Abstract
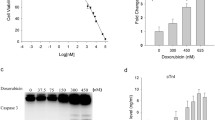
Doxorubicin is a commonly used cytotoxic drug for effective treatment of both solid tumors and leukemias, which may cause severe cardiac adverse effects leading to heart failure. In certain tumor cells, doxorubicin-induced cell death is mediated by death receptors such as CD95/Apo-1/Fas. Here we studied the role of death receptors for doxorubicin-induced cell death in primary neonatal rat cardiomyocytes and the embryonic cardiomyocytic cell line H9c2.1. Doxorubicin-induced cell death of cardiomyocytes was associated with cleavage of caspases 3 and 8, a drop in mitochondrial transmembrane potential, and release of cytochrome c. Doxorubicin-treated cardiomyocytes secreted death-inducing ligands into the culture supernatant, but remained resistant toward cell death induction by death receptor triggering. In contrast to the chelator dexrazoxane, blockade of death receptor signaling by stable overexpression of transdominant negative adapter molecule FADD did not inhibit doxorubicin-induced cell death. Our data suggest that cultured cardiomyocytes secrete death-inducing ligands, but undergo death receptor–independent cell death upon exposure to doxorubicin.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arola OJ, Saraste A, Pulkki K, Kallajoki M, Parvinen M, Voipio-Pulkki LM (2000) Acute doxorubicin cardiotoxicity involves cardiomyocyte apoptosis. Cancer Res 60:1789
Bergmann MW, Loser P, Dietz R, von Harsdorf R (2001) Effect of NF-kappa B inhibition on TNF-alpha-induced apoptosis and downstream pathways in cardiomyocytes. J Mol Cell Cardiol 33:1223
Bonavita F, Stefanelli C, Giordano E, Columbaro M, Facchini A, Bonafe F, Caldera CM, Guaneri C (2003) H9c2 cardiac myoblasts undergo apoptosis in a model of ischemia consisting of serum deprivation and hypoxia: inhibition by PMA. FEBS Lett 536:85
Chao W, Shen Y, Li L, Rosenzweig A (2002) Importance of FADD signaling in serum-deprivation- and hypoxia-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis. J Biol Chem 277:31639
Childs AC, Phaneuf SL, Dirks AJ, Phillips T, Leeuwenburgh C (2002) Doxorubicin treatment in vivo causes cytochrome C release and cardiomyocyte apoptosis, as well as increased mitochondrial efficiency, superoxide dismutase activity, and Bcl-2:Bax ratio. Cancer Res 62:4592
Chinnaiyan AM, O’Rourke K, Tewari M, Dixit VM (1995) FADD, a novel death domain-containing protein, interacts with the death domain of Fas and initiates apoptosis. Cell 81:505
Clementi ME, Giardina B, Di Stasio E, Mordente A, Misiti F (2003) Doxorubicin-derived metabolites induce release of cytochrome C and inhibition of respiration on cardiac isolated mitochondria. Anticancer Res 23:2445
Cusack BJ, Young SP, Driskell J, Olson RD (1993) Doxorubicin and doxorubicinol pharmacokinetics and tissue concentrations following bolus injection and continuous infusion of doxorubicin in the rabbit. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 32:53
Friesen C, Herr I, Krammer PH, Debatin KM (1996) Involvement of the CD95 (APO-1/Fas) receptor/ligand system in drug-induced apoptosis in leukemia cells. Nat Med 2:574
Friesen C, Fulda S, Debatin KM (1999) Induction of CD95 ligand and apoptosis by doxorubicin is modulated by the redox state in chemosensitive- and drug-resistant tumor cells. Cell Death Differ 6:471
Fulda S, Sieverts H, Friesen C, Herr I, Debatin KM (1997) The CD95 (APO-1/Fas) system mediates drug-induced apoptosis in neuroblastoma cells. Cancer Res 57:3823
Hasinoff BB (1989) The interaction of the cardioprotective agent ICRF-187 [+]-1,2-bis(3,5-dioxopiperazinyl-1-yL)propane; its hydrolysis product (ICRF-198); and other chelating agents with the Fe(III) and Cu(II) complexes of adriamycin. Agents Actions 26:378
Herr I, Debatin KM (2001) Cellular stress response and apoptosis in cancer therapy. Blood 98:2603
Janin A, Deschaumes C, Daneshpouy M, Estaquier J, Micic-Polianski J, Rajagopalan-Levasseur P, Akarid K, Mounier N, Gluckman E, Socie G, Ameisen JC (2002) CD95 engagement induces disseminated endothelial cell apoptosis in vivo: immunopathologic implications. Blood 99:2940
Jemmerson R, Liu J, Hausauer D, Lam KP, Mondino A, Nelson RD (1999) A conformational change in cytochrome c of apoptotic and necrotic cells is detected by monoclonal antibody binding and mimicked by association of the native antigen with synthetic phospholipid vesicles. Biochemistry 38:3599
