Abstract
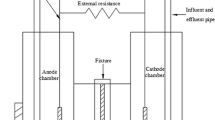
The effect of a magnetic field (MF) on electricity production and wastewater treatment in two-chamber microbial fuel cells (MFCs) has been investigated. Electricity production capacity could be improved by the application of a low-intensity static MF. When a MF of 50 mT was applied to MFCs, the maximum voltage, total phosphorus (TP) removal efficiency, and chemical oxygen demand (COD) removal efficiency increased from 523 ± 2 to 553 ± 2 mV, ∼93 to ∼96 %, and ∼80 to >90 %, respectively, while the start-up time and coulombic efficiency decreased from 16 to 10 days and ∼50 to ∼43 %, respectively. The MF effects were immediate, reversible, and not long lasting, and negative effects on electricity generation and COD removal seemed to occur after the MF was removed. The start-up and voltage output were less affected by the MF direction. Nitrogen compounds in magnetic MFCs were nitrified more thoroughly; furthermore, a higher proportion of electrochemically inactive microorganisms were found in magnetic systems. TP was effectively removed by the co-effects of microbe absorption and chemical precipitation. Chemical precipitates were analyzed by a scanning electron microscope capable of energy-dispersive spectroscopy (SEM-EDS) to be a mixture of phosphate, carbonate, and hydroxyl compounds.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
APHA (2005) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 19th edn. American Public Health Association, Washington
Butler CS, Nerenberg R (2010) Performance and microbial ecology of air-cathode microbial fuel cells with layered electrode assemblies. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 86:1399–1408
Chen SS, Liu GL, Zhang RD, Qin BY, Luo Y, Hou YP (2012) Improved performance of the microbial electrolysis desalination and chemical-production cell using the stack structure. Bioresour Technol 116:507–511
Cusick RD, Logan BE (2012) Phosphate recovery as struvite within a single chamber microbial electrolysis cell. Bioresour Technol 107:110–115
Domagalski J, Lin C, Luo Y, Kang J, Wang S, Brown LR, Munn MD (2007) Eutrophication study at the Panjiakou-Daheiting reservoir system, northern Hebei province, People’s Republic of China: chlorophyll-A model and sources of phosphorus and nitrogen. Agr Water Manag 94(1–3):43–53
Ichihashi O, Hirooka K (2012) Removal and recovery of phosphorus as struvite from swine wastewater using microbial fuel cell. Bioresour Technol 114:303–307
Ichihashi O, Yamamoto N, Hirooka K (2012) Power generation by and microbial community structure in microbial fuel cell treating animal wastewater. J Jpn Soc Water Environ 35(1):19–26
Jiang D, Li B, Jia W, Lei Y (2010a) Effect of inoculum types on bacterial adhesion and power production in microbial fuel cells. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 160(1):182–196
Jiang D, Li X, Raymond D, Mooradain J, Li B (2010b) Power recovery with multi-anode/cathode microbial fuel cells suitable for future large-scale applications. Int J Hydrog Energy 35(16):8683–8689
Jiang D, Curtis M, Troop E, Scheible K, McGrath J, Boxun H, Suib S, Raymond D, Baikun L (2011) A pilot-scale study on utilizing multi-anode/cathode microbial fuel cells (MAC MFCs) to enhance the power production in wastewater treatment. Int J Hydrog Energy 36(1):876–884
Jones AR, Hay S, Woodward JR, Scrutton NS (2007) Magnetic field effect studies indicate reduced geminate recombination of the radical pair in substrate-bound adenosylcobalamin-dependent ethanolamine ammonia lyase. J Am Chem Soc 129(50):15718–15727
Jung JT, Sofer S (1997) Enhancement of phenol biodegradation by south magnetic field exposure. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 70(3):229–303
Jung JT, Sanji B, Godbole S, Sofer S (1993) Biodegradation of phenol: a comparative study with and without applying magnetic fields. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 56(1):73–76
Li WW, Sheng GP, Liu XW, Cai PJ, Sun M, Xiao X, Wang YK, Tong ZH, Dong F, Yu HQ (2011) Impact of a static magnetic field on the electricity production of Shewanella-inoculated microbial fuel cells. Biosens Bioelectron 26(10):3987–3992
Liu H, Logan BE (2004) Electricity generation using an air-cathode single chamber microbial fuel cell in the presence and absence of a proton exchange membrane. Environ Sci Technol 38(14):4040–4046
Liu H, Cheng SA, Logan BE (2005) Power generation in fed-batch microbial fuel cells as a function of ionic strength, temperature, and reactor configuration. Environ Sci Technol 39(14):5488–5493
Liu ST, Yang FL, Meng FG, Chen HH, Gong Z (2008) Enhanced anammox consortium activity for nitrogen removal: impacts of static magnetic field. J Biotechnol 138(3–4):96–102
Logan BE (2009) Exoelectrogenic bacteria that power microbial fuel cells. Nat Rev Microbiol 7(5):375–381
Lovley DR (2008) The microbe electric: conversion of organic matter to electricity. Curr Opin Biotechnol 19(6):564–571
Nelson NO, Mikkelsen RL, Hesterberg DL (2003) Struvite precipitation in anaerobic swine lagoon liquid: effect of pH and Mg: P ratio and determination of rate constant. Bioresour Technol 89(3):229–236
Puig S, Serra M, Vilar-Sanz A, Cabré M, Bañeras L, Colprim J, Balaguer MD (2011) Autotrophic nitrite removal in the cathode of microbial fuel cells. Bioresour Technol 102(6):4462–4467
Puig S, Coma M, Desloover J, Boon N, Colprim J, Balaguer MD (2012) Autotrophic denitrification in microbial fuel cells treating low ionic strength waters. Environ Sci Technol 46:2309–2315
Rabaey K, Lissens G, Siciliano SD, Verstraete W (2003) A microbial fuel cell capable of converting glucose to electricity at high rate and efficiency. Biotechnol Lett 25(18):1531–1535
Rozendal RA, Leone E, Keller J, Rabaey K (2009) Efficient hydrogen peroxide generation from organic matter in a bioelectrochemical system. Electrochem Commun 11(9):1752–1755
Tao QQ, Luo JJ, Zhou J, Zhou SQ, Liu GL, Zhang RD (2014) Effect of dissolved oxygen on nitrogen and phosphorus removal and electricity production in microbial fuel cell. Bioresour Technol 164:402–407
Tomska A, Wolny L (2008) Enhancement of biological wastewater treatment by magnetic field exposure. Desalination 222(1–3):368–373
Virdis B, Rabaey K, Yuan Z, Keller J (2008) Microbial fuel cells for simultaneous carbon and nitrogen removal. Water Res 42(12):3013–3024
Virdis B, Rabaey K, Yuan Z, Rozendal RA, Keller J (2009) Electron fluxes in a microbial fuel cell performing carbon and nitrogen removal. Environ Sci Technol 43(13):5144–5149
Virdis B, Rabaey K, Rozendal RA, Yuan Z, Keller J (2010) Simultaneous nitrification, denitrification and carbon removal in microbial fuel cells. Water Res 44(9):2970–2980
Watanabe K (2008) Recent developments in microbial fuel cell technologies for sustainable bioenergy. J Biosci Bioeng 106(6):528–536
Yavus H, Celebi SS (2000) Effects of magnetic field on activity of activated sludge in wastewater treatment. Enzym Microbiol Technol 26(1):22–27
Yin Y, Huang GT, Tong YR, Liu YD, Zhang LH (2013) Electricity production and electrochemical impedance modeling of microbial fuel cells under static magnetic field. J Power Sources 237:58–63
Zhang QM, Tokiwa M, Doi T, Nakahara T, Chang P, Nakamura N, Hori M, Miyakoshi J, Yonei S (2003) Strong static magnetic field and the induction of mutations through elevated production of reactive oxygen species in Escherichia coli soxR. Int J Radiat Biol 79(4):281–286
Acknowledgments
Financial supports from the National Natural Science Foundation (21277052), the Department of Guangdong Education and the Science and Technology Bureau (2010), the State Key Laboratory of Subtropical Building Science (2013ZC03, 2014ZB04), and the Environmental Protection Bureau (201203) are gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tao, Q., Zhou, S. Effect of static magnetic field on electricity production and wastewater treatment in microbial fuel cells. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98, 9879–9887 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-014-6136-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-014-6136-2