Abstract
Introduction
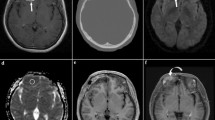
An appropriate surgical approach for posterior fossa lesions is to start tumor removal from areas with a defined plane to where tumor is infiltrating the brainstem or peduncles. This surgical approach minimizes risk of damage to eloquent areas. Although magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is the current standard preoperative imaging obtained for diagnosis and surgical planning of pediatric posterior fossa tumors, it offers limited information on the infiltrative planes between tumor and normal structures in patients with medulloblastomas. Because medulloblastomas demonstrate diffusion restriction on apparent diffusion coefficient map (ADC map) sequences, we investigated the role of ADC map in predicting infiltrative and non-infiltrative planes along the brain stem and/or cerebellar peduncles by medulloblastomas prior to surgery.
Methods
Thirty-four pediatric patients with pathologically confirmed medulloblastomas underwent surgical resection at our facility from 2004 to 2012. An experienced pediatric neuroradiologist reviewed the brain MRIs/ADC map, assessing the planes between the tumor and cerebellar peduncles/brain stem. An independent evaluator documented surgical findings from operative reports for comparison to the radiographic findings. The radiographic findings were statistically compared to the documented intraoperative findings to determine predictive value of the test in identifying tumor infiltration of the brain stem cerebellar peduncles.
Results
Twenty-six patients had preoperative ADC mapping completed and thereby, met inclusion criteria. Mean age at time of surgery was 8.3 ± 4.6 years. Positive predictive value of ADC maps to predict tumor invasion of the brain stem and cerebellar peduncles ranged from 69 to 88 %; negative predictive values ranged from 70 to 89 %. Sensitivity approached 93 % while specificity approached 78 %.
Conclusions
ADC maps are valuable in predicting the infiltrative and non-infiltrative planes along the tumor and brain stem interface in medulloblastomas. Inclusion and evaluation of ADC maps in preoperative evaluation can assist in surgical resection planning in patients with medulloblastoma.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yin Z, Glaser KJ, Manduca A, Van Gompel JJ, Link MJ, Hughes JD, Romano A, Ehman RL, Huston J 3rd (2015) Slip interface imaging predicts tumor-brain adhesion in vestibular schwannomas. Radiology 277:507–517
Rowley HA, Grant PE, Roberts TP (1999) Diffusion MR imaging. Theory and applications. Neuroimaging Clin N Am 9:343–361
Schaefer PW, Grant PE, Gonzalez RG (2000) Diffusion-weighted MR imaging of the brain. Radiology 217:331–345
Bulakbasi N, Guvenc I, Onguru O, Erdogan E, Tayfun C, Ucoz T (2004) The added value of the apparent diffusion coefficient calculation to magnetic resonance imaging in the differentiation and grading of malignant brain tumors. J Comput Assist Tomogr 28:735–746
Castillo M, Smith JK, Kwock L, Wilber K (2001) Apparent diffusion coefficients in the evaluation of high-grade cerebral gliomas. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:60–64
Gupta RK, Cloughesy TF, Sinha U, Garakian J, Lazareff J, Rubino G, Rubino L, Becker DP, Vinters HV, Alger JR (2000) Relationships between choline magnetic resonance spectroscopy, apparent diffusion coefficient and quantitative histopathology in human glioma. J Neuro-Oncol 50:215–226
Kono K, Inoue Y, Nakayama K, Shakudo M, Morino M, Ohata K, Wakasa K, Yamada R (2001) The role of diffusion-weighted imaging in patients with brain tumors. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:1081–1088
Rumboldt Z, Camacho DL, Lake D, Welsh CT, Castillo M (2006) Apparent diffusion coefficients for differentiation of cerebellar tumors in children. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 27:1362–1369
Sugahara T, Korogi Y, Kochi M, Ikushima I, Shigematu Y, Hirai T, Okuda T, Liang L, Ge Y, Komohara Y, Ushio Y, Takahashi M (1999) Usefulness of diffusion-weighted MRI with echo-planar technique in the evaluation of cellularity in gliomas. J Magn Reson Imaging 9:53–60
Yamasaki F, Kurisu K, Satoh K, Arita K, Sugiyama K, Ohtaki M, Takaba J, Tominaga A, Hanaya R, Yoshioka H, Hama S, Ito Y, Kajiwara Y, Yahara K, Saito T, Thohar MA (2005) Apparent diffusion coefficient of human brain tumors at MR imaging. Radiology 235:985–991
Koral K, Mathis D, Gimi B, Gargan L, Weprin B, Bowers DC, Margraf L (2013) Common pediatric cerebellar tumors: correlation between cell densities and apparent diffusion coefficient metrics. Radiology 268:532–537
Kan P, Liu JK, Hedlund G, Brockmeyer DL, Walker ML, Kestle JR (2006) The role of diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging in pediatric brain tumors. Childs Nerv Syst 22:1435–1439
Rodriguez Gutierrez D, Awwad A, Meijer L, Manita M, Jaspan T, Dineen RA, Grundy RG, Auer DP (2014) Metrics and textural features of MRI diffusion to improve classification of pediatric posterior fossa tumors. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 35:1009–1015
Koral K, Alford R, Choudhury N, Mossa-Basha M, Gargan L, Gimi B, Gao A, Zhang S, Bowers DC, Koral KM, Izbudak I (2014) Applicability of apparent diffusion coefficient ratios in preoperative diagnosis of common pediatric cerebellar tumors across two institutions. Neuroradiology 56:781–788
Koeller KK, Rushing EJ (2003) From the archives of the AFIP: medulloblastoma: a comprehensive review with radiologic-pathologic correlation. Radiographics 23:1613–1637
Gauvain KM, McKinstry RC, Mukherjee P, Perry A, Neil JJ, Kaufman BA, Hayashi RJ (2001) Evaluating pediatric brain tumor cellularity with diffusion-tensor imaging. AJR Am J Roentgenol 177:449–454
Kotsenas AL, Roth TC, Manness WK, Faerber EN (1999) Abnormal diffusion-weighted MRI in medulloblastoma: does it reflect small cell histology? Pediatr Radiol 29:524–526
Pauleit D, Langen KJ, Floeth F, Hautzel H, Riemenschneider MJ, Reifenberger G, Shah NJ, Muller HW (2004) Can the apparent diffusion coefficient be used as a noninvasive parameter to distinguish tumor tissue from peritumoral tissue in cerebral gliomas? J Magn Reson Imaging 20:758–764
Kido A, Kataoka M, Yamamoto A, Nakamoto Y, Umeoka S, Koyama T, Maetani Y, Isoda H, Tamai K, Morisawa N, Saga T, Mori S, Togashi K (2010) Diffusion tensor MRI of the kidney at 3.0 and 1.5 tesla. Acta Radiol 51:1059–1063
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosures
The authors report no conflict of interest concerning the materials or methods used in this study or the findings specified in this paper.
Author contribution
Author contributions to the study and manuscript preparation include the following. Conception and design: Sood, Altinok, Marupudi. Acquisition of data: Marupudi, Goncalves, Altinok. Analysis and interpretation of data: Marupudi, Goncalves, Sood. Drafting the article: Marupudi. Critically revising the article: Sood, Marupudi, Altinok. Reviewed submitted version of manuscript: all authors.
Additional information
This paper was presented as an oral presentation at the 42nd Annual AANS/CNS Section on Pediatric Neurological Surgery (December 3–6, 2013) in Toronto, CA.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Marupudi, N.I., Altinok, D., Goncalves, L. et al. Apparent diffusion coefficient mapping in medulloblastoma predicts non-infiltrative surgical planes. Childs Nerv Syst 32, 2183–2187 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-016-3168-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-016-3168-1