Jeremias I, Herr I, Boehler T, Debatin KM (1998) TRAIL/Apo-2-Ligand induced apoptosis in T-cells. Eur J Immunol 28:143
Jeremias I, Kupatt C, Martin-Villalba A, Habazettl H, Schenkel J, Boekstegers P, Debatin KM (2000) Involvement of CD95/Apo1/Fas in cell death after myocardial ischemia. Circulation 102:915
Kayagaki N, Kawasaki A, Ebata T, Ohmoto H, Ikeda S, Inoue S, Yoshino K, Okumura K, Yagita H (1995) Metalloproteinase-mediated release of human Fas ligand. J Exp Med 182:1777
Keefe DL (2001) Anthracycline-induced cardiomyopathy. Semin Oncol 28:2
Kumar D, Kirshenbaum LA, Li T, Danelisen I, Singal PK (2001) Apoptosis in adriamycin cardiomyopathy and its modulation by probucol. Antioxid Redox Signal 3:135
Lebrecht D, Setzer B, Ketelsen UP, Haberstroh J, Walker UA (2003) Time-dependent and tissue-specific accumulation of mtDNA and respiratory chain defects in chronic doxorubicin cardiomyopathy. Circulation 108:2423
Nakamura T, Ueda Y, Juan Y, Katsuda S, Takahashi H, Koh E (2000) Fas-mediated apoptosis in adriamycin-induced cardiomyopathy in rats: in vivo study. Circulation 102:572
Newton K, Strasser A (2000) Ionizing radiation and chemotherapeutic drugs induce apoptosis in lymphocytes in the absence of Fas or FADD/MORT1 signaling: implications for cancer therapy. J Exp Med 191:195
Nicoletti I, Migliorati G, Pagliacci MC, Grignani F, Riccardi C (1991) A rapid and simple method for measuring thymocyte apoptosis by propidium iodide staining and flow cytometry. J Immunol Methods 139:271
Nitobe J, Yamaguchi S, Okuyama M, Nozaki N, Sata M, Miyamoto T, Takeishi Y, Kubota I, Tomoike H (2003) Reactive oxygen species regulate FLICE inhibitory protein (FLIP) and susceptibility to Fas-mediated apoptosis in cardiac myocytes. Cardiovasc Res 57:119
Olson RD, Mushlin PS (1990) Doxorubicin cardiotoxicity: analysis of prevailing hypotheses. FASEB J 4:3076
Pastorino F, Brignole C, Marimpietri D, Cilli M, Gambini C, Ribatti D, Longhi R, Allen TM, Corti A, Ponzoni M (2003) Vascular damage and anti-angiogenic effects of tumor vessel-targeted liposomal chemotherapy. Cancer Res 63:7400
Petak I, Houghton JA (2001) Shared pathways: death receptors and cytotoxic drugs in cancer therapy. Pathol Oncol Res 7:95
Scaffidi C, Fulda S, Srinivasan A, Friesen C, Li F, Tomaselli KJ, Debatin KM, Krammer PH, Peter ME (1998) Two CD95 (APO-1/Fas) signaling pathways. EMBO J 17:1675
Springhorn JP, Claycomb WC (1989) Preproenkephalin mRNA expression in developing rat heart and in cultured ventricular cardiac muscle cells. Biochem J 258:73
Swain SM, Vici P (2004) The current and future role of dexrazoxane as a cardioprotectant in anthracycline treatment: expert panel review. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 130:1
Um HD, Orenstein JM, Wahl SM (1996) Fas mediates apoptosis in human monocytes by a reactive oxygen intermediate dependent pathway. J Immunol 156:3469
Walczak H, Krammer PH (2000) The CD95 (APO-1/Fas) and the TRAIL (APO-2L) apoptosis systems. Exp Cell Res 256:58
Wallace KB (2003) Doxorubicin-induced cardiac mitochondrionopathy. Pharmacol Toxicol 93:105
Wang L, Ma W, Markovich R, Lee WL, Wang PH (1998) Insulin-like growth factor I modulates induction of apoptotic signaling in H9C2 cardiac muscle cells. Endocrinology 139:1354
Webb J (1963) Enzyme and metabolic inhibitors. Academic Press, New York
Wu S, Ko YS, Teng MS, Ko YL, Hsu LA, Hsueh C, Chou YY, Liew CC, Lee YS (2002) Adriamycin-induced cardiomyocyte and endothelial cell apoptosis: in vitro and in vivo studies. J Mol Cell Cardiol 34:1595
Yamaoka M, Yamaguchi S, Suzuki T, Okuyama M, Nitobe J, Nakamura N, Mitsui Y, Tomoike H (2000) Apoptosis in rat cardiac myocytes induced by Fas ligand: priming for Fas-mediated apoptosis with doxorubicin. J Mol Cell Cardiol 32:881
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Renata Zucic, Petra Berger, and Ursula Nägele for excellent technical help.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was supported by Wilhelm Sander Stiftung and Bettina-Bräu-Stiftung.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jeremias, I., Stahnke, K. & Debatin, K.M. CD95/Apo-1/Fas: independent cell death induced by doxorubicin in normal cultured cardiomyocytes. Cancer Immunol Immunother 54, 655–662 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00262-004-0604-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00262-004-0604-y