Abstract
Objectives
Real costs of teleradiology services have not been systematically calculated. Pricing policies are not evidence-based. This study aims to prove the feasibility of performing an original cost analysis for teleradiology services and show break-even points to perform cost-effective practice.
Methods
Based on the teleradiology services provided by the Greifswald University Hospital in northeastern Germany, a detailed process analysis and an activity-based costing model revealed costs per service unit according to eight examination categories. The Monte Carlo method was used to simulate the cost amplitude and identify pricing thresholds.
Results
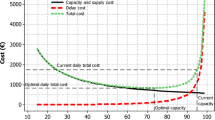
Twenty-two sub-processes and four staff categories were identified. The average working time for one unit was 55 (x-ray) to 72 min (whole-body CT). Personnel costs were dominant (up to 68 %), representing lower limit costs. The Monte Carlo method showed the cost distribution per category according to the deficiency risk. Avoiding deficient pricing by a likelihood of 90 % increased the cost of a cranial CT almost twofold as compared with the lower limit cost.
Conclusions
Original cost analysis is possible when providing teleradiology services with complex statutory requirements in place. Methodology and results provide useful data to help enhance efficiency in hospital management as well as implement realistic reimbursement fees.
Key Points
• Analysis of original costs of teleradiology is possible for a providing hospital
• Results discriminate pricing thresholds and lower limit costs to perform cost-effective practice
• The study methods represent a managing tool to enhance efficiency in providing facilities
• The data are useful to help represent telemedicine services in regular medical fee schedules





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barneveld Binkhuysen FH (1998) Socioeconomic trends in radiology. Eur Radiol 8:323–325
Loose RW (2000) Telematics: relevance for effectiveness of radiology. Eur Radiol 10:S357–S359
Koehler F, Winkler S, Schieber M et al (2012) Telemedicine in heart failure: Pre-specified and exploratory subgroup analyses from the TIM-HF trial, in: Int J Cardiol 161:143–150
Boland GW (2009) The impact of teleradiology in the United States over the last decade: driving consolidation and commoditization of radiologists and radiology services. Clin Radiol 64:457–460
Fitzgerald R (2008) Medical regulation in the telemedicine era. Lancet 372:1795–1796
Margulis AR, Sunshine JH (2000) Radiology at the turn of the millennium. Radiology 214:15–23
Steinbrook R (2007) The age of teleradiology. N Engl J Med 357:5–7
Thrall JH (2007) Teleradiology. Part I. History and clinical applications. Radiology 243:613–617
Jarvis L, Stanberry B (2005) Teleradiology: threat or opportunity? Clin Radiol 60:840–845
Rosenberg C, Langner S, Rosenberg B, Hosten N (2011) Medical and legal aspects of teleradiology in Germany. Fortschr Roentgenstr 183:804–811
Thrall JH (2009) Teleradiology: two-edged sword or friend of radiology practice? J Am Coll Radiol 6:73–75
Boland GW (2009) Teleradiology for auction: the radiologist commoditized and how to prevent it. J Am Coll Radiol 6:137–138
Levin DC, Rao VM (2011) Outsourcing to teleradiology companies: bad for radiology, bad for radiologists. J Am Coll Radiol 8:104–108
Commission of the European Communities (04.11.2008) Communication from the Commission to the European Parliament, the Council, the European Economic and Social Committee and the Committee of the Regions on telemedicine for the benefit of patients, healthcare systems and society. Commission of the European Communities, Brussels. Available via http://eur-lex.europa.eu/LexUriServ/LexUriServ.do?uri=OJ:C:2009:317:0084:01:DE:HTML. Accessed 15 Dec 2012
European Society of Radiology (2009) Position on telemedicine. European Society of Radiology, Vienna. Available via http://www.myesr.org/cms/website.php?id=/en/eu_affairs/ec_communication_on_telemedicine/esr.htm. Accessed 15 Dec 2012
Walz M, Brill C, Bolte R et al (2000) Teleradiology requirements and aims in Germany and Europe: status at the beginning of 2000. Eur Radiol 10:1472–1482
German Federal Ministery of Justice (2003) “Verordnung über den Schutz vor Schäden durch Röntgenstrahlen” in the declaration version of 30 Apr 2003. In: German Federal Ministery of Justice (ed) BGBl. I, Berlin. http://www.bfs.de/de/bfs/recht/rsh/volltext/1A_Atomrecht/1A_14_RoeV_1011.pdf. Accessed 15 Dec 2012
Schneider G (2001) Abrechnung telemedizinischer Leistungen. In: Dierks C, Feussner H, Wienke A (eds) Rechtsfragen der Telemedizin. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 109–118
Plathow C, Walz M, Essig M et al (2005) Teleradiology: economic research analysis of CT investigations in a small hospital. Fortschr Roentgenstr 177:1016–1026
Walz M, Bolte R, Lehmann KJ, Lutgemeier J, Georgi M (1999) Economic analysis of teleradiology applications with KAMEDIN. Stud Health Technol Inform 64:208–216
Federal Statistical Office (2012) Area and Population. Federal Statistical Office, Wiesbaden. Available via http://www.statistik-portal.de/Statistik-Portal/de_jb01_jahrtab1.asp. Accessed 15 Dec 2012
Eriksen SD, Urrutia I, Cunningham GM (2011) Design of an activity based costing system for a public hospital: a case study. Int J Manag Financ Account 3:20
Herrmann R, Flessa S, Fusch C (2007) Kalkulation der Falleinzelkosten im Krankenhaus. Das Krankenhaus 99:1088–1092
Kasch R, Merk S, Drescher W et al (2012) Marginal contribution of UKS versus TKA in varus arthritis of the knee. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 132:1165–1172
Swierk T, Jurgens C, Grossjohann R, Flessa S, Tost F (2011) Health economical aspects of telemedical glaucoma monitoring. Ophthalmologe 108:342–350
Green L (2006) Queuing Analysis in Healthcare. In: Hall RW (ed) Patient Flow: Reducing Delay in Healthcare Delivery. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, p 26
Flessa S (2010) Grundzüge der Krankenhausbetriebslehre. Oldenbourg, München
Cremers H, Sanddorf-Koehle W (2013) Einführung in das Risikomanagement. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Müller-Gronbach T, Novak E, Ritter K (2012) Monte Carlo-Algorithmen. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rosenberg, C., Kroos, K., Rosenberg, B. et al. Teleradiology from the provider’s perspective—cost analysis for a mid-size university hospital. Eur Radiol 23, 2197–2205 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-013-2810-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-013-2810-5