Abstract
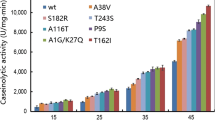
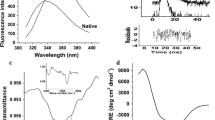
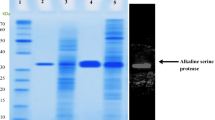
Artificial cold adaptation of a mesophilic protease, subtilisin BPN′, was attempted by means of random mutagenesis of its entire gene coupled with screening of cleared-zone-forming colonies on skim-milk plates at a low temperature. Out of sixty clones screened at 10 °C, one mutant enzyme (termed M-15) was found to acquire higher proteolytic activities, specifically dependent on low temperatures ranging from 10 °C to 1 °C, in comparison with those of the wild-type. DNA sequencing analysis revealed that, by this mutation, the 84th amino acid residue, valine, was substituted by isoleucine, which is located 1.5 nm from the center of the catalytic triad in the tertiary structure of subtilisin. By kinetic analysis of the purified enzyme samples, the higher proteolytic activities of M-15 at low temperatures were found to be due to the decrease in the K m value. There was no difference in thermostability between the wild-type and mutant enzymes, when tested by heat treatment. Circular dichroism spectra also showed no difference between them at 10 °C, indicating that the mutation of V84I had no effect on the secondary structure of subtilisin.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 22 April 1996 / Received last revision: 29 July 1996 / Accepted: 24 August 1996
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kano, H., Taguchi, S. & Momose, H. Cold adaptation of a mesophilic serine protease, subtilisin, by in vitro random mutagenesis. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 47, 46–51 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002530050886
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002530050886