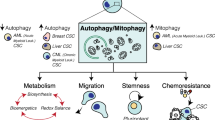
Abstract
Macroautophagy is widely accepted as a cytoprotective mechanism against various environmental stresses. While inhibition of autophagy is generally considered to increase the susceptibility of cancer cells to therapeutic agents, whether it also plays a similar role in tumor stem cells is unclear and still controversial. With increased attention and efforts focused on the cytoprotective feature of autophagy in cancer, it is also essential to understand its role in the biology of cancer stem cells, including self-renewal, differentiation, and tumorigenicity. Although there are very few studies that evaluate autophagy in cancer stem/progenitor cells, understanding the mechanisms governing autophagic responses in various cancer stem cells could provide support for the future development of clinical therapeutics. The present review summarizes current studies that assess the role of autophagy in various types of cancer stem cells and those that evaluate the application of inhibitors of key components within the autophagy pathway in cancer stem/progenitor cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- 3-MA:
-
3-Methyladenine
- ALL:
-
Acute lymphoblastic leukemia
- BFA:
-
Bafilomycin A1
- CSC:
-
Cancer stem cell
- CML:
-
Chronic myeloid leukemia
- CXCR4:
-
C-X-C chemokine receptor 4
- DNA-PKcs:
-
DNA-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit
- DNMT1:
-
DNA methyltransferase 1
- FIP200:
-
Focal adhesion kinase family interacting protein of 200 kD
- GBM:
-
Glioblastoma multiform
- HSC:
-
Hematopoietic stem cell
- IM:
-
Imatinib mesylate
- Jak2:
-
Janus activated kinase 2
- mTOR:
-
Mammalian target of rapamycin
- PDAC:
-
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma
- Ph+ :
-
Philadelphia chromosome-positive
- TKI:
-
Tyrosine-kinase inhibitor
References
Pan H, Cai N, Li M, Liu GH, Izpisua Belmonte JC (2013) Autophagic control of cell ‘stemness’. EMBO Mol Med 5(3):327–331. doi:10.1002/emmm.201201999
Galavotti S, Bartesaghi S, Faccenda D, Shaked-Rabi M, Sanzone S, McEvoy A, Dinsdale D, Condorelli F, Brandner S, Campanella M, Grose R, Jones C, Salomoni P (2013) The autophagy-associated factors DRAM1 and p62 regulate cell migration and invasion in glioblastoma stem cells. Oncogene 32(6):699–712. doi:10.1038/onc.2012.111
Huang X, Bai HM, Chen L, Li B, Lu YC (2010) Reduced expression of LC3B-II and Beclin 1 in glioblastoma multiforme indicates a down-regulated autophagic capacity that relates to the progression of astrocytic tumors. J Clin Neurosci 17(12):1515–1519. doi:10.1016/j.jocn.2010.03.051
Zhao Y, Huang Q, Yang J, Lou M, Wang A, Dong J, Qin Z, Zhang T (2010) Autophagy impairment inhibits differentiation of glioma stem/progenitor cells. Brain Res 1313:250–258. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2009.12.004
Filippi-Chiela EC, Villodre ES, Zamin LL, Lenz G (2011) Autophagy interplay with apoptosis and cell cycle regulation in the growth inhibiting effect of resveratrol in glioma cells. PLoS ONE 6(6):e20849. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0020849
Liu WM, Huang P, Kar N, Burgett M, Muller-Greven G, Nowacki AS, Distelhorst CW, Lathia JD, Rich JN, Kappes JC, Gladson CL (2013) Lyn facilitates glioblastoma cell survival under conditions of nutrient deprivation by promoting autophagy. PLoS ONE 8(8):e70804. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0070804
