Abstract
Purpose
To evaluate treatment effects, complications, and outcome of percutaneous stereotactic radiofrequency ablation (SRFA) of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (ICC).
Patients and Methods
Eleven consecutive patients (nine men and two women) with a total of 36 inoperable ICCs (18 initial lesions, 16 lesions newly detected during follow-up, and two local recurrences) underwent SRFA between December 2004 and June 2010. Two different radiofrequency ablation (RFA) devices with internally cooled electrodes were used. Tumor diameters ranged from 0.5 to 10 cm (median 3.0 cm). A total of 23 SRFA sessions were performed. The efficacy of SRFA was evaluated by contrast-enhanced computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging 1 month after treatment and then every 3 months.
Results
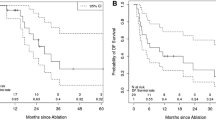
Primary technical effectiveness rate was 92%. Further follow-up every 3 months revealed three local recurrences (8%), two of which were successfully retreated, resulting in a secondary technical effectiveness rate of 98%. After a total of 23 RFA sessions, three major complications occurred (13%) that could be managed interventionally. Mean follow-up time was 35 months (range 12–81 months). One- and 3-year overall survival rates were 91 and 71%, respectively. The median overall survival was 60 months (according to the life table method). Eight (73%) of 11 patients were still alive at the end of follow-up.
Conclusion
SRFA is effective in the treatment of unresectable ICC even if the tumor is large and located close to major vessels. SRFA shows a survival benefit compared to other palliative treatment options and may also be considered as the first-line local treatment of ICCs in selected patients.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Khan SA, Thomas HC, Davidson BR, Taylor-Robinson SD (2005) Cholangiocarcinoma. Lancet 366(9493):1303–1314
DeOliveira ML, Cunningham SC, Cameron JL et al (2007) Cholangiocarcinoma: thirty-one-year experience with 564 patients at a single institution. Ann Surg 245:755–762
Endo I, Gonen M, Yopp AC et al (2008) Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: rising frequency, improved survival, and determinants of outcome after resection. Ann Surg 248:84–96
Aljiffry M, Abdulelah A, Walsh M et al (2009) Evidence-based approach to cholangiocarcinoma: a systematic review of the current literature. J Am Coll Surg 208:134–147
Blechacz B, Gores GJ (2008) Cholangiocarcinoma: advances in pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment. Hepatology 48:308–321
McGahan JP, Browning PD, Brock JM et al (1990) Hepatic ablation using radiofrequency electrocautery. Invest Radiol 25:267–270
Rossi S, Fornari F, Pathies C et al (1990) Thermal lesions induced by 480 KHz localized current field in guinea pig and pig liver. Tumori 76:54–57
Lau WY, Lai EC (2009) The current role of radiofrequency ablation in the management of hepatocellular carcinoma: a systematic review. Ann Surg 249:20–25
Chiou YY, Hwang JI, Chou YH et al (2005) Percutaneous ultrasound-guided radiofrequency ablation of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Kaohsiung J Med Sci 21:304–309
Rai R, Manas D, Rose J (2005) Radiofrequency ablation of recurrent cholangiocarcinoma after orthotopic liver transplantation—a case report. World J Gastroenterol 11:612–613
Zgodzinski W, Espat NJ (2005) Radiofrequency ablation for incidentally identified primary intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 11:5239–5240
Slakey DP (2002) Radiofrequency ablation of recurrent cholangiocarcinoma. Am Surg 68:395–397
Carrafiello G, Lagana D, Cotta E et al (2010) Radiofrequency ablation of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: preliminary experience. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 33:835–839
Kim JH, Won HJ, Shin YM et al (2011) Radiofrequency ablation for the treatment of primary intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Am J Roentgenol 196:W205–W209
Widmann G, Haidu M, Schullian P et al (2011) Stereotactic radiofrequency ablation (SRFA) of liver lesions: technique effectiveness, safety, and inter-operator performance. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. doi:10.1007/s00270-011-0200-4
Greene F, Page D, Fleming I et al (2002) AJCC cancer staging manual, 6th edn. Springer, New York
Bale R, Widmann G, Haidu M (2011) Stereotactic radiofrequency ablation. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 34:852–856
Bale R, Widmann G, Stoffner R (2010) Stereotaxy: breaking the limits of current radiofrequency ablation techniques. Eur J Radiol 75:32–36
Widmann G, Schullian P, Haidu M et al (2010) Respiratory motion control for stereotactic and robotic liver interventions. Int J Med Robot 6:343–349
Nevinny-Stickel M, Sweeney RA, Bale RJ et al (2004) Reproducibility of patient positioning for fractionated extracranial stereotactic radiotherapy using a double-vacuum technique. Strahlenther Onkol 180:117–122
Bale RJ, Vogele M, Rieger M et al (1999) A new vacuum device for extremity immobilization. AJR Am J Roentgenol 172:1093–1094
