Abstract
Purpose
The purpose of this study is to evaluate a noninvasive device to assess intracranial pressure wave form in children with hydrocephalus.
Methods
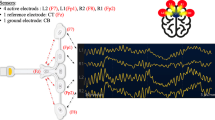
A prospective and non-experimental descriptive-analytic study was performed. Fifty-six patients were enrolled in this study. They were divided in four groups: group A, children with clinically compensated hydrocephalus; B, surgically treated hydrocephalus; C, patients with acute intracranial hypertension due to hydrocephalus; and D, children without neurological disease (control). Data were collected through the installation of an extracranial deformation sensor, coupled to the children’s scalp, which allowed registration of noninvasive intracranial pressure curves. Parameters obtained were analyzed: P2/P1 ratio, “classification P1 and P2 and P1 slope.
Results
P2/P1 index and “classification of P1 and P2” had a sensitivity of 80% and specificity of 100% for predicting intracranial hypertension. “P1 slope” presented no statistical difference.
Conclusion
This study showed a useful and noninvasive method for monitoring intracranial pressure, which was able to indicate the intracranial hypertension in children with hydrocephalus and, thus, should be further investigated for clinical applications.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams JP, Bell D, McKinlay J (2010) Neurocritical care: a guide to practical management. Springer, London
Ballestero MFM (2016 ) Evaluation of a non-invasive method to monitoring intracranial pressure in children and adolescents with hydrocephalus. Master’s dissertation, Universidade de Sao Paulo, Ribeirao Preto
Cabella B, Vilela GHF, Mascarenhas S, Czosnyka M, Smielewski P, Dias C, Cardim DA, Wang CC, Mascarenhas P, Andrade R (2016) Validation of a new noninvasive intracranial pressure monitoring method by direct comparison with an invasive technique. In: intracranial pressure and brain monitoring XV, vol 122. 2016/05/12 edn. Springer, pp 93–96. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-22533-3_18
Cardoso ER, Piatek D (1989) Intracranial and venous pressures part I: intracranial pulse wave changes during hemodynamic maneuvers in humans. In: Intracranial Pressure VII. Springer, pp 203–205
Cardoso ER, Rowan JO, Galbraith S (1983) Analysis of the cerebrospinal fluid pulse wave in intracranial pressure. J Neurosurg 59:817–821. doi:10.3171/jns.1983.59.5.0817
Chambers IR, Daubaris G, Jarzemskas E, Fountas K, Kvascevicius R, Ragauskas A, Rocka S, Robinson JS, Sitkauskas A (2005) The clinical application of non-invasive intracranial blood volume pulse wave monitoring. Physiol Meas 26:1019–1032. doi:10.1088/0967-3334/26/6/011
Contant CF Jr, Robertson CS, Crouch J, Gopinath SP, Narayan RK, Grossman RG (1995) Intracranial pressure waveform indices in transient and refractory intracranial hypertension. J Neurosci Methods 57:15–25
Czosnyka M, Pickard JD (2004) Monitoring and interpretation of intracranial pressure. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 75:813–821. doi:10.1136/jnnp.2003.033126
Czosnyka M, Smielewski P, Timofeev I, Lavinio A, Guazzo E, Hutchinson P, Pickard JD (2007) Intracranial pressure: more than a number. Neurosurg Focus 22:E10
Czosnyka Z, Keong N, Kim DJ, Radolovich D, Smielewski P, Lavinio A, Schmidt EA, Momjian S, Owler B, Pickard JD, Czosnyka M (2008) Pulse amplitude of intracranial pressure waveform in hydrocephalus. Acta Neurochir Suppl 102:137–140. doi:10.1007/978-3-211-85578-2_28
Czosnyka ZH, Czosnyka M, Whitfield PC, Donovan T, Pickard JD (2002) Cerebral autoregulation among patients with symptoms of hydrocephalus. Neurosurgery 50:526–532 discussion 532-523
de Oliveira RS, Machado HR (2003) Transcranial color-coded Doppler ultrasonography for evaluation of children with hydrocephalus. Neurosurg Focus 15:1–7
Dias C, Maia I, Cerejo A, Varsos G, Smielewski P, Paiva JA, Czosnyka M (2014) Pressures, flow, and brain oxygenation during plateau waves of intracranial pressure. Neurocrit Care 21:124–132. doi:10.1007/s12028-013-9918-y
Fan JY, Kirkness C, Vicini P, Burr R, Mitchell P (2008) Intracranial pressure waveform morphology and intracranial adaptive capacity. Am J Crit Care 17:545–554
Gallagher ER, Hing AV, Cunningham ML (2013) Evaluating fontanels in the newborn skull.
