Abstract
Purpose
To develop a prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA)-targeted radiotherapeutic for metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC) with optimized efficacy and minimized toxicity employing the β-particle radiation of 177Lu.
Methods
We synthesized 14 new PSMA-targeted, 177Lu-labeled radioligands (177Lu-L1–177Lu-L14) using different chelating agents and linkers. We evaluated them in vitro using human prostate cancer PSMA(+) PC3 PIP and PSMA(−) PC3 flu cells and in corresponding flank tumor models. Efficacy and toxicity after 8 weeks were evaluated at a single administration of 111 MBq for 177Lu-L1, 177Lu-L3, 177Lu-L5 and 177Lu-PSMA-617. Efficacy of 177Lu-L1 was further investigated using different doses, and long-term toxicity was determined in healthy immunocompetent mice.
Results
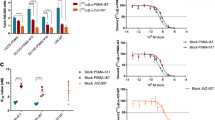
Radioligands were produced in high radiochemical yield and purity. Cell uptake and internalization indicated specific uptake only in PSMA(+) PC3 cells. 177Lu-L1, 177Lu-L3 and 177Lu-L5 demonstrated comparable uptake to 177Lu-PSMA-617 and 177Lu-PSMA-I&T in PSMA-expressing tumors up to 72 h post-injection. 177Lu-L1, 177Lu-L3 and 177Lu-L5 also demonstrated efficient tumor regression at 8 weeks. 177Lu-L1 enabled the highest survival rate. Necropsy studies of the treated group at 8 weeks revealed subacute damage to lacrimal glands and testes. No radiation nephropathy was observed 1 year post-treatment in healthy mice receiving 111 MBq of 177Lu-L1, most likely related to the fast renal clearance of this agent.
Conclusions
177Lu-L1 is a viable clinical candidate for radionuclide therapy of PSMA-expressing malignancies because of its high tumor-targeting ability and low off-target radiotoxic effects.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- PC:
-
Prostate cancer
- SAR:
-
Structure–activity relationships
- PSMA:
-
Prostate-specific membrane antigen
- DCIBzL:
-
2-[3-[1-Carboxy-5-(4-(125)I-iodo-benzoylamino)-pentyl]-ureido]-pentanedioic acid
- PET:
-
Positron emission tomography
- SPECT:
-
Single-photon emission computed tomography.
References
Kiess AP, Banerjee SR, Mease RC, Rowe SP, Rao A, Foss CA, et al. Prostate-specific membrane antigen as a target for cancer imaging and therapy. Quarterly J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2015;59:241–68.
Haberkorn U, Eder M, Kopka K, Babich JW, Eisenhut M. New strategies in prostate cancer: prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA) ligands for diagnosis and therapy. Clin Cancer Res. 2016;22:9–15.
Osborne JR, Akhtar NH, Vallabhajosula S, Anand A, Deh K, Tagawa ST. Prostate-specific membrane antigen-based imaging. Urol Oncol. 2013;31:144–54.
Salas Fragomeni RA, Amir T, Sheikhbahaei S, Harvey SC, Javadi MS, Solnes LB, et al. Imaging of nonprostate cancers using PSMA-targeted radiotracers: rationale, current state of the field, and a call to arms. J Nucl Med. 2018;59:871–7.
Chang SS, O’Keefe DS, Bacich DJ, Reuter VE, Heston WD, Gaudin PB. Prostate-specific membrane antigen is produced in tumor-associated neovasculature. Clin Cancer Res. 1999;5:2674–81.
Baccala A, Sercia L, Li J, Heston W, Zhou M. Expression of prostate-specific membrane antigen in tumor-associated neovasculature of renal neoplasms. Urology. 2007;70:385–90.
Spatz S, Tolkach Y, Jung K, Stephan C, Busch J, Ralla B, et al. Comprehensive evaluation of prostate specific membrane antigen expression in the vasculature of renal tumors: implications for imaging studies and prognostic role. J Urol. 2018;199:370–7.
Silver DA, Pellicer I, Fair WR, Heston WD, Cordon-Cardo C. Prostate-specific membrane antigen expression in normal and malignant human tissues. Clin Cancer Res. 1997;3:81–5.
Hrkach J, Von Hoff D, Ali MM, Andrianova E, Auer J, Campbell T, et al. Preclinical development and clinical translation of a PSMA-targeted docetaxel nanoparticle with a differentiated pharmacological profile. Sci Transl Med. 2012;4:128ra39.
Sterzing F, Kratochwil C, Fiedler H, Katayama S, Habl G, Kopka K, et al. 68Ga-PSMA-11 PET/CT: a new technique with high potential for the radiotherapeutic management of prostate cancer patients. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2016;43:34–41.
