Abstract
Key message
The TPS5 negatively regulates ABA signaling by mediating ROS level and NR activity during seed germination and stomatal closure in Arabidopsis thaliana.
Abstract
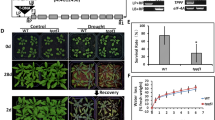
Trehalose metabolism is important in plant growth and development and in abiotic stress response. Eleven TPS genes were identified in Arabidopsis, divided into Class I (TPS1–TPS4) and Class II (TPS5–TPS11). Although Class I has been shown to have TPS activity, the function of most members of Class II remains enigmatic. Here, we characterized the biological function of the trehalose-6-phosphate synthase TPS5 in ABA signaling in Arabidopsis. TPS5 expression was induced by ABA and abiotic stress, and expression in epidermal and guard cells was dramatically increased after ABA treatment. Loss-of-function analysis revealed that tps5 mutants (tps5-1 and tps5-cas9) are more sensitive to ABA during seed germination and ABA-mediated stomatal closure. Furthermore, the H2O2 level increased in the tps5-1 and tps5-cas9 mutants, which was consistent with the changes in the expression of RbohD and RbohF, key genes responsible for H2O2 production. Further, TPS5 knockout reduced the amounts of trehalose and other soluble carbohydrates as well as nitrate reductase (NR) activity. In vitro, trehalose and other soluble carbohydrates promoted NR activity, which was blocked by the tricarboxylic acid cycle inhibitor iodoacetic acid. Thus, this study identified that TPS5 functions as a negative regulator of ABA signaling and is involved in altering the trehalose content and NR activity.








Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ABA:
-
Abscisic acid
- ER:
-
Endoplasmic reticulum
- GFP:
-
Green fluorescent protein
- NR:
-
Nitrate reductase
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- T6P:
-
Trehalose-6-phosphasynthetase
References
Avonce N, Leyman B, Mascorro-Gallardo JO, Van Dijck P, Thevelein JM, Iturriaga G (2004) The Arabidopsis trehalose-6-P synthase AtTPS1 gene is a regulator of glucose, abscisic acid, and stress signaling. Plant Physiol 136:3649–3659
Baena-Gonzalez E, Rolland F, Thevelein JM, Sheen J (2007) A central integrator of transcription networks in plant stress and energy signalling. Nature 448:938–942
Bates GW, Rosenthal DM, Sun J, Chattopadhyay M, Peffer E, Yang J, Ort DR, Jones AM (2012) A comparative study of the Arabidopsis thaliana guard-cell transcriptome and its modulation by sucrose. PLoS ONE 7:e49641
Blázquez MA, Santos E, Flores CL, Martínezzapater JM, Salinas J, Gancedo C (1998) Isolation and molecular characterization of the Arabidopsis TPS1 gene, encoding trehalose-6-phosphate synthase. Plant J 13:685–689
Chary SN, Hicks GR, Choi YG, Carter D, Raikhel NV (2008) Trehalose-6-phosphate synthase/phosphatase regulates cell shape and plant architecture in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 146:97–107
Chen ZH, Wang Y, Wang JW, Babla M, Zhao C, Garcia-Mata C, Sani E, Differ C, Mak M, Hills A, Amtmann A, Blatt MR (2016) Nitrate reductase mutation alters potassium nutrition as well as nitric oxide-mediated control of guard cell ion channels in Arabidopsis. New Phytol 209:1456–1469
Clough SJ, Bent AF (1998) Floral dip: a simplified method for Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 16:735–743
Crowe JH, Carpenter JF, Crowe LM (2003) The role of vitrification in anhydrobiosis. Annu Rev Physiol 60:73–103
Ding S, Zhang B, Qin F (2015) Arabidopsis RZFP34/CHYR1, a ubiquitin E3 ligase, regulates stomatal movement and drought tolerance via SnRK2.6-mediated phosphorylation. Plant Cell 27:3228–3244
Eastmond PJ, Graham IA (2003) Trehalose metabolism: a regulatory role for trehalose-6-phosphate? Curr Opin Plant Biol 6:231–235
Eastmond PJ, Van Dijken AJ, Spielman M, Kerr A, Tissier AF, Dickinson HG, Graham IA (2002) Trehalose-6-phosphate synthase 1, which catalyses the first step in trehalose synthesis, is essential for Arabidopsis embryo maturation. Plant J 29:225–235
