Abstract
Background
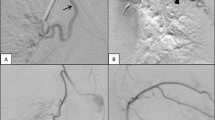
Bronchial artery embolisation (BAE) is recommended for the treatment of massive haemoptysis in cystic fibrosis (CF), but there are no randomised controlled trials of this therapy and its role in sub-massive haemoptysis is unclear. This study aimed to determine the outcomes and safety of BAE in adults with CF.
Materials and Methods
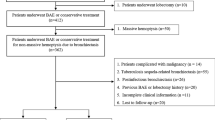
All patients with CF undergoing BAE at our centre between March 2011 and January 2015 were identified at the time of the procedure. Patient records were reviewed at hospital discharge, death or one month post-procedure (whichever was soonest). Follow-up continued to January 2016. Severity of haemoptysis was classified as: massive (>240 ml/24 h or >100 ml/day for ≥2 days), moderate–severe (>20 ml/24 h) or mild (<20 ml/24 h).
Results
Twenty-seven patients underwent 51 BAE procedures over a median follow-up period of 26 months (range 1–54). Ten patients (37%) required more than one BAE during the study. BAE was performed for massive haemoptysis in 18 cases (35%). Haemoptysis recurred after 31 (61%) of BAE procedures with no difference in recurrence rates between massive and sub-massive haemoptysis. Side effects were reported after 61% of procedures with chest pain the most common adverse event . Mortality after first BAE in the study was 3.9% at 30 days and 14.8% at 12 months. No significant predictors of mortality were identified.
Conclusions
BAE is often effective in controlling haemoptysis but is associated with considerable morbidity and high recurrence rates.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Flume PA, Mogayzel PJ, Robinson KA, Rosenblatt RL, Quittell L, Marshall BC, et al. Cystic fibrosis pulmonary guidelines: pulmonary complications: hemoptysis and pneumothorax. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2010;182(3):298–306.
Smyth AR, Bell SC, Bojcin S, Bryon M, Duff A, Flume P, et al. European cystic fibrosis society standards of care: best practice guidelines. J Cyst Fibros. 2014;13(Suppl 1):S23–42.
Antonelli M, Midulla F, Tancredi G, Salvatori FM, Bonci E, Cimino G, et al. Bronchial artery embolization for the management of nonmassive hemoptysis in cystic fibrosis. Chest. 2002;121(3):796–801.
Flume PA, Yankaskas JR, Ebeling M, Hulsey T, Clark LL. Massive hemoptysis in cystic fibrosis. Chest. 2005;128(2):729–38.
Thompson V, Mayer-Hamblett N, Kloster M, Bilton D, Flume PA. Risk of hemoptysis in cystic fibrosis clinical trials: a retrospective cohort study. J Cyst Fibros. 2015;14(5):632–8.
Flight WG, Barry PJ, Bright-Thomas RJ, Butterfield S, Ashleigh R, Jones AM. S53 Outcomes following bronchial artery embolisation for haemoptysis in adults with cystic fibrosis. Thorax. 2015;70(Suppl 3):A33.
Barben JU, Ditchfield M, Carlin JB, Robertson CF, Robinson PJ, Olinsky A. Major haemoptysis in children with cystic fibrosis: a 20-year retrospective study. J Cyst Fibros. 2003;2(3):105–11.
Brinson GM, Noone PG, Mauro MA, Knowles MR, Yankaskas JR, Sandhu JS, et al. Bronchial artery embolization for the treatment of hemoptysis in patients with cystic fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1998;157(6 Pt 1):1951–8.
Sweezey NB, Fellows KE. Bronchial artery embolization for severe hemoptysis in cystic fibrosis. Chest. 1990;97(6):1322–6.
Efrati O, Harash O, Rivlin J, Bibi H, Meir MZ, Blau H, et al. Hemoptysis in Israeli CF patients–prevalence, treatment, and clinical characteristics. J Cyst Fibros. 2008;7(4):301–6.
Mal H, Rullon I, Mellot F, Brugière O, Sleiman C, Menu Y, et al. Immediate and long-term results of bronchial artery embolization for life-threatening hemoptysis. Chest. 1999;115(4):996–1001.
Pathak V, Stavas JM, Ford HJ, Austin CA, Aris RM. Long-term outcomes of the bronchial artery embolization are diagnosis dependent. Lung India. 2016;33(1):3–8.
Ker K, Roberts I, Shakur H, Coats TJ. Antifibrinolytic drugs for acute traumatic injury. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD004896.pub4.
Sukeik M, Alshryda S, Haddad FS, Mason JM. Systematic review and meta-analysis of the use of tranexamic acid in total hip replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2011;93(1):39–46.
Bonnar J, Sheppard BL. Treatment of menorrhagia during menstruation: randomised controlled trial of ethamsylate, mefenamic acid, and tranexamic acid. BMJ. 1996;313(7057):579–82.
Prutsky G, Domecq JP, Salazar CA, Accinelli R. Antifibrinolytic therapy to reduce haemoptysis from any cause. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD008711.pub2.
Moen CA, Burrell A, Dunning J. Does tranexamic acid stop haemoptysis? Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2013;17(6):991–4.
Hurley M, Bhatt J, Smyth A. Treatment massive haemoptysis in cystic fibrosis with tranexamic acid. J R Soc Med. 2011;104(Suppl 1):S49–52.
Moua J, Nussbaum E, Liao E, Randhawa IS. Beta-blocker management of refractory hemoptysis in cystic fibrosis: a novel treatment approach. Ther Adv Respir Dis. 2013;7(4):217–23.
Conlan AA, Hurwitz SS, Krige L, Nicolaou N, Pool R. Massive hemoptysis. Review of 123 cases. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1983;85(1):120–4.
Jean-Baptiste E. Clinical assessment and management of massive hemoptysis. Crit Care Med. 2000;28(5):1642–7.
Authors’ Contributions
All authors contributed to the study design and manuscript development. WGF and PJB undertook the data analysis. WGF wrote the first draft of the manuscript.
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author confirms that there is no conflict of interest.
Informed Consent
Informed consent does not apply as this was an evaluation of routine clinical practice with no patient identifiable data included.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Flight, W.G., Barry, P.J., Bright-Thomas, R.J. et al. Outcomes Following Bronchial Artery Embolisation for Haemoptysis in Cystic Fibrosis. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 40, 1164–1168 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-017-1626-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-017-1626-0