Smith KR, Frank KJ, Bucholz RD (1994) The NeuroStation—a highly accurate, minimally invasive solution to frameless stereotactic neurosurgery. Comput Med Imaging Graph 18:247–256
Bale RJ, Laimer I, Martin A et al (2006) Frameless stereotactic cannulation of the foramen ovale for ablative treatment of trigeminal neuralgia. Neurosurgery 59(4 suppl 2):ONS394–ONS3401
Bucholz RD, Ho HW, Rubin JP (1993) Variables affecting the accuracy of stereotactic localization using computerized tomography. J Neurosurg 79:667–673
Seror O, N’Kontchou G, Ibraheem M et al (2008) Large HCCs: multipolar RF ablation with three internally cooled bipolar electrodes—initial experience in 26 patients. Radiology 248:288–296
Bruners P, Schmitz-Rode T, Gunther RW et al (2008) Multipolar hepatic radiofrequency ablation using up to six applicators: preliminary results. Rofo 180:216–222
Frericks BB, Ritz JP, Roggan A et al (2005) Multipolar radiofrequency ablation of hepatic tumors: initial experience. Radiology 237:1056–1062
Laeseke PF, Sampson LA, Haemmerich D et al (2006) Multiple-electrode radiofrequency ablation creates confluent areas of necrosis: in vivo porcine liver results. Radiology 241:116–124
Goldberg SN, Grassi CJ, Cardella JF et al (2005) Image-guided tumor ablation: standardization of terminology and reporting criteria. Radiology 235:728–739
Poon RT, Ng KK, Lam CM et al (2004) Learning curve for radiofrequency ablation of liver tumors: prospective analysis of initial 100 patients in a tertiary institution. Ann Surg 239:441–449
Ercolani G, Vetrone G, Grazi GL et al (2010) Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: primary liver resection and aggressive multimodal treatment of recurrence significantly prolong survival. Ann Surg 252:107–114
Meyer CG, Penn I, James L (2000) Liver transplantation for cholangiocarcinoma: results in 207 patients. Transplantation 69:1633–1637
Madariaga JR, Iwatsuki S, Todo S et al (1998) Liver resection for hilar and peripheral cholangiocarcinomas: a study of 62 cases. Ann Surg 227:70–79
de Groen PC, Gores GJ, LaRusso NF et al (1999) Biliary tract cancers. N Engl J Med 341:1368–1378
Anderson CD, Pinson CW, Berlin J et al (2004) Diagnosis and treatment of cholangiocarcinoma. Oncologist 9:43–57
Burger I, Hong K, Schulick R et al (2005) Transcatheter arterial chemoembolization in unresectable cholangiocarcinoma: initial experience in a single institution. J Vasc Interv Radiol 16:353–361
Kim JH, Yoon HK, Sung KB et al (2008) Transcatheter arterial chemoembolization or chemoinfusion for unresectable intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: clinical efficacy and factors influencing outcomes. Cancer 113:1614–1622
Aliberti C, Benea G, Tilli M et al (2008) Chemoembolization (TACE) of unresectable intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma with slow-release doxorubicin-eluting beads: preliminary results. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 31:883–888
Hammill CW, Wong LL (2008) Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: a malignancy of increasing importance. J Am Coll Surg 207:594–603
Wang SC, Bester L, Burnes JP et al (2010) Clinical care and technical recommendations for 90yttrium microsphere treatment of liver cancer. J Med Imaging Radiat Oncol 54:178–187
Thongprasert S (2005) The role of chemotherapy in cholangiocarcinoma. Ann Oncol 16(suppl 2):ii93–ii96
Chen MS, Li JQ, Zheng Y et al (2006) A prospective randomized trial comparing percutaneous local ablative therapy and partial hepatectomy for small hepatocellular carcinoma. Ann Surg 243:321–328
Mulier S, Ni Y, Jamart J et al (2005) Local recurrence after hepatic radiofrequency coagulation: multivariate meta-analysis and review of contributing factors. Ann Surg 242:158–171
Lu DS, Raman SS, Limanond P et al (2003) Influence of large peritumoral vessels on outcome of radiofrequency ablation of liver tumors. J Vasc Interv Radiol 14:1267–1274
Curley SA, Marra P, Beaty K et al (2004) Early and late complications after radiofrequency ablation of malignant liver tumors in 608 patients. Ann Surg 239:450–458
Mulier S, Mulier P, Ni Y et al (2002) Complications of radiofrequency coagulation of liver tumours. Br J Surg 89:1206–1222
Cunningham SC, Choti MA, Bellavance EC et al (2007) Palliation of hepatic tumors. Surg Oncol 16:277–291
Acknowledgment
The authors would like to thank Michael Vogele, MD for the technical support and the radiation technicians Thomas Lang, Martin Knoflach, Christoph Hinterleithner, Martin Fasser, Julia Mahlknecht and Florian Schanda for their assistance.
Conflict of interest
R.B. is a coinventor of the Atlas aiming device and coshareholder in its financial returns
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Haidu, M., Dobrozemsky, G., Schullian, P. et al. Stereotactic Radiofrequency Ablation of Unresectable Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinomas: A Retrospective Study. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 35, 1074–1082 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-011-0288-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-011-0288-6