Abstract
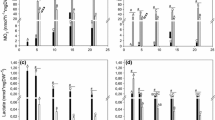
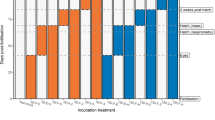
Embryos of Austrofundulus limnaeus are exceptional in their ability to tolerate prolonged bouts of complete anoxia. Hypoxia and anoxia are a normal part of their developmental environment. Here, we exposed embryos to a range of PO2 levels at two different temperatures (25 and 30 °C) to study the combined effects of reduced oxygen and increased temperature on developmental rate, heart rate, and metabolic enzyme capacity. Hypoxia decreased overall developmental rate and caused a stage-specific decline in heart rate. However, the rate of early development prior to the onset of organogenesis is insensitive to PO2. Increased incubation temperature caused an increase in the developmental rate at high PO2s, but hindered developmental progression under severe hypoxia. Embryonic DNA content in pre-hatching embryos was positively correlated with PO2. Citrate synthase, lactate dehydrogenase, and phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase capacity were all reduced in embryos developing under hypoxic conditions. Embryos of A. limnaeus are able to develop normally across a wide range of PO2s and contrary to most other vertebrates severe hypoxia is not a teratogen. Embryos of A. limnaeus do not respond to hypoxia through an increase in the capacity for enzymatic activity of the metabolic enzymes lactate dehydrogenase, citrate synthase, or phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase. Instead they appear to adjust whole-embryo metabolic capacity to match oxygen availability. However, decreased DNA content in hypoxia-reared embryos suggests that cellular enzymatic capacity may remain unchanged in response to hypoxia, and the reduced capacity may rather indicate reduced cell number in hypoxic embryos.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alderdice DF, Wickett WP, Brett JR (1958) Some effects of temporary exposure to low dissolved oxygen levels on Pacific Salmon eggs. J Fish Res Board Can 15(2):229–249
Altimiras J, Phu L (2000) Lack of physiological plasticity in the early chicken embryo exposed to acute hypoxia. J Exp Zool 286(5):450–456
Bagatto B (2005) Ontogeny of cardiovascular control in zebrafish (Danio rerio): effects of developmental environment. Comp Biochem Physiol A 141(4):391–400
Baltus E, Hanocq-Quertier J, Brachet J (1968) Isolation of deoxyribonucleic acid from the yolk platelets of Xenopus laevis oocyte. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 61:469–476
Barrionuevo WR, Burggren WW (1999) O2 consumption and heart rate in developing zebrafish (Danio rerio): influence of temperature and ambient O2. Am J Physiol 276(2):R505–R513
Barry MJ, Logan DC, Ahokas JT, Holdway DA (1995) Sublethal effects of endosulfan and oxygen concentration on embryos of the Australian crimson-spotted rainbowfish (Melanotaenia fluviatilis). Aust J Ecotoxicol 1(1):71–76
Bradford DF, Seymour RS (1988) Influence of environmental PO2 on embryonic oxygen consumption, rate of development, and hatching in the frog Pseudophryne bibroni. Physiol Zool 61(6):475–482
Brahimi-Horn MC, Pouyssegur J (2007) Oxygen, a source of life and stress. FEBS Lett 581:3582–3591
Carlson AR, Siefert RE (1974) Effects of reduced oxygen on the embryos and larvae of Lake Trout (Salvelinus namaycush) and Largemouth Bass (Micropterus salmoides). J Fish Res Board Can 31(8):1393–1396
Carlson A, Siefert R, Herman L (1974) Effects of lowered dissolved oxygen concentrations on channel catfish (Ictalurus punctatus) embryos and larvae. Trans Am Fish Soc 103:623–626
Chennault T, Podrabsky JE (2010) Aerobic and anaerobic capacities differ in embryos of the annual killifish Austrofundulus limnaeus that develop on alternate developmental trajectories. J Exp Zool A 313A(9):587–596. doi:10.1002/jez.632
Cooper RU, Clough LM, Farwell MA, West TL (2002) Hypoxia-induced metabolic and antioxidant enzymatic activities in the estuarine fish Leiostomus xanthurus. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 279:1–20
Crawford RB, Wilde CE Jr (1966) Cellular differentiation in the anamniota II. Oxygen dependency and energetics requirements during early development of teleosts and urodeles. Exp Cell Res 44(2–3):453–470
Czerkies P, Kordalski K, Golas T, Krysinski D, Luczynski M (2002) Oxygen requirements of whitefish and vendace (Coregoninae) embryos at final stages of their development. Aquaculture 211(1–4):375–385