Lomonaco SL, Finniss S, Xiang C, Decarvalho A, Umansky F, Kalkanis SN, Mikkelsen T, Brodie C (2009) The induction of autophagy by gamma-radiation contributes to the radioresistance of glioma stem cells. Int J Cancer 125(3):717–722. doi:10.1002/ijc.24402
Zhuang W, Li B, Long L, Chen L, Huang Q, Liang Z (2011) Induction of autophagy promotes differentiation of glioma-initiating cells and their radiosensitivity. Int J Cancer 129(11):2720–2731. doi:10.1002/ijc.25975
Zhuang WZ, Long LM, Ji WJ, Liang ZQ (2011) Rapamycin induces differentiation of glioma stem/progenitor cells by activating autophagy. Chin J Cancer 30(10):712–720. doi:10.5732/cjc.011.10234
Zhuang W, Li B, Long L, Chen L, Huang Q, Liang ZQ (2011) Knockdown of the DNA-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit radiosensitizes glioma-initiating cells by inducing autophagy. Brain Res 1371:7–15. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2010.11.044
Zeng M, Zhou JN (2008) Roles of autophagy and mTOR signaling in neuronal differentiation of mouse neuroblastoma cells. Cell Signal 20(4):659–665. doi:10.1016/j.cellsig.2007.11.015
Lomonaco SL, Finniss S, Xiang C, Lee HK, Jiang W, Lemke N, Rempel SA, Mikkelsen T, Brodie C (2011) Cilengitide induces autophagy-mediated cell death in glioma cells. Neuro-oncology 13(8):857–865. doi:10.1093/neuonc/nor073
Jiang H, Gomez-Manzano C, Aoki H, Alonso MM, Kondo S, McCormick F, Xu J, Kondo Y, Bekele BN, Colman H, Lang FF, Fueyo J (2007) Examination of the therapeutic potential of Delta-24-RGD in brain tumor stem cells: role of autophagic cell death. J Natl Cancer Inst 99(18):1410–1414. doi:10.1093/jnci/djm102
Ueda Y, Wei FY, Hide T, Michiue H, Takayama K, Kaitsuka T, Nakamura H, Makino K, Kuratsu J, Futaki S, Tomizawa K (2012) Induction of autophagic cell death of glioma-initiating cells by cell-penetrating D-isomer peptides consisting of Pas and the p53 C-terminus. Biomaterials 33(35):9061–9069. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2012.09.003
Cufi S, Vazquez-Martin A, Oliveras-Ferraros C, Martin-Castillo B, Vellon L, Menendez JA (2011) Autophagy positively regulates the CD44(+) CD24(−/low) breast cancer stem-like phenotype. Cell cycle 10(22):3871–3885. doi:10.4161/cc.10.22.17976
Wolf J, Dewi DL, Fredebohm J, Muller-Decker K, Flechtenmacher C, Hoheisel JD, Boettcher M (2013) A mammosphere formation RNAi screen reveals that ATG4A promotes a breast cancer stem-like phenotype. Breast Cancer Res 15(6):R109. doi:10.1186/bcr3576
Yue Z, Jin S, Yang C, Levine AJ, Heintz N (2003) Beclin 1, an autophagy gene essential for early embryonic development, is a haploinsufficient tumor suppressor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100(25):15077–15082. doi:10.1073/pnas.2436255100
Qu X, Yu J, Bhagat G, Furuya N, Hibshoosh H, Troxel A, Rosen J, Eskelinen EL, Mizushima N, Ohsumi Y, Cattoretti G, Levine B (2003) Promotion of tumorigenesis by heterozygous disruption of the beclin 1 autophagy gene. J Clin Investig 112(12):1809–1820. doi:10.1172/jci200320039
Saito H, Inazawa J, Saito S, Kasumi F, Koi S, Sagae S, Kudo R, Saito J, Noda K, Nakamura Y (1993) Detailed deletion mapping of chromosome 17q in ovarian and breast cancers: 2-cM region on 17q21.3 often and commonly deleted in tumors. Cancer Res 53(14):3382–3385
Futreal PA, Soderkvist P, Marks JR, Iglehart JD, Cochran C, Barrett JC, Wiseman RW (1992) Detection of frequent allelic loss on proximal chromosome 17q in sporadic breast carcinoma using microsatellite length polymorphisms. Cancer Res 52(9):2624–2627
