Abstract
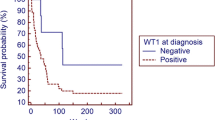
Several studies have evaluated the prognostic value of the individual expression of certain genes in patients with myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS). However, none of them includes their simultaneous analysis by quantitative polymerase chain reaction (PCR). We evaluated relative expression levels of 14 molecular markers in 193 peripheral blood samples from untreated MDS patients using real-time PCR. Detectable WT1 expression levels, low TET2, and low IER3 gene expression were the only markers showing in univariate analysis a poor prognostic value for all treatment-free (TFS), progression-free (PFS), and overall survival (OS). In multivariate analysis, molecular parameters associated with a shorter TFS were: WT1 detection (p = 0.014), low TET2 (p = 0.002), and low IER3 expression (p = 0.025). WT1 detection (p = 0.006) and low TET2 (p = 0.006) expression were associated with a shorter PFS when multivariate analysis was carried out by including only molecular markers. Molecular values with an independent value in OS were: WT1 detection (p = 0.003), high EVI1 expression (p = 0.001), and undetectatable p15-CDKN2B (p = 0.037). WT1 expressers were associated with adverse clinical–biological features, high IPSS and WPSS scoring, and unfavorable molecular expression profile. In summary, detectable WT1 expression levels, and low TET2 and low IER3 expression in peripheral blood showed a strong association with adverse prognosis in MDS patients at diagnosis. However, WT1 was the only molecular marker displaying an independent prognostic value in both OS and TFS.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tefferi A, Vardiman JW (2009) Myelodysplastic syndromes. N Engl J Med 361:1872–1885
Cazzola M, Malcovati L (2005) Myelodysplastic syndromes—coping with ineffective hematopoiesis. N Engl J Med 352:536–538
Bennett JM, Catovsky D, Daniel MT, Flandrin G, Galton DA, Gralnick HR, Sultan C (1985) Proposed revised criteria for the classification of acute myeloid leukemia. A report of the French-American-British Cooperative Group. Ann Intern Med 103:620–625
Vardiman JW, Harris NL, Brunning RD (2002) The World Health Organization (WHO) classification of the myeloid neoplasms. Blood 100:2292–2302
Vardiman JW, Thiele J, Arber DA, Brunning RD, Borowitz MJ, Porwit A, Harris NL, Le Beau MM, Hellstrom-Lindberg E, Tefferi A, Bloomfield CD (2009) The 2008 revision of the World Health Organization (WHO) classification of myeloid neoplasms and acute leukemia: rationale and important changes. Blood 114:937–951
Cazzola M, Malcovati L (2010) Prognostic classification and risk assessment in myelodysplastic syndromes. Hematol Oncol Clin N Am 24:459–468
Nimer SD (2008) Myelodysplastic syndromes. Blood 111:4841–4851
Greenberg P, Cox C, LeBeau MM, Fenaux P, Morel P, Sanz G, Sanz M, Vallespi T, Hamblin T, Oscier D, Ohyashiki K, Toyama K, Aul C, Mufti G, Bennett J (1997) International scoring system for evaluating prognosis in myelodysplastic syndromes. Blood 89:2079–2088
Malcovati L, Germing U, Kuendgen A, la Porta MG, Pascutto C, Invernizzi R, Giagounidis A, Hildebrandt B, Bernasconi P, Knipp S, Strupp C, Lazzarino M, Aul C, Cazzola M (2007) Time-dependent prognostic scoring system for predicting survival and leukemic evolution in myelodysplastic syndromes. J Clin Oncol 25:3503–3510
