Abstract
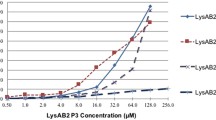
To investigate the nature and origin of the antibacterial activity of the lytic phage ϕAB2 toward Acinetobacter baumannii, we successfully isolated and characterized a novel phage lysozyme (endolysin) from ϕAB2 and named it LysAB2. To analyze antibacterial activity of LysAB2, the complete LysAB2 and two deletion derivatives were constructed, purified and characterized. Zymographic assays showed that only the intact LysAB2 could lyse the peptidoglycan of A. baumannii and the Staphylococcus aureus cell wall. Antibacterial analysis also showed that only the intact LysAB2 retained the complete bactericidal activity. When applied exogenously, LysAB2 exhibited a broad bacteriolytic activity against a number of Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria. Thermostability assays indicated that LysAB2 was stable at 20∼40°C. Its optimal pH was 6.0, and it was active from pH 4 to 8. Scanning electron microscopy revealed that exposure to 500 μg ml−1 LysAB2 for up to 60 min caused a remarkable modification of the cell shape of the bacteria. Treating bacteria with LysAB2 clearly enhanced permeation of the bacterial cytoplasmic membrane. These results indicate that LysAB2 is an effective lysozyme against bacteria, and they suggest that it is a good candidate for a therapeutic/disinfectant agent to control nosocomial infections caused by multiple drug-resistant bacteria.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barrow PA, Soothill JS (1997) Bacteriophage therapy and prophylaxis: rediscovery and renewed assessment of potential. Trends Microbiol 5:268–271
Bergogne-Berezin E, Towner KJ (1996) Acinetobacter spp. as nosocomial pathogens: microbiological, clinical, and epidemiological features. Clin Microbiol Rev 9:148–165
Borysowski J, Weber-Dabrowska B, Gorski A (2006) Bacteriophage endolysins as a novel class of antibacterial agents. Exp Biol Med (Maywood) 231:366–377
Brunner F, Stintzi A, Fritig B, Legrand M (1998) Substrate specificities of tobacco chitinases. Plant J 14:225–234
Ceyssens PJ, Lavigne R, Mattheus W, Chibeu A, Hertveldt K, Mast J, Robben J, Volckaert G (2006) Genomic analysis of Pseudomonas aeruginosa phages LKD16 and LKA1: establishment of the phiKMV subgroup within the T7 supergroup. J Bacteriol 188:6924–6931
Dijkshoorn L, Nemec A, Seifert H (2007) An increasing threat in hospitals: multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Nat Rev Microbiol 5:939–951
During K, Porsch P, Mahn A, Brinkmann O, Gieffers W (1999) The non-enzymatic microbicidal activity of lysozymes. FEBS Lett 449:93–100
Entenza JM, Loeffler JM, Grandgirard D, Fischetti VA, Moreillon P (2005) Therapeutic effects of bacteriophage Cpl-1 lysin against Streptococcus pneumoniae endocarditis in rats. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 49:4789–4792
Gille C, Frommel C (2001) STRAP: editor for STRuctural alignments of proteins. Bioinformatics 17:377–378
Hahn M, Hennig M, Schlesier B, Hohne W (2000) Structure of jack bean chitinase. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 56:1096–1099
Hart PJ, Pfluger HD, Monzingo AF, Hollis T, Robertus JD (1995) The refined crystal structure of an endochitinase from Hordeum vulgare L. seeds at 1.8 a resolution. J Mol Biol 248:402–413
Hermoso JA, Garcia JL, Garcia P (2007) Taking aim on bacterial pathogens: from phage therapy to enzybiotics. Curr Opin Microbiol 10:461–472
Johnson M, Zaretskaya I, Raytselis Y, Merezhuk Y, McGinnis S, Madden TL (2008) NCBI BLAST: a better web interface. Nucleic Acids Res 36 (Web Server issue):W5–9
Kakikawa M, Yokoi KJ, Kimoto H, Nakano M, Kawasaki K, Taketo A, Kodaira K (2002) Molecular analysis of the lysis protein Lys encoded by Lactobacillus plantarum phage phig1e. Gene 299:227–234
Lavigne R, Burkal'tseva MV, Robben J, Sykilinda NN, Kurochkina LP, Grymonprez B, Jonckx B, Krylov VN, Mesyanzhinov VV, Volckaert G (2003) The genome of bacteriophage phiKMV, a T7-like virus infecting Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Virology 312:49–59