Dawid IB (1965) Deoxyribonucleic acid in amphibian eggs. J Mol Biol 12:581–599
Dawid IB (1966) Evidence for the mitochondrial origin of frog egg cytoplasmic DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 56:269–276
DiMichele L, Powers DA (1984) Developmental and oxygen consumption rate differences between lactate dehydrogenase-B genotypes of Fundulus heteroclitus and their effect on hatching time. Physiol Zool 57(1):52–56
DiMichele L, Taylor MH (1980) The environmental control of hatching in Fundulus heteroclitus. J Exp Zool 214(2):181–187
DiMichele L, Taylor MH (1981) The mechanism of hatching in Fundulus heteroclitus: development and physiology. J Exp Zool 217(1):73–79
Dudley R, Eipper A (1975) Survival of largemouth bass embryos at low dissolved oxygen concentration. Trans Am Fish Soc 104:122–128
Duodoroff P, Warren CE (1965) Dissolved oxygen requirements of fishes. Biological Problems in Water Pollution PHS Publ. No. 999-WP-25, pp 145–155
Fergusson-Kolmes L, Podrabsky JE (2007) Differential effects of anoxia on heart rate in developmental stages of the annual killifish Austrofundulus limnaeus that differ in their tolerance of anoxia. J Exp Zool 307A:419–423
Finn RN, Widdows J, Fyhn HJ (1995) Calorespirometry of developing embryos and yolk-sac larvae of turbot (Scophthalmus maximus). MarBiol 122(1):157–163
Garside E (1959) Some effects of oxygen in relation to temperature on the development of lake trout embryos. Can J Zool 37:689–698
Grabowski CT (1961) A quantitative study of the lethal and teratogenic effects of hypoxia on the three-day chick embryo. Am J Anat 109(1):25–35. doi:10.1002/aja.1001090104
Grabowski CT, Paar JA (1958) The teratogenic effects of graded doses of hypoxia on the chick embryo. Am J Anat 103(3):313–347. doi:10.1002/aja.1001030302
Grabowski CT, Schroeder RE (1968) A time-lapse photographic study of chick embryos exposed to teratogenic doses of hypoxia. J Embryol Exp Morphol 19(3):347–362
Hassell KL, Coutin PC, Nugegoda D (2008) Hypoxia impairs embryo development and survival in black bream (Acanthopagrus butcheri). Mar Pollut Bull 57(6–12):302–306
Hrbek T, Taphorn DC, Thomerson JE (2005) Molecular phylogeny of Austrofundulus Myers (Cyprinodontiformes: Rivulidae), with revision of the genus and the description of four new species. Zootaxa 825:1–39
Jaffee OC (1974) The effects of moderate hypoxia and moderate hypoxia plus hypercapnea on cardiac development in chick embryos. Teratology 10:275–282
Kaur K, Toor HS (1978) Effect of dissolved oxygen on the survival and hatching of eggs of Scale Carp. Prog Fish Cult 40(1):35–37
Keckeis H, Bauer-Nemeschkal E, Kamler E (1996) Effects of reduced oxygen level on the mortality and hatching rate of Chondrostoma nasus embryos. J Fish Biol 49:430–440
Kinne O, Kinne EM (1962) Rates of development in embryos of a cyprinodont fish exposed to different temperature–salinity–oxygen combinations. Can J Zool 40(2):231–253
Lockwood BL, Somero GN (2012) Functional determinants of temperature adaptation in enzymes of cold- versus warm-adapted mussels (Genus Mytilus). Mol Biol Evol 29:3061–3070. doi:10.1093/molbev/mss111
Machado BE, Podrabsky JE (2007) Salinity tolerance in diapausing embryos of the annual killifish Austrofundulus limnaeus is supported by exceptionally low water and ion permeability. J Comp Physiol B 177(7):809–820. doi:10.1007/s00360-007-0177-0
Matschak TW, Tyler DD, Stickland NC (1998) Metabolic enzyme activities in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.) embryos respond more to chronic changes in oxygen availability than to environmental temperature. Fish Physiol Biochem 18(2):115–123
Mueller CA, Seymour RS (2011) The regulation index: a new method for assessing the relationship between oxygen consumption and environmental oxygen. Physiol Biochem Zool 84(5):522–532
Mueller C, Joss J, Seymour RS (2011) Effects of environmental oxygen on development and respiration of Australian lungfish (Neoceratodus forsteri) embryos. J Comp Physiol B 181(7):941–952. doi:10.1007/s00360-011-0573-3
Myers GS (1952) Annual fishes. Aquarium J 23:125–141
Papandreou I, Cairns RA, Fontana L, Lim AL, Denko NC (2006) HIF-1 mediates adaptation to hypoxia by actively downregulating mitochondrial oxygen consumption. Cell Metabolism 3(187–197). doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2006.01.012
Parer JT (1998) Effects of fetal asphyxia on brain cell structure and function: limits of tolerance. Comp Biochem Physiol A 119(3):711–716
Paynter KT, DiMichele L, Hand SC, Powers DA (1991) Metabolic implications of Ldh-B genotype during early development in Fundulus heteroclitus. J Exp Zool 257(1):24–33
Pelster B, Burggren WW (1996) Disruption of hemoglobin oxygen transport does not impact oxygen-dependent physiological processes in developing embryos of zebra fish (Danio rerio). Circ Res 79(2):358–362
Podrabsky JE (1999) Husbandry of the annual killifish Austrofundulus limnaeus with special emphasis on the collection and rearing of embryos. Env Biol Fish 54(4):421–431
Podrabsky JE, Hand SC (1999) The bioenergetics of embryonic diapause in an annual killifish, Austrofundulus limnaeus. J Exp Biol 202(19):2567–2580
Podrabsky JE, Hrbek T, Hand SC (1998) Physical and chemical characteristics of ephemeral pond habitats in the Maracaibo basin and Llanos region of Venezuela. Hydrobiologia 362(1–3):67–78
Podrabsky JE, Carpenter JF, Hand SC (2001) Survival of water stress in annual fish embryos: dehydration avoidance and egg envelope amyloid fibers. Am J Physiol 280(1):R123–R131
Podrabsky JE, Lopez JP, Fan TWM, Higashi R, Somero GN (2007) Extreme anoxia tolerance in embryos of the annual killifish Austrofundulus limnaeus: insights from a metabolomics analysis. J Exp Biol 210(13):2253–2266. doi:10.1242/jeb.005116
Podrabsky JE, Garrett IDF, Kohl ZF (2010a) Alternative developmental pathways associated with diapause regulated by temperature and maternal influences in embryos of the annual killifish Austrofundulus limnaeus. J Exp Biol 213(19):3280–3288. doi:10.1242/jeb.045906
Podrabsky JE, Tingaud-Sequeira A, Cerdà J (2010b) Metabolic dormancy and responses to environmental desiccation in fish embryos. In: Dormancy and resistance in harsh environments. Springer, Berlin, pp 203–226
Podrabsky JE, Menze MA, Hand SC (2012a) Rapid Communication: long-term survival of anoxia despite rapid ATP decline in embryos of the annual killifish Austrofundulus limnaeus. J Exp Zool A 317:524–532
Podrabsky JE, Riggs CL, Duerr JM (2012b) Anoxia tolerance during vertebrate development—insights from studies on the annual killifish Austrofundulus limnaeus. In: Padilla P (ed) Anoxia. InTech, pp 3–24
Seymour RS, Roberts JD, Mitchell NJ, Blaylock AJ (2000) Influence of environmental oxygen on development and hatching of aquatic eggs of the Australian frog, Crinia georgiana. Physiol Biochem Zool 73(4):501–507
Shang EHH, Wu RSS (2004) Aquatic hypoxia is a teratogen and affects fish embryonic development. Environ Sci Technol 38(18):4763–4767. doi:10.1021/es0496423
Siefert RE, Spoor WA, Syrett RF (1973) Effects of reduced oxygen concentrations on northern pike (Esox lucius) embryos and larvae. J Fish Res Board Can 30(6):849–852
Siefert RE, Carlson AR, Herman LJ (1974) Effects of reduced oxygen concentrations on the early life stages of mountain whitefish, smallmouth bass, and white bass. Prog Fish Cult 36(4):186–190
Sloper JJ, Johnson P, Powell TPS (1980) Selective degeneration of interneurons in the motor cortex of infant monkeys following controlled hypoxia: a possible cause of epilepsy. Brain Res 198:204–209
Spoor WA (1977) Oxygen requirements of embryos and larvae of the largemouth bass, Micropterus salmoides (Lacepede). J Fish Biol 11(2):77–86
Strecker R, Seiler T-B, Hollert H, Braunbeck T (2011) Oxygen requirements of zebrafish Danio rerio embryos in embryo toxicity tests with environmental samples. Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol 153(3):318–327
Withers PC (1992) Comparative animal physiology. Saunders College Publishing, Philadelphia
Wourms JP (1972a) Developmental biology of annual fishes I. Stages in the normal development of Austrofundulus myersi Dahl. J Exp Zool 182(2):143–168
Wourms JP (1972b) The developmental biology of annual fishes III. Pre-embryonic and embryonic diapause of variable duration in the eggs of annual fishes. J Exp Zool 182(3):389–414
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by NIH Grant R01-HL095454. The Bactrox hypoxic chamber was kindly provided Sheldon Manufacturing.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by H.V. Carey.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Anderson, S.N., Podrabsky, J.E. The effects of hypoxia and temperature on metabolic aspects of embryonic development in the annual killifish Austrofundulus limnaeus . J Comp Physiol B 184, 355–370 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00360-014-0803-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00360-014-0803-6