Emanuelle S, Hossain MI, Moller IE, Pedersen HL, van de Meene AM, Doblin MS, Koay A, Oakhill JS, Scott JW, Willats WG, Kemp BE, Bacic A, Gooley PR, Stapleton DI (2015) SnRK1 from Arabidopsis thaliana is an atypical AMPK. Plant J 82:183–192
Fernandez O, Vandesteene L, Feil R, Baillieul F, Lunn JE, Clément C (2012) Trehalose metabolism is activated upon chilling in grapevine and might participate in Burkholderia phytofirmans induced chilling tolerance. Planta 236:355–369
Figueroa CM, Lunn JE (2016) A tale of two sugars: trehalose 6-phosphate and sucrose. Plant Physiol 172:7–27
Figueroa CM, Feil R, Ishihara H, Watanabe M, Kolling K, Krause U, Hohne M, Encke B, Plaxton WC, Zeeman SC, Li Z, Schulze WX, Hoefgen R, Stitt M, Lunn JE (2016) Trehalose 6-phosphate coordinates organic and amino acid metabolism with carbon availability. Plant J 85:410–423
Foster AJ, Jenkinson JM, Talbot NJ (2014) Trehalose synthesis and metabolism are required at different stages of plant infection by Magnaporthe grisea. EMBO J 22:225–235
Genome IA (2000) Analysis of the genome sequence of the flowering plant Arabidopsis thaliana. Nature 408:796–815
Goddijn O, Verwoerd TC, Voogd E, Krutwagen R, Graff PD, Poels J, Dun KV, Ponstein AS, Damm B, Pen J (1997) Inhibition of trehalase activity enhances trehalose accumulation in transgenic plants. Plant Physiol 113:181–190
Gomez LD, Baud SA, Li Y, Graham IA (2010a) Delayed embryo development in the Arabidopsis trehalose-6-phosphate synthase 1 mutant is associated with altered cell wall structure, decreased cell division and starch accumulation. Plant J 46:69–84
Gomez LD, Gilday A, Feil R, Lunn JE, Graham IA (2010b) AtTPS1-mediated trehalose 6-phosphate synthesis is essential for embryogenic and vegetative growth and responsiveness to ABA in germinating seeds and stomatal guard cells. Plant J 64:1–13
Harthill JE, Meek SE, Morrice N, Peggie MW, Borch J, Wong BH, Mackintosh C (2006) Phosphorylation and 14-3-3 binding of Arabidopsis trehalose-phosphate synthase 5 in response to 2-deoxyglucose. Plant J 47:211–223
Joachim M, Thomas B, Andres W (1995) Effects of validamycin A, a potent trehalase inhibitor, and phytohormones on trehalose metabolism in roots and root nodules of soybean and cowpea. Planta 197:362–368
Lee J, Lee H, Kim J, Lee S, Kim DH, Kim S, Hwang I (2011) Both the hydrophobicity and a positively charged region flanking the C-terminal region of the transmembrane domain of signal-anchored proteins play critical roles in determining their targeting specificity to the endoplasmic reticulum or endosymbiotic organelles in Arabidopsis cells. Plant Cell 23:1588–1607
Leyman B, Dijck PV, Thevelein JM (2001) An unexpected plethora of trehalose biosynthesis genes in Arabidopsis thaliana. Trends Plant Sci 6:510–513
Li J, Huang Y, Tan H, Yang X, Tian L, Luan S, Chen L, Li D (2015) An endoplasmic reticulum magnesium transporter is essential for pollen development in Arabidopsis. Plant Sci 231:212–220
Lu C, Yu F, Tian L, Huang X, Tan H, Xie Z, Hao X, Li D, Luan S, Chen L (2017) RPS9 M, a mitochondrial ribosomal protein, is essential for central cell maturation and endosperm development in Arabidopsis. Front Plant Sci 8:2171
Lunn JE, Delorge I, Figueroa CM, Van Dijck P, Stitt M (2014) Trehalose metabolism in plants. Plant J 79:544–567
Ramon M, De Smet I, Vandesteene L, Naudts M, Leyman B, Van Dijck P, Rolland F, Beeckman T, Thevelein JM (2009) Extensive expression regulation and lack of heterologous enzymatic activity of the Class II trehalose metabolism proteins from Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant, Cell Environ 32:1015–1032
Rodriguez-Salazar J, Suarez R, Caballero-Mellado J, Iturriaga G (2009) Trehalose accumulation in Azospirillum brasilense improves drought tolerance and biomass in maize plants. FEMS Microbiol Lett 296:52–59
Scheible WR, Morcuende R, Czechowski T, Fritz C, Osuna D, Palacios-Rojas N, Schindelasch D, Thimm O, Udvardi MK, Stitt M (2004) Genome-wide reprogramming of primary and secondary metabolism, protein synthesis, cellular growth processes, and the regulatory infrastructure of Arabidopsis in response to nitrogen. Plant Physiol 136:2483–2499
Suzuki N, Bajad S, Shuman J, Shulaev V, Mittler R (2008) The transcriptional co-activator MBF1c is a key regulator of thermotolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana. J Biol Chem 283:9269–9275
Thordal-Christensen H, Zhang Z, Wei Y, Collinge DB (1997) Subcellular localization of H2O2 in plants. H2O2 accumulation in papillae and hypersensitive response during the barley—powdery mildew interaction. Plant J 11:1187–1194
Usadel B, Blasing OE, Gibon Y, Retzlaff K, Hohne M, Gunther M, Stitt M (2008) Global transcript levels respond to small changes of the carbon status during progressive exhaustion of carbohydrates in Arabidopsis rosettes. Plant Physiol 146:1834–1861
van Dijken AJ, Schluepmann H, Smeekens SC (2004) Arabidopsis trehalose-6-phosphate synthase 1 is essential for normal vegetative growth and transition to flowering. Plant Physiol 135:969–977
Van Houtte H, Vandesteene L, Lopez-Galvis L, Lemmens L, Kissel E, Carpentier S, Feil R, Avonce N, Beeckman T, Lunn JE, Van Dijck P (2013) Overexpression of the trehalase gene AtTRE1 leads to increased drought stress tolerance in Arabidopsis and is involved in abscisic acid-induced stomatal closure. Plant Physiol 161:1158–1171
Vandesteene L, Lopez-Galvis L, Vanneste K, Feil R, Maere S, Lammens W, Rolland F, Lunn JE, Avonce N, Beeckman T, Van Dijck P (2012) Expansive evolution of the trehalose-6-phosphate phosphatase gene family in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 160:884–896
Vishal B, Krishnamurthy P, Ramamoorthy R, Kumar PP (2019) OsTPS8 controls yield-related traits and confers salt stress tolerance in rice by enhancing suberin deposition. New Phytol 221:1369–1386
Wahl V, Ponnu J, Schlereth A, Arrivault S, Langenecker T, Franke A, Feil R, Lunn JE, Stitt M, Schmid M (2013) Regulation of flowering by trehalose-6-phosphate signaling in Arabidopsis thaliana. Science 339:704–707
Wang R, Okamoto M, Xing X, Crawford NM (2003) Microarray analysis of the nitrate response in Arabidopsis roots and shoots reveals over 1,000 rapidly responding genes and new linkages to glucose, trehalose-6-phosphate, iron, and sulfate metabolism. Plant Physiol 132:556–567
Wang P, Du Y, Hou YJ, Zhao Y, Hsu CC, Yuan F, Zhu X, Tao WA, Song CP, Zhu JK (2015a) Nitric oxide negatively regulates abscisic acid signaling in guard cells by S-nitrosylation of OST1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 112:613–618
Wang P, Zhu JK, Lang Z (2015b) Nitric oxide suppresses the inhibitory effect of abscisic acid on seed germination by S-nitrosylation of SnRK2 proteins. Plant Signal Behav 10:e1031939
Zhang X, Zhang L, Dong F, Gao J, Galbraith DW, Song CP (2001) Hydrogen peroxide is involved in abscisic acid-induced stomatal closure in Vicia faba. Plant Physiol 126:1438–1448
Zhang Y, Primavesi LF, Jhurreea D, Andralojc PJ, Mitchell RA, Powers SJ, Schluepmann H, Delatte T, Wingler A, Paul MJ (2009) Inhibition of SNF1-related protein kinase1 activity and regulation of metabolic pathways by trehalose-6-phosphate. Plant Physiol 149:1860–1871
Acknowledgements
We thank Jiankang Zhu for kindly providing CRISPR/cas9 vectors. This work was supported by grants of NSFC (31570316; 31371244), HNNSF (2016JJ2089), Project of Hunan Provincial Education Department (17C0974, 13C638), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2013M542118).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by Prakash P. Kumar.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tian, L., Xie, Z., Lu, C. et al. The trehalose-6-phosphate synthase TPS5 negatively regulates ABA signaling in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell Rep 38, 869–882 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-019-02408-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-019-02408-y