
Smith RS, Gregory JM (2009) A study of the sensitivity of ocean overturning circulation and climate to freshwater input in different regions of the North Atlantic. Geophys Res Lett 36(15):1–5. https://doi.org/10.1029/2009GL038607
Smith RS, Gregory JM, Osprey A (2008) A description of the FAMOUS (version XDBUA) climate model and control run. Geosci Model Dev 1(1):53–68. https://doi.org/10.5194/gmd-1-53-2008
Stommel H (1961) Thermohaline convection with two stable regimes of flow. Tellus 13:224–230
Stouffer RJ, Manabe S (1999) Response of a coupled ocean–atmosphere model to increasing atmospheric carbon dioxide: sensitivity to the rate of increase. J Clim 12:2224–2237
Stouffer RJ, Yin J, Gregory JM, Dixon KW, Spelman MJ, Hurlin W, Weaver AJ, Eby M, Flato GM, Hasumi H, Hu A, Jungclaus JH, Kamenkovich IV, Levermann A, Montoya M, Murakami S, Nawrath S, Oka A, Peltier WR, Robitaille DY, Sokolov A, Vettoretti G, Weber SL (2006) Investigating the causes of the response of the thermohaline circulation to past and future climate changes. J Clim 19:1365–1387. https://doi.org/10.1175/JCLI3689.1
Thorpe RB, Gregory JM, Johns TC, Wood RA, Mitchell JFB (2001) Mechanisms determining the Atlantic thermohaline circulation response to greenhouse gas forcing in a non-adjusted coupled climate model. J Clim 14:3102–3116
Vellinga M, Wood RA (2002) Global climatic impacts of a collapse of the Atlantic thermohaline circulation. Clim Change 54(3):251–267. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1016168827653
Vellinga M, Wood RA, Gregory JM (2002) Processes governing the recovery of a perturbed Thermohaline Circulation in HadCM3. J Clim 15:764–780
Weijer W, de Ruijter W, Dijkstra H, van Leeuwen P (1999) Impact of interbasin exchange on the Atlantic overturning circulation. J Phys Oceanogr 29:2266–2284
Wu P, Jackson L, Pardaens A, Schaller N (2011) Extended warming of the northern high latitudes due to an overshoot of the Atlantic meridional overturning circulation. Geophys Res Lett 38:L24704. https://doi.org/10.1029/2011GL049998
Acknowledgements
This project was funded by a NERC Industrial CASE studentship in partnership with the Met Office (NE/M010295/1). We would like to thank Robin Smith and Jeff Blundell for their support and guidance in the running of FAMOUS.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
About this article
Cite this article
Haskins, R.K., Oliver, K.I.C., Jackson, L.C. et al. Explaining asymmetry between weakening and recovery of the AMOC in a coupled climate model. Clim Dyn 53, 67–79 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-018-4570-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-018-4570-z