Abstract
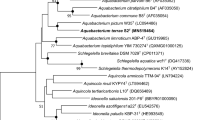
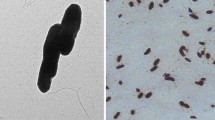
Vanillin is undoubtedly one of the most popular and widely used flavoring agents in the world. Taking into consideration the worldwide demand for natural vanillin and its limited supply, alternative routes for its production including biotransformation are being constantly explored. In this regard, a novel soil bacterium capable of converting isoeugenol to vanillin was isolated by conventional enrichment process from soils of Ocimum field. On the basis of morphological and physiochemical characteristics and 16S rRNA gene sequence analysis, the isolate was identified as Pseudomonas chlororaphis CDAE5 (EMBL # AM158279). Vanillin formation was analyzed by gas chromatography (GC), and its structure was confirmed by GC-mass spectrometry and nuclear magnetic resonance. After 24-h reaction, the vanillin concentration reached 1.2 g L−1 from 10 g L−1 isoeugenol in 20-mL reaction solution at 25°C and 180 rpm. The strain showed potential to be a good candidate for biotechnological production of vanillin from isoeugenol. Further studies for standardization and optimization for higher yield of vanillin production needs to be investigated.




Similar content being viewed by others
Literature Cited
Abraham WR, Arfmann HA, Stumpf S, Washausen P, Kieslich K (1988) Microbial transformations of some terpenoids and natural compounds. In: Schreier P (ed) Bioflavour ‘87. Analysis, biochemistry, biotechnology. Proceedings of an International Conference. Berlin: de Gruyter, pp 399–414
Benedict CO, Victorio V (1999) Constructions of recombinants Pseudomonas putida BO14 and Escherichia coli QEFCA8 for Ferulic acid biotransformation to vanillin. J Biosci Bioeng 88:103–110
Cowan ST, Steel KJ (1974) Manual for the identification of medical bacteria, 2nd ed. London: Cambridge University Press
Furukawa H, Morita H, Yoshida T, et al. (2003) Conversion of isoeugenol into vanillic acid by Pseudomonas putida 158 cells exhibiting high isoeugenol-degrading activity. J Biosci Bioeng 96:401–403
Holt JG, Krieg NR, Sneath PHA, et al. (1994) In: Bergey’s manual of determinative bacteriology, 9th ed. Baltimore: Williams and Wilkins
Karmakar B, Vohra RM, Nandanwar H, et al. (2000) Rapid degradation of Ferulic acid via 4-vinylguiacol and vanillin by a newly isolated strain of Bacillus coagulans. J Biotechnol 80:195–202
Kimura M (1980) A simple method for estimating evolutionary rates base substitution through comparative studies nucleotide sequences. J Mol Evol 16:111–120
Li YH, Sun ZH, Zhao LQ, et al. (2005) Biotransformation of isoeugenol to vanillin by crude enzyme extracted from soybean. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 125:1–10
Li YH, Sun ZH, Zheng P (2004) Determination of vanillin, eugenol and isoeugenol by RP-HPLC. Chromatographia 60:709–713
Lomascolo A, Stentelaire C, Asther M, et al. (1999) Basidiomycetes as new biotechnological tools to generate natural aromatic flavours for the food industry. Trends Biotechnol 17:282–289
Markus PH, Peters ALJ, Roos R (1992) Process for the preparation of phenylaldehydes. European Patent EP 542348
Muheim A, Muller B. Munch T, et al. (2001) Microbiological process for producing vanillin. US Patent 6235507
Narbad A, Gasson MJ (1998) Metabolism of ferulic acid via vanillin using a novel CoA-dependent pathway in a newly isolated strain of Pseudomonas fluorescens. Microbiol 144:1397–1405
Narbad A, Rhodes MJC, Gasson MJ, et al. (2001) Production of vanillin. US Patent 2001014467
Overhage J, Priefert H, Rabenhorst J, et al. (1999) Biotransformation of eugenol to vanillin by a mutant of Pseudomonas sp. Strain HR199 constructed by disruption of the vanillin dehydrogenase (vdh) gene. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 52:820–828
Priefert H, Rabenhorst J, Steinbüchel A (2001) Biotechnological production of vanillin. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 56:296–314
Rabenhorst J, Hopp R (1991) Process for the preparation of vanillin. US Patent 5017388
Rabenhorst J, Hopp R (2000) Process for the preparation of vanillin and microorganisms suitable therefor. US Patent 6133003
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor joining method: a new method for reconstructing the phylogenetic tree. Mol Biol Evol 4:406–425
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, 2nd ed. Cold Spring Harbor, New York: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory
Shimoni E, Ravid U, Shoham Y (2000) Isolation of a Bacillus sp. capable of transforming isoeugenol to vanillin. J Biotechnol 78:1–9
Stentelaire C, Laurence L-M, Oddou J, et al. (2000) Design of a fungal bioprocess for vanillin production from vanillin acid at scalable level by Pycnoporus cinnabarinus. J Biosci Bioeng 89:223–230
Thompson JD, Higgins DG, Gibson DJ (1994) CLUSTAL W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence weighing, position specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acid Res 22:4673–4680
Van den Heuvel RHH, Fraaije MW, Laane C, et al. (2001) Enzymatic synthesis of vanillin. J Agric Food Chem 49:2954–2958
Yukio W, Tetsushi A, Naomi H, et al. (1993) Production of vanillin and its related compound by fermentation. Japanese Patent 5227980
Zhao LQ, Sun ZH, Zheng P, et al. (2005) Biotransformation of isoeugenol to vanillin by a novel strain of Bacillus fusiformis. Biotechnol Lett 27:1505–1509
Zhao LQ, Sun ZH, Zheng P, et al. (2006) Biotransformation of isoeugenol to vanillin by Bacillus fusiformis CGMCC1347 with addition of resin H D-8. Process Biochem 41:1673–1676
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by a project (SMM-0002) sponsored by Council of Scientific & Industrial Research, New Delhi, India. The authors gratefully acknowledge the Director, IHBT, Palampur, for providing the necessary facilities during the course of the project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
†IHBT Communication No. 0676
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kasana, R.C., Sharma, U.K., Sharma, N. et al. Isolation and Identification of a Novel Strain of Pseudomonas chlororaphis Capable of Transforming Isoeugenol to Vanillin† . Curr Microbiol 54, 457–461 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-006-0627-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-006-0627-z