Rowe SP, Macura KJ, Ciarallo A, Mena E, Blackford A, Nadal R, et al. Comparison of prostate-specific membrane antigen–based 18F-DCFBC PET/CT to conventional imaging modalities for detection of hormone-naïve and castration-resistant metastatic prostate cancer. J Nucl Med. 2016;57:46–53.
Rahbar K, Afshar-Oromieh A, Seifert R, Wagner S, Schäfers M, Bögemann M, et al. Diagnostic performance of 18F-PSMA-1007 PET/CT in patients with biochemical recurrent prostate cancer. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2018;45:2055–61.
Benesova M, Schafer M, Bauder-Wust U, Afshar-Oromieh A, Kratochwil C, Mier W, et al. Preclinical evaluation of a tailor-made DOTA-conjugated PSMA inhibitor with optimized linker moiety for imaging and endoradiotherapy of prostate cancer. J Nucl Med. 2015;56:914–20.
Weineisen M, Schottelius M, Simecek J, Baum RP, Yildiz A, Beykan S, et al. 68Ga- and 177Lu-labeled PSMA I&T: optimization of a PSMA-targeted theranostic concept and first proof-of-concept human studies. J Nucl Med. 2015;56:1169–76.
Fendler WP, Rahbar K, Herrmann K, Kratochwil C, Eiber M. 177Lu-PSMA radioligand therapy for prostate cancer. J Nucl Med. 2017;58:1196–200.
Zechmann CM, Afshar-Oromieh A, Armor T, Stubbs JB, Mier W, Hadaschik B, et al. Radiation dosimetry and first therapy results with a 124I/131I-labeled small molecule (MIP-1095) targeting PSMA for prostate cancer therapy. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2014;41:1280–92.
Langbein T, Chausse G, Baum RP. Salivary gland toxicity of PSMA radioligand therapy: relevance and preventive strategies. J Nucl Med. 2018;59:1172–3.
Kopka K, Benešová M, Bařinka C, Haberkorn U, Babich J. Glu–ureido-based inhibitors of prostate-specific membrane antigen: lessons learned during the development of a novel class of low-molecular-weight theranostic radiotracers. J Nucl Med. 2017;58:17S–26S.
Trover JK, Beckett ML, Wright GL. Detection and characterization of the prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA) in tissue extracts and body fluids. Int J Cancer. 1995;62:552–8.
Ray Banerjee S, Pullambhatla M, Foss CA, Falk A, Byun Y, Nimmagadda S, et al. Effect of chelators on the pharmacokinetics of (99m)Tc-labeled imaging agents for the prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA). J Med Chem. 2013;56:6108–21.
Banerjee SR, Pullambhatla M, Foss CA, Nimmagadda S, Ferdani R, Anderson CJ, et al. 64Cu-labeled inhibitors of prostate-specific membrane antigen for PET imaging of prostate cancer. J Med Chem. 2014;57:2657–69.
Eder M, Schaefer M, Bauder-Wuest U, Hull W-E, Waengler C, Mier W, et al. 68Ga-complex lipophilicity and the targeting property of a urea-based PSMA inhibitor for PET imaging. Bioconjug Chem. 2012;23:688–97.
Choy CJ, Ling X, Geruntho JJ, Beyer SK, Latoche JD, Langton-Webster B, et al. 177Lu-labeled phosphoramidate-based PSMA inhibitors: the effect of an albumin binder on biodistribution and therapeutic efficacy in prostate tumor-bearing mice. Theranostics. 2017;7:1928–39.
Umbricht CA, Benesova M, Schibli R, Muller C. Preclinical development of novel PSMA-targeting radioligands: modulation of albumin-binding properties to improve prostate cancer therapy. Mol Pharm. 2018;15:2297–306.
Kelly J, Amor-Coarasa A, Ponnala S, Nikolopoulou A, Williams C Jr, Schlyer D, et al. Trifunctional PSMA-targeting constructs for prostate cancer with unprecedented localization to LNCaP tumors. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2018.2018;45:1841–1851.
Banerjee SR, Foss CA, Pullambhatla M, Wang Y, Srinivasan S, Hobbs RF, et al. Preclinical evaluation of 86Y-labeled inhibitors of prostate-specific membrane antigen for dosimetry estimates. J Nucl Med. 2015;56:628–34.
Chen Y, Foss CA, Byun Y, Nimmagadda S, Pullambahatla M, Fox JJ, et al. Radiohalogenated prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA)-based ureas as imaging agents for prostate cancer. J Med Chem. 2008;51:7933–43.
Kiess AP, Minn I, Vaidyanathan G, Hobbs RF, Josefsson A, Shen C, et al. (2S)-2-(3-(1-Carboxy-5-(4-211At-astatobenzamido)pentyl)ureido)-pentanedioic acid for PSMA-targeted alpha-particle radiopharmaceutical therapy. J Nucl Med. 2016;57:1569–75.