Li Z, Chen B, Wu Y, Jin F, Xia Y, Liu X (2010) Genetic and epigenetic silencing of the beclin 1 gene in sporadic breast tumors. BMC Cancer 10:98. doi:10.1186/1471-2407-10-98
Gong C, Bauvy C, Tonelli G, Yue W, Delomenie C, Nicolas V, Zhu Y, Domergue V, Marin-Esteban V, Tharinger H, Delbos L, Gary-Gouy H, Morel AP, Ghavami S, Song E, Codogno P, Mehrpour M (2013) Beclin 1 and autophagy are required for the tumorigenicity of breast cancer stem-like/progenitor cells. Oncogene 32(18):2261–2272. doi:10.1038/onc.2012.252 2272e 2261–2211
Mai TT, Moon J, Song Y, Viet PQ, Phuc PV, Lee JM, Yi TH, Cho M, Cho SK (2012) Ginsenoside F2 induces apoptosis accompanied by protective autophagy in breast cancer stem cells. Cancer Lett 321(2):144–153. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2012.01.045
Chaterjee M, van Golen KL (2011) Breast cancer stem cells survive periods of farnesyl-transferase inhibitor-induced dormancy by undergoing autophagy. Bone Marrow Res 2011:362938. doi:10.1155/2011/362938
Espina V, Mariani BD, Gallagher RI, Tran K, Banks S, Wiedemann J, Huryk H, Mueller C, Adamo L, Deng J, Petricoin EF, Pastore L, Zaman S, Menezes G, Mize J, Johal J, Edmiston K, Liotta LA (2010) Malignant precursor cells pre-exist in human breast DCIS and require autophagy for survival. PLoS ONE 5(4):e10240. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0010240
Akalay I, Janji B, Hasmim M, Noman MZ, Andre F, De Cremoux P, Bertheau P, Badoual C, Vielh P, Larsen AK, Sabbah M, Tan TZ, Keira JH, Hung NT, Thiery JP, Mami-Chouaib F, Chouaib S (2013) Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and autophagy induction in breast carcinoma promote escape from T-cell-mediated lysis. Cancer Res 73(8):2418–2427. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.can-12-2432
Sanchez CG, Penfornis P, Oskowitz AZ, Boonjindasup AG, Cai DZ, Dhule SS, Rowan BG, Kelekar A, Krause DS, Pochampally RR (2011) Activation of autophagy in mesenchymal stem cells provides tumor stromal support. Carcinogenesis 32(7):964–972. doi:10.1093/carcin/bgr029
Gupta PB, Onder TT, Jiang G, Tao K, Kuperwasser C, Weinberg RA, Lander ES (2009) Identification of selective inhibitors of cancer stem cells by high-throughput screening. Cell 138(4):645–659. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2009.06.034
Yue W, Hamai A, Tonelli G, Bauvy C, Nicolas V, Tharinger H, Codogno P, Mehrpour M (2013) Inhibition of the autophagic flux by salinomycin in breast cancer stem-like/progenitor cells interferes with their maintenance. Autophagy 9(5):714–729. doi:10.4161/auto.23997
Liu F, Guan JL (2011) FIP200, an essential component of mammalian autophagy is indispensible for fetal hematopoiesis. Autophagy 7(2):229–230
Liu F, Lee JY, Wei H, Tanabe O, Engel JD, Morrison SJ, Guan JL (2010) FIP200 is required for the cell-autonomous maintenance of fetal hematopoietic stem cells. Blood 116(23):4806–4814. doi:10.1182/blood-2010-06-288589
Mortensen M, Soilleux EJ, Djordjevic G, Tripp R, Lutteropp M, Sadighi-Akha E, Stranks AJ, Glanville J, Knight S, Jacobsen SE, Kranc KR, Simon AK (2011) The autophagy protein Atg7 is essential for hematopoietic stem cell maintenance. J Exp Med 208(3):455–467. doi:10.1084/jem.20101145
Gurumurthy S, Xie SZ, Alagesan B, Kim J, Yusuf RZ, Saez B, Tzatsos A, Ozsolak F, Milos P, Ferrari F, Park PJ, Shirihai OS, Scadden DT, Bardeesy N (2010) The Lkb1 metabolic sensor maintains haematopoietic stem cell survival. Nature 468(7324):659–663. doi:10.1038/nature09572
