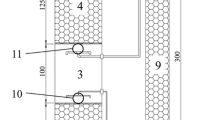
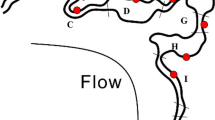
Abstract
High levels of nitrate are present in groundwater migrating from the former waste disposal ponds at the Y-12 National Security Complex in Oak Ridge, TN. A field-scale denitrifying fluidized bed reactor (FBR) was designed, constructed, and operated with ethanol as an electron donor for the removal of nitrate. After inoculation, biofilms developed on the granular activated carbon particles. Changes in the bacterial community of the FBR were evaluated with clone libraries (n=500 partial sequences) of the small-subunit rRNA gene for samples taken over a 4-month start-up period. Early phases of start-up operation were characterized by a period of selection, followed by low diversity and predominance by Azoarcus-like sequences. Possible explanations were high pH and nutrient limitations. After amelioration of these conditions, diversification increased rapidly, with the appearance of Dechloromonas, Pseudomonas, and Hydrogenophaga sequences. Changes in NO3, SO4, and pH also likely contributed to shifts in community composition. The detection of sulfate-reducing-bacteria-like sequences closely related to Desulfovibrio and Desulfuromonas in the FBR have important implications for downstream applications at the field site.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boga HI, Brune A (2003) Hydrogen-dependent oxygen reduction by homoacetogenic bacteria isolated from termite guts. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:779–786
Brooks SC, Fredrickson JK, Carroll SL, Kennedy DW, Zachara JM, Plymale AE, Kelly SD, Kemner KM, Fendorf S (2003) Inhibition of bacterial U(VI) reduction by calcium. Environ Sci Technol 37:1850–1858
Brown MV, Bowman JP (2001) A molecular phylogenetic survey of sea–ice microbial communities (SIMCO). FEMS Microbiol Ecol 35:267–275
Do YS, Schmidt TM, Zahn JA, Boyd ES, de la Mora A, DiSpirito AA (2003) Role of Rhodobacter sp. strain PS9, a purple non-sulfur photosynthetic bacterium isolated from an anaerobic swine waste lagoon, in odor remediation. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:1710–1720
Fields MW, Yan T, Rhee S-K, Carroll SL, Jardine PM, Watson DB, Criddle CS, Zhou J (2005) Impacts on microbial communities and cultivable isolates from groundwater contaminated with high levels of nitric acid–uranium waste. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 53:417–428
Gentile M, Yan T, Tiquia SM, Fields MW, Nyman J, Zhou J, Criddle CS (2005) Stability in a denitrifying fluidized bed reactor. Microb Ecol (in press)
Gu B, Brooks SC, Roh Y, Jardine PM (2003) Geochemical reactions and dynamics during titration of a contaminated groundwater with high uranium, aluminum, and calcium. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 67:2749–2761
Gu B, Wu WM, Ginder-Vogel MA, Yan H, Fields MW, Zhou J, Fendorf S, Criddle CS, Jardine PM (2005) Bioreduction of uranium in a contaminated soil column. Environ Sci Technol 39:4841–4847
Kampfer P, Schulze R, Jackel U, Malik KA, Amann R, Spring S (2005) Hydrogenophaga defluvii sp. nov. and Hydrogenophaga atypica sp. nov., isolated from activated sludge. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 55:341–334
Khan ST, Hiraishi A (2002) Diaphorobacter nitroreducens gen nov., sp nov., a poly(3-hydroxybutyrate)-degrading denitrifying bacterium isolated from activated sludge. J Gen Appl Microbiol 48:299–308
Kim BH, Park HS, Kim HJ, Kim GT, Chang IS, Lee J, Phung NT (2004) Enrichment of microbial community generating electricity using a fuel-cell-type electrochemical cell. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 63:672–681
Kniemeyer O, Probian C, Rossello-Mora R, Harder J (1999) Anaerobic mineralization of quaternary carbon atoms: isolation of denitrifying bacterial on dimethylmalonate. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:3319–3324
Kumar S, Tamura K, Jakobsen IB, Nei M (2001) MEGA2: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis software. Bioinformatics 17:1244–1245
Luo J, Wu W, Fienen MN, Jardine PM, Mehlhorn TL, Watson DB, Cirpka OA, Criddle CS, Kitanidis PK (2005) A nested-cell approach for in situ remediation. Groundwater (in press)
Massol-Deya A, Weller R, Rios-Hernandez L, Zhou JZ, Hickey RF, Tiedje JM (1997) Succession and convergence of biofilm communities in fixed-film reactors treating aromatic hydrocarbons in groundwater. Appl Environ Microbiol 63:270–276
Mogensen GL, Kjeldsen KU, Ingvorsen K (2005) Desulfovibrio aerotolerans sp. nov., an oxygen tolerant sulfate-reducing bacterium isolated from activated sludge. Anaerobe 11:339–349
Matthies C, Evers S, Ludwig W, Schink B (2000) Anaerovorax odorimutans gen. nov., sp. nov., a putrescine-fermenting, strictly anaerobic bacterium. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 50:1591–1594
Ozdemir G, Ozturk T, Ceyhan N, Isler R, Cosar T (2003) Heavy metal biosorption by biomass of Ochrobactrum anthropi producing exopolysaccharide in activated sludge. Bioresour Technol 90:71–74
Pfennig N, Widdel F (1982) The bacteria of the sulphur cycle. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 298:433–441
Qiu X, Wu L, Huang H, McDonel PE, Palumbo AV, Tiedje JM, Zhou J (2001) Evaluation of PCR-generated chimeras, mutations, and heteroduplexes with 16S rRNA gene-based cloning. Appl Envir Microbiol 67:880–887
Rosencrantz D, Rainey FA, Janssen PH (1999) Culturable populations of Sporomusa spp. and Desulfovibrio spp. in the anoxic bulk soil of flooded rice microcosms. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:3526–3533
Rittimann BE, McCarty PL (2001) Environmental biotechnology: principles and applications. McGraw-Hill, Boston, pp 126–164, pp 497–534
Senko JM, Istok JD, Suflita JM, Krumholz LR (2002) In situ evidence for uranium immobilization and remobilization. Environ Sci Technol 36:1491–1496
Singleton DR, Furlong MA, Rathbun SL, Whitman WB (2001) Quantitