Abstract.
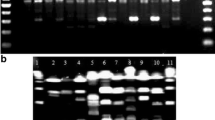
Lactobacillus plantarum and Lactobacillus pentosus grouped into one protein profile cluster at r ≥ 0.70, separate from Lactobacillus casei, Lactobacillus sake, and Lactobacillus curvatus. Similar sugar fermentation reactions were recorded for representative strains of L. plantarum and L. pentosus. Representative strains, including the type of each species, were selected from the different protein profile clusters and their genetic relatedness determined by using numerical analysis of random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD)-PCR. The type strains of L. plantarum (ATCC 14917T) and L. pentosus (NCFB 363T) displayed different RAPD profiles and grouped into two independent clusters, well separated from L. casei, L. curvatus, and L. sake. Numerical analysis of RAPD-PCR proved a reliable and accurate method to distinguish between strains of L. plantarum and L. pentosus.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Van Reenen, C., Dicks, L. Evaluation of Numerical Analysis of Random Amplified Polymorphic DNA (RAPD)-PCR as a Method to Differentiate Lactobacillus plantarum and Lactobacillus pentosus . Curr Microbiol 32, 183–187 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002849900033
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002849900033