Rothe K, Lin H, Lin KB, Leung A, Wang HM, Malekesmaeili M, Brinkman RR, Forrest DL, Gorski SM, Jiang X (2014) Identification of the core autophagy protein ATG4B as a potential biomarker and therapeutic target in CML stem/progenitor cells. Blood. doi:10.1182/blood-2013-07-516807
Bellodi C, Lidonnici MR, Hamilton A, Helgason GV, Soliera AR, Ronchetti M, Galavotti S, Young KW, Selmi T, Yacobi R, Van Etten RA, Donato N, Hunter A, Dinsdale D, Tirro E, Vigneri P, Nicotera P, Dyer MJ, Holyoake T, Salomoni P, Calabretta B (2009) Targeting autophagy potentiates tyrosine kinase inhibitor-induced cell death in Philadelphia chromosome-positive cells, including primary CML stem cells. J Clin Investig 119(5):1109–1123. doi:10.1172/jci35660
Yang X, He G, Gong Y, Zheng B, Shi F, Shi R, Yang X (2014) Mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitor rapamycin enhances anti-leukemia effect of imatinib on Ph+ acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells. Eur J Haematol 92(2):111–120. doi:10.1111/ejh.12202
Wiesner J, Ortmann R, Jomaa H, Schlitzer M (2003) New antimalarial drugs. Angewandte Chemie (International ed in English) 42(43):5274–5293. doi:10.1002/anie.200200569
Firat E, Weyerbrock A, Gaedicke S, Grosu AL, Niedermann G (2012) Chloroquine or chloroquine-PI3K/Akt pathway inhibitor combinations strongly promote gamma-irradiation-induced cell death in primary stem-like glioma cells. PLoS ONE 7(10):e47357. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0047357
Song YJ, Zhang SS, Guo XL, Sun K, Han ZP, Li R, Zhao QD, Deng WJ, Xie XQ, Zhang JW, Wu MC, Wei LX (2013) Autophagy contributes to the survival of CD133+ liver cancer stem cells in the hypoxic and nutrient-deprived tumor microenvironment. Cancer Lett 339(1):70–81. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2013.07.021
Choi DS, Blanco E, Kim YS, Rodriguez AA, Zhao H, Huang TH, Chen CL, Jin G, Landis MD, Burey LA, Qian W, Granados SM, Dave B, Wong HH, Ferrari M, Wong ST, Chang JC (2014) Chloroquine eliminates cancer stem cells through deregulation of Jak2 and DNMT1. Stem cells. doi:10.1002/stem.1746
Maycotte P, Aryal S, Cummings CT, Thorburn J, Morgan MJ, Thorburn A (2012) Chloroquine sensitizes breast cancer cells to chemotherapy independent of autophagy. Autophagy 8(2):200–212. doi:10.4161/auto.8.2.18554
Balic A, Draeby Sorensen M, Trabulo SM, Sainz B Jr, Cioffi M, Vieira CR, Miranda-Lorenzo I, Hidalgo M, Kleeff J, Erkan M, Heeschen C (2014) Chloroquine targets pancreatic cancer stem cells via inhibition of CXCR4 and hedgehog signaling. Mol Cancer Ther. doi:10.1158/1535-7163.mct-13-0948
Gan B, Sahin E, Jiang S, Sanchez-Aguilera A, Scott KL, Chin L, Williams DA, Kwiatkowski DJ, DePinho RA (2008) mTORC1-dependent and -independent regulation of stem cell renewal, differentiation, and mobilization. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105(49):19384–19389. doi:10.1073/pnas.0810584105
Chen C, Liu Y, Liu R, Ikenoue T, Guan KL, Liu Y, Zheng P (2008) TSC-mTOR maintains quiescence and function of hematopoietic stem cells by repressing mitochondrial biogenesis and reactive oxygen species. J Exp Med 205(10):2397–2408. doi:10.1084/jem.20081297