Bowen DT, Fenaux P, Hellstrom-Lindberg E, de Witte T (2008) Time-dependent prognostic scoring system for myelodysplastic syndromes has significant limitations that may influence its reproducibility and practical application. J Clin Oncol 26:1180–1182
Nowell PC (1992) Chromosome abnormalities in myelodysplastic syndromes. Semin Oncol 19:25–33
Bejar R, Stevenson K, Bdel-Wahab O, Galili N, Nilsson B, Garcia-Manero G, Kantarjian H, Raza A, Levine RL, Neuberg D, Ebert BL (2011) Clinical effect of point mutations in myelodysplastic syndromes. N Engl J Med 364:2496–2506
Delhommeau F, Dupont S, Della VV, James C, Trannoy S, Masse A, Kosmider O, Le Couedic JP, Robert F, Alberdi A, Lecluse Y, Plo I, Dreyfus FJ, Marzac C, Casadevall N, Lacombe C, Romana SP, Dessen P, Soulier J, Viguie F, Fontenay M, Vainchenker W, Bernard OA (2009) Mutation in TET2 in myeloid cancers. N Engl J Med 360:2289–2301
Kosmider O, Gelsi-Boyer V, Slama L, Dreyfus F, Beyne-Rauzy O, Quesnel B, Hunault-Berger M, Slama B, Vey N, Lacombe C, Solary E, Birnbaum D, Bernard OA, Fontenay M (2010) Mutations of IDH1 and IDH2 genes in early and accelerated phases of myelodysplastic syndromes and MDS/myeloproliferative neoplasms. Leukemia 24:1094–1096
Thol F, Weissinger EM, Krauter J, Wagner K, Damm F, Wichmann M, Gohring G, Schumann C, Bug G, Ottmann O, Hofmann WK, Schlegelberger B, Ganser A, Heuser M (2010) IDH1 mutations in patients with myelodysplastic syndromes are associated with an unfavorable prognosis. Haematologica 95:1668–1674
Rocquain J, Carbuccia N, Trouplin V, Raynaud S, Murati A, Nezri M, Tadrist Z, Olschwang S, Vey N, Birbaum D, Gelsi-Boyer V, Mozziconacci MJ (2010) Combined mutations of ASXL1, CBL, FLT3, IDH1, IDH2, JAK2, KRAS, NPM1, NRAS, RUNX1, TET2 and WT1 genes in myelodysplastic syndromes and acute myeloid leukemias. BMC Cancer 10:401
Langemeijer SM, Kuiper RP, Berends M, Knops R, Aslanyan MG, Massop M, Stevens-Linders E, van Hoogen P, van Kessel AG, Raymakers RA, Kamping EJ, Verhoef GE, Verburgh E, Hagemeijer A, Vandenberghe P, de Witte T, van der Reijden BA, Jansen JH (2009) Acquired mutations in TET2 are common in myelodysplastic syndromes. Nat Genet 41:838–842
Abdel-Wahab O, Mullally A, Hedvat C, Garcia-Manero G, Patel J, Wadleigh M, Malinge S, Yao J, Kilpivaara O, Bhat R, Huberman K, Thomas S, Dolgalev I, Heguy A, Paietta E, Le Beau MM, Beran M, Tallman MS, Ebert BL, Kantarjian HM, Stone RM, Gilliland DG, Crispino JD, Levine RL (2009) Genetic characterization of TET1, TET2, and TET3 alterations in myeloid malignancies. Blood 114:144–147
Kosmider O, Gelsi-Boyer V, Cheok M, Grabar S, La-Valle V, Picard F, Viguie F, Quesnel B, Beyne-Rauzy O, Solary E, Vey N, Hunault-Berger M, Fenaux P, Mansat-De Mas V, Delabesse E, Guardiola P, Lacombe C, Vainchenker W, Preudhomme C, Dreyfus F, Bernard OA, Birnbaum D, Fontenay M (2009) TET2 mutation is an independent favorable prognostic factor in myelodysplastic syndromes (MDSs). Blood 114:3285–3291
Hofmann WK, de Vos S, Komor M, Hoelzer D, Wachsman W, Koeffler HP (2002) Characterization of gene expression of CD34+ cells from normal and myelodysplastic bone marrow. Blood 100:3553–3560
Mills KI, Kohlmann A, Williams PM, Wieczorek L, Liu WM, Li R, Wei W, Bowen DT, Loeffler H, Hernandez JM, Hofmann WK, Haferlach T (2009) Microarray-based classifiers and prognosis models identify subgroups with distinct clinical outcomes and high risk of AML transformation of myelodysplastic syndrome. Blood 114:1063–1072