Garne E, Loane M, Addor MC, Boyd PA, Barisic I, Dolk H (2010) Congenital hydrocephalus—prevalence, prenatal diagnosis and outcome of pregnancy in four European regions. Eur J Paediatr Neurol 14:150–155. doi:10.1016/j.ejpn.2009.03.005
Hashimoto M, Higashi S, Tokuda K, Yamamoto Y, Yamashita J (1993) Changes of intracranial pressure and pulse wave form induced by various mechanical stresses upon intracranial hemodynamics. In: Intracranial Pressure VIII. Springer, pp 367–371
Huang X, Lin J, Demner-Fushman D (2006) PICO as a Knowledge Representation for Clinical Questions. In: AMIA 2006 Symposium Proceedings. pp 359–363
Jeng S, Gupta N, Wrensch M, Zhao S, Wu YW (2011) Prevalence of congenital hydrocephalus in California, 1991-2000. Pediatr Neurol 45:67–71. doi:10.1016/j.pediatrneurol.2011.03.009
Kirkness CJ, Mitchell PH, Burr RL, March KS, Newell DW (2000) Intracranial pressure waveform analysis: clinical and research implications. J Neurosci Nurs J Am Assoc Neurosci Nurs 32:271–277
Levine DN (2008) Intracranial pressure and ventricular expansion in hydrocephalus: have we been asking the wrong question? J Neurol Sci 269:1–11
Marmarou A, Beaumont A (2011) Physiology of the cerebrospinal fluid and intracranial pressure. In: Elsevier (ed) Youmans neurological surgery. Winn,. H, Filadélfia, pp 169–182
Mascarenhas S, Vilela GH, Carlotti C, Damiano LE, Seluque W, Colli B, Tanaka K, Wang CC, Nonaka KO (2012) The new ICP minimally invasive method shows that the Monro-Kellie doctrine is not valid. Acta Neurochir Suppl 114:117–120. doi:10.1007/978-3-7091-0956-4_21
Owler BK, Fong KCS, Czosnyka Z (2001) Importance of ICP monitoring in the investigation of CSF circulation disorders. Br J Neurosurg 15:439–440. doi:10.1080/02688690120082477
Padayachy LC (2016) Non-invasive intracranial pressure assessment. Childs Nerv Syst. doi:10.1007/s00381-016-3159-2
Patwardhan RV, Nanda A (2005) Implanted ventricular shunts in the United States: the billion-dollar-a-year cost of hydrocephalus treatment. Neurosurgery 56:139–144 discussion 144–135
Pople IK, Muhlbauer MS, Sanford RA, Kirk E (1995) Results and complications of intracranial pressure monitoring in 303 children. Pediatr Neurosurg 23:64–67
Raboel PH, Bartek J Jr, Andresen M, Bellander BM, Romner B (2012) Intracranial pressure monitoring: invasive versus non-invasive methods-a review. Crit Care Res Pract 2012:950393. doi:10.1155/2012/950393
Rauch ME, Mitchell PH, Tyler ML (1990) Validation of risk factors for the nursing diagnosis decreased intracranial adaptive capacity. J Neurosci Nurs 22:173–178
Schardt C, Adams MB, Owens T, Keitz S, Fontelo P (2007) Utilization of the PICO framework to improve searching PubMed for clinical questions. BMC Med Inf Decis Mak 7:16
Vilela GH, Cabella B, Mascarenhas S, Czosnyka M, Smielewski P, Dias C, Cardim DA, Mascarenhas YM, Wang CC, Andrade R, Tanaka K, Lopes LS, Colli BO (2016) Validation of a new minimally invasive intracranial pressure monitoring method by direct comparison with an invasive technique. Acta Neurochir Suppl 122:97–100. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-22533-3_19
Welch K (1980) The intracranial pressure in infants. J Neurosurg 52:693–699. doi:10.3171/jns.1980.52.5.0693
Xu W, Gerety P, Aleman T, Swanson J, Taylor J (2016) Noninvasive methods of detecting increased intracranial pressure. Childs Nerv Syst 32:1371–1386. doi:10.1007/s00381-016-3143-x
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
This study was approved by the local ethics committee and consent forms were obtained from the patient’s legal representative.
Conflict of interest
Gustavo Frigieri and Sergio Mascarenhas de Oliveira are paid consultants of BrainCare Corp. The other authors have no personal, financial, or institutional interest in any of the materials, or devices described in this article.
The NI system discussed is still investigational and not labeled for clinical use.
Funding
This study was funded by São Paulo Research Foundation–FAPESP.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ballestero, M.F.M., Frigieri, G., Cabella, B.C.T. et al. Prediction of intracranial hypertension through noninvasive intracranial pressure waveform analysis in pediatric hydrocephalus. Childs Nerv Syst 33, 1517–1524 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-017-3475-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-017-3475-1