Lee JY, Nakada D, Yilmaz OH, Tothova Z, Joseph NM, Lim MS, Gilliland DG, Morrison SJ (2010) mTOR activation induces tumor suppressors that inhibit leukemogenesis and deplete hematopoietic stem cells after Pten deletion. Cell Stem Cell 7(5):593–605. doi:10.1016/j.stem.2010.09.015
Francipane MG, Lagasse E (2013) Selective targeting of human colon cancer stem-like cells by the mTOR inhibitor torin-1. Oncotarget 4(11):1948–1962
Zhang H, Gao C, Fang L, Zhao HC, Yao SK (2013) Metformin and reduced risk of hepatocellular carcinoma in diabetic patients: a meta-analysis. Scand J Gastroenterol 48(1):78–87. doi:10.3109/00365521.2012.719926
Soranna D, Scotti L, Zambon A, Bosetti C, Grassi G, Catapano A, La Vecchia C, Mancia G, Corrao G (2012) Cancer risk associated with use of metformin and sulfonylurea in type 2 diabetes: a meta-analysis. Oncologist 17(6):813–822. doi:10.1634/theoncologist.2011-0462
Wang Z, Lai ST, Xie L, Zhao JD, Ma NY, Zhu J, Ren ZG, Jiang GL (2014) Metformin is associated with reduced risk of pancreatic cancer in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. doi:10.1016/j.diabres.2014.04.007
Harhaji-Trajkovic L, Vilimanovich U, Kravic-Stevovic T, Bumbasirevic V, Trajkovic V (2009) AMPK-mediated autophagy inhibits apoptosis in cisplatin-treated tumour cells. J Cell Mol Med 13(9B):3644–3654. doi:10.1111/j.1582-4934.2009.00663.x
Jiang T, Yu JT, Zhu XC, Wang HF, Tan MS, Cao L, Zhang QQ, Gao L, Shi JQ, Zhang YD, Tan L (2014) Acute metformin preconditioning confers neuroprotection against focal cerebral ischaemia by pre-activation of AMPK-dependent autophagy. Br J Pharmacol 171(13):3146–3157. doi:10.1111/bph.12655
Mohammed A, Janakiram NB, Brewer M, Ritchie RL, Marya A, Lightfoot S, Steele VE, Rao CV (2013) Antidiabetic drug metformin prevents progression of pancreatic cancer by targeting in part cancer stem cells and mtor signaling. Transl oncol 6(6):649–659
Sunayama J, Matsuda K, Sato A, Tachibana K, Suzuki K, Narita Y, Shibui S, Sakurada K, Kayama T, Tomiyama A, Kitanaka C (2010) Crosstalk between the PI3K/mTOR and MEK/ERK pathways involved in the maintenance of self-renewal and tumorigenicity of glioblastoma stem-like cells. Stem cells 28(11):1930–1939. doi:10.1002/stem.521
Wang WJ, Long LM, Yang N, Zhang QQ, Ji WJ, Zhao JH, Qin ZH, Wang Z, Chen G, Liang ZQ (2013) NVP-BEZ235, a novel dual PI3K/mTOR inhibitor, enhances the radiosensitivity of human glioma stem cells in vitro. Acta Pharmacol Sin 34(5):681–690. doi:10.1038/aps.2013.22
Oliveras-Ferraros C, Vazquez-Martin A, Cuyas E, Corominas-Faja B, Rodriguez-Gallego E, Fernandez-Arroyo S, Martin-Castillo B, Joven J, Menendez JA (2014) Acquired resistance to metformin in breast cancer cells triggers transcriptome reprogramming toward a degradome-related metastatic stem-like profile. Cell Cycle 13(7):1132–1144. doi:10.4161/cc.27982
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Grant NSC99-2314-B-010-041-MY3 and NSC100-2314-B-075-065-MY3 from the National Science Council, grant V100C-117, V101C-101, and V102C-138 from Taipei Veterans General Hospital, and Grant CMU101-N2-02 from China Medical University.
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Yi-Hui Lin and Yu-Chun Huang have contributed equally to this manuscript.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, YH., Huang, YC., Chen, LH. et al. Autophagy in cancer stem/progenitor cells. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 75, 879–886 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-014-2634-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-014-2634-2