Sridhar K, Ross DT, Tibshirani R, Butte AJ, Greenberg PL (2009) Relationship of differential gene expression profiles in CD34+ myelodysplastic syndrome marrow cells to disease subtype and progression. Blood 114:4847–4858
Wang YY, Cen JN, He J, Shen HJ, Liu DD, Yao L, Qi XF, Chen ZX (2009) Accelerated cellular senescence in myelodysplastic syndrome. Exp Hematol 37:1310–1317
Pellagatti A, Cazzola M, Giagounidis AA, Malcovati L, Porta MG, Killick S, Campbell LJ, Wang L, Langford CF, Fidler C, Oscier D, Aul C, Wainscoat JS, Boultwood J (2006) Gene expression profiles of CD34+ cells in myelodysplastic syndromes: involvement of interferon-stimulated genes and correlation to FAB subtype and karyotype. Blood 108:337–345
Pellagatti A, Marafioti T, Paterson JC, Malcovati L, la Porta MG, Jadersten M, Pushkaran B, George TI, Arber DA, Killick S, Giagounidis A, Hellstrom-Lindberg E, Cazzola M, Wainscoat JS, Boultwood J (2009) Marked downregulation of the granulopoiesis regulator LEF1 is associated with disease progression in the myelodysplastic syndromes. Br J Haematol 146:86–90
Santamaria CM, Chillon MC, Garcia-Sanz R, Perez C, Caballero MD, Ramos F, de Coca AG, Alonso JM, Giraldo P, Bernal T, Queizan JA, Rodriguez JN, Fernandez-Abellan P, Barez A, Penarrubia MJ, Balanzategui A, Vidriales MB, Sarasquete ME, Alcoceba M, Az-Mediavilla J, San Miguel JF, Gonzalez M (2009) Molecular stratification model for prognosis in cytogenetically normal acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 114:148–152
Briatore F, Barrera G, Pizzimenti S, Toaldo C, Casa CD, Laurora S, Pettazzoni P, Dianzani MU, Ferrero D (2009) Increase of telomerase activity and hTERT expression in myelodysplastic syndromes. Cancer Biol Ther 8:883–889
Cilloni D, Gottardi E, Messa F, Fava M, Scaravaglio P, Bertini M, Girotto M, Marinone C, Ferrero D, Gallamini A, Levis A, Saglio G (2003) Significant correlation between the degree of WT1 expression and the International Prognostic Scoring System Score in patients with myelodysplastic syndromes. J Clin Oncol 21:1988–1995
Prall WC, Czibere A, Grall F, Spentzos D, Steidl U, Giagounidis AA, Kuendgen A, Otu H, Rong A, Libermann TA, Germing U, Gattermann N, Haas R, Aivado M (2009) Differential gene expression of bone marrow-derived CD34+ cells is associated with survival of patients suffering from myelodysplastic syndrome. Int J Hematol 89:173–187
Steensma DP, Neiger JD, Porcher JC, Keats JJ, Bergsagel PL, Dennis TR, Knudson RA, Jenkins RB, Santana-Davila R, Kumar R, Ketterling RP (2009) Rearrangements and amplification of IER3 (IEX-1) represent a novel and recurrent molecular abnormality in myelodysplastic syndromes. Cancer Res 69:7518–7523
Metzeler KH, Maharry K, Radmacher MD, Mrozek K, Margeson D, Becker H, Curfman J, Holland KB, Schwind S, Whitman SP, Wu YZ, Blum W, Powell BL, Carter TH, Wetzler M, Moore JO, Kolitz JE, Baer MR, Carroll AJ, Larson RA, Caligiuri MA, Marcucci G, Bloomfield CD (2011) TET2 mutations improve the new European LeukemiaNet risk classification of acute myeloid leukemia: a Cancer and Leukemia Group B study. J Clin Oncol 29:1373–1381
Chou WC, Chou SC, Liu CY, Chen CY, Hou HA, Kuo YY, Lee MC, Ko BS, Tang JL, Yao M, Tsay W, Wu SJ, Huang SY, Hsu SC, Chen YC, Chang YC, Kuo YY, Kuo KT, Lee FY, Liu MC, Liu CW, Tseng MH, Huang CF, Tien HF (2011) TET2 mutation is an unfavorable prognostic factor in acute myeloid leukemia patients with intermediate-risk cytogenetics. Blood 118:3803–3810