Lin NT, Chiou PY, Chang KC, Chen LK, Lai MJ (2010) Isolation and characterization of phi AB2: a novel bacteriophage of Acinetobacter baumannii. Res Microbiol 161:308–314
Mangoni ML, Papo N, Barra D, Simmaco M, Bozzi A, Di Giulio A, Rinaldi AC (2004) Effects of the antimicrobial peptide temporin L on cell morphology, membrane permeability and viability of Escherichia coli. Biochem J 380:859–865
Marchler-Bauer A, Anderson JB, Chitsaz F, Derbyshire MK, DeWeese-Scott C, Fong JH, Geer LY, Geer RC, Gonzales NR, Gwadz M, He S, Hurwitz DI, Jackson JD, Ke Z, Lanczycki CJ, Liebert CA, Liu C, Lu F, Lu S, Marchler GH, Mullokandov M, Song JS, Tasneem A, Thanki N, Yamashita RA, Zhang D, Zhang N, Bryant SH (2009) CDD: specific functional annotation with the Conserved Domain Database. Nucleic Acids Res 37 (Database issue):D205–D210
McGuffin LJ, Bryson K, Jones DT (2000) The PSIPRED protein structure prediction server. Bioinformatics 16:404–405
Monzingo AF, Marcotte EM, Hart PJ, Robertus JD (1996) Chitinases, chitosanases, and lysozymes can be divided into procaryotic and eucaryotic families sharing a conserved core. Nat Struct Biol 3:133–140
Morita M, Tanji Y, Orito Y, Mizoguchi K, Soejima A, Unno H (2001) Functional analysis of antibacterial activity of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens phage endolysin against Gram-negative bacteria. FEBS Lett 500:56–59
Notredame C, Higgins DG, Heringa J (2000) T-Coffee: a novel method for fast and accurate multiple sequence alignment. J Mol Biol 302:205–217
Orito Y, Morita M, Hori K, Unno H, Tanji Y (2004) Bacillus amyloliquefaciens phage endolysin can enhance permeability of Pseudomonas aeruginosa outer membrane and induce cell lysis. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 65:105–109
Patil RS, Ghormade VV, Deshpande MV (2000) Chitinolytic enzymes: an exploration. Enzyme Microb Technol 26:473–483
Peleg AY, Seifert H, Paterson DL (2008) Acinetobacter baumannii: emergence of a successful pathogen. Clin Microbiol Rev 21:538–582
Perez F, Hujer AM, Hujer KM, Decker BK, Rather PN, Bonomo RA (2007) Global challenge of multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 51:3471–3484
Stone R (2002) Bacteriophage therapy. Stalin’s forgotten cure. Science 298:728–731
Sulakvelidze A, Alavidze Z, Morris JG Jr (2001) Bacteriophage therapy. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 45:649–659
Ubhayasekera W, Rawat R, Ho SW, Wiweger M, Von Arnold S, Chye ML, Mowbray SL (2009) The first crystal structures of a family 19 class IV chitinase: the enzyme from Norway spruce. Plant Mol Biol 71:277–289
Vaara M (1992) Agents that increase the permeability of the outer membrane. Microbiol Rev 56:395–411
van Hengel AJ, Tadesse Z, Immerzeel P, Schols H, van Kammen A, de Vries SC (2001) N-acetylglucosamine and glucosamine-containing arabinogalactan proteins control somatic embryogenesis. Plant Physiol 125:1880–1890
Waterhouse AM, Procter JB, Martin DM, Clamp M, Barton GJ (2009) Jalview Version 2—a multiple sequence alignment editor and analysis workbench. Bioinformatics 25:1189–1191
Wroblewska M (2006) Novel therapies of multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Acinetobacter spp. infections: the state of the art. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz) 54:113–120
Acknowledgments
We thank the Electron Microscopy Laboratory of the Department of Anatomy of Tzu Chi University for technical assistance. This work was supported by grants TCSP-0302 from the Buddhist Tzu Chi General Hospital and TCIRP99002-03 from Tzu Chi University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Meng-Jiun Lai and Nien-Tsung Lin contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lai, MJ., Lin, NT., Hu, A. et al. Antibacterial activity of Acinetobacter baumannii phage ϕAB2 endolysin (LysAB2) against both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 90, 529–539 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-011-3104-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-011-3104-y