Banerjee SR, Pullambhatla M, Byun Y, Nimmagadda S, Foss CA, Green G, et al. Sequential SPECT and optical imaging of experimental models of prostate cancer with a dual modality inhibitor of the prostate-specific membrane antigen. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2011;50:9167–70.
Ray Banerjee S, Chen Z, Pullambhatla M, Lisok A, Chen J, Mease RC, et al. Preclinical comparative study of 68Ga-labeled DOTA, NOTA, and HBED-CC chelated radiotracers for targeting PSMA. Bioconjug Chem. 2016;27:1447–55.
Kiess AP, Minn I, Chen Y, Hobbs R, Sgouros G, Mease RC, et al. Auger radiopharmaceutical therapy targeting prostate-specific membrane antigen. J Nucl Med. 2015;56:1401–7.
Chen Y, Chatterjee S, Lisok A, Minn I, Pullambhatla M, Wharram B, et al. A PSMA-targeted theranostic agent for photodynamic therapy. J Photochem Photobiol B Biol. 2017;167:111–6.
Fendler WP, Stuparu AD, Evans-Axelsson S, Luckerath K, Wei L, Kim W, et al. Establishing 177Lu-PSMA-617 radioligand therapy in a syngeneic model of murine prostate cancer. J Nucl Med. 2017;58:1786–92.
Bouchet LG, Bolch WE, Blanco HP, Wessels BW, Siegel JA, Rajon DA, et al. MIRD Pamphlet No. 19: absorbed fractions and radionuclide S values for six age-dependent multiregion models of the kidney. J Nucl Med. 2003;44:1113–47.
Olszewski RT, Bukhari N, Zhou J, Kozikowski AP, Wroblewski JT, Shamimi-Noori S, et al. NAAG peptidase inhibition reduces locomotor activity and some stereotypes in the PCP model of schizophrenia via group II mGluR. J Neurochem. 2004;89:876–85.
Brayton C. Chapter 25 - spontaneous diseases in commonly used mouse strains. In: Fox JG, Davisson MT, Quimby FW, Barthold SW, Newcomer CE, Smith AL, editors. The mouse in biomedical research. second ed. Burlington: Academic; 2007. p. 623–717.
Brayton CF, Treuting PM, Ward JM. Pathobiology of aging mice and GEM: background strains and experimental design. Vet Pathol. 2012;49:85–105.
Serfilippi LM, Pallman DR, Russell B. Serum clinical chemistry and hematology reference values in outbred stocks of albino mice from three commonly used vendors and two inbred strains of albino mice. Contemp Top Lab Anim Sci. 2003;42:46–52.
Banerjee SR, Foss CA, Castanares M, Mease RC, Byun Y, Fox JJ, et al. Synthesis and evaluation of technetium-99m- and rhenium-labeled inhibitors of the prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA). J Med Chem. 2008;51:4504–17.
Ray Banerjee S, Pullambhatla M, Foss CA, Falk A, Byun Y, Nimmagadda S, et al. Effect of chelators on the pharmacokinetics of 99mTc-labeled imaging agents for the prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA). J Med Chem. 2013;56:6108–21.
Zang J, Fan X, Wang H, Liu Q, Wang J, Li H, et al. First-in-human study of 177Lu-EB-PSMA-617 in patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2019;46:148–58.
Taïeb D, Foletti J-M, Bardiès M, Rocchi P, Hicks RJ, Haberkorn U. PSMA-targeted radionuclide therapy and salivary gland toxicity: why does it matter? J Nucl Med. 2018;59:747–8.
Kratochwil C, Bruchertseifer F, Rathke H, Bronzel M, Apostolidis C, Weichert W, et al. Targeted alpha therapy of mCRPC with 225Actinium-PSMA-617: dosimetry estimate and empirical dose finding. J Nucl Med. 2017;58:1624–31.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Dr. R. Mease for his helpful comments.
Funding
We are grateful for the following sources of support: K25 CA148901 and the Patrick C. Walsh Prostate Cancer Research Fund (SRB), CA134675, CA184228, EB024495, and the Commonwealth Foundation (MGP).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Drs. Banerjee and Pomper are co-inventors on one or more U.S. patents covering compounds discussed in this submission, and as such are entitled to a portion of any licensing fees and royalties generated by this technology. This arrangement has been reviewed and approved by the Johns Hopkins University in accordance with its conflict-of-interest policies. No other authors have declared any relevant conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
All animal studies were carried out in compliance with the regulations of the Johns Hopkins Animal Care and Use Committee.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Oncology – Genitourinary
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Banerjee, S.R., Kumar, V., Lisok, A. et al. 177Lu-labeled low-molecular-weight agents for PSMA-targeted radiopharmaceutical therapy. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 46, 2545–2557 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-019-04434-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-019-04434-0