Albano F, Anelli L, Zagaria A, Coccaro N, Minervini A, Rossi AR, Specchia G (2011) Decreased TET2 gene expression during chronic myeloid leukemia progression. Leuk Res 35:e220-e222
Haber DA, Buckler AJ, Glaser T, Call KM, Pelletier J, Sohn RL, Douglass EC, Housman DE (1990) An internal deletion within an 11p13 zinc finger gene contributes to the development of Wilms’ tumor. Cell 61:1257–1269
Saglio G, Carturan S, Grillo S, Capella S, Arruga F, Defilippi I, Rosso V, Rauco M, Marina LA, Cilloni D (2005) WT1 overexpression: a clinically useful marker in acute and chronic myeloid leukemias. Hematology 10(Suppl 1):76–78
Barragán E, Cervera J, Bolufer P, Ballester S, Martin G, Fernandez P, Collado R, Sayas MJ, Sanz MA (2004) Prognostic implications of Wilms’ tumor gene (WT1) expression in patients with de novo acute myeloid leukemia. Haematologica 89:926–933
Lange T, Hubmann M, Burkhardt R, Franke GN, Cross M, Scholz M, Leiblein S, Al-Ali HK, Edelmann J, Thiery J, Niederwieser D (2011) Monitoring of WT1 expression in PB and CD34(+) donor chimerism of BM predicts early relapse in AML and MDS patients after hematopoietic cell transplantation with reduced-intensity conditioning. Leukemia 25:498–505
Miyawaki S, Hatsumi N, Tamaki T, Naoe T, Ozawa K, Kitamura K, Karasuno T, Mitani K, Kodera Y, Yamagami T, Koga D (2010) Prognostic potential of detection of WT1 mRNA level in peripheral blood in adult acute myeloid leukemia. Leuk Lymphoma 51:1855–1861
Tamaki H, Ogawa H, Ohyashiki K, Ohyashiki JH, Iwama H, Inoue K, Soma T, Oka Y, Tatekawa T, Oji Y, Tsuboi A, Kim EH, Kawakami M, Fuchigami K, Tomonaga M, Toyama K, Aozasa K, Kishimoto T, Sugiyama H (1999) The Wilms’ tumor gene WT1 is a good marker for diagnosis of disease progression of myelodysplastic syndromes. Leukemia 13:393–399
Tamura H, Dan K, Yokose N, Iwakiri R, Ohta M, Sakamaki H, Tohyama K, Kondo A, Hyodo H, Nakamura K, Yamashita T, Elisseeva OA, Oka Y, Oji Y, Sugiyama H, Ogata K (2010) Prognostic significance of WT1 mRNA and anti-WT1 antibody levels in peripheral blood in patients with myelodysplastic syndromes. Leuk Res 34:986–990
Lugthart S, Drunen EV, Norden YV, Hoven AV, Erpelinck CA, Valk PJ, Beverloo HB, Lowenberg B, Delwel R (2008) High EVI1 levels predict adverse outcome in acute myeloid leukemia: prevalence of EVI1 overexpression and chromosome 3q26 abnormalities underestimated. Blood 111:4329–4337
Acknowledgments
The Spanish MDS Group (GESMD), provided samples and clinical information from patients participating in the INBIOMED HEMA-001/2006 project (sponsored by Celgene S.L., Madrid). This work has been partially supported by the grants PI061351 and 00/0023-00 from the Spanish “Fondo de Investigaciones Sanitarias de la Seguridad Social”, 89/A/06 from the “Gerencia Regional de Salud, Junta Castilla y León”, and CIC, IBMCC (USAL-CSIC), Spain.
Conflicts of interest
All the authors have no conflict of interest to report.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Table 1
Clinical and biological characteristics of MDS patients at diagnosis according to WT1 expression levels (DOC 46 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Santamaría, C., Ramos, F., Puig, N. et al. Simultaneous analysis of the expression of 14 genes with individual prognostic value in myelodysplastic syndrome patients at diagnosis: WT1 detection in peripheral blood adversely affects survival. Ann Hematol 91, 1887–1895 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-012-1538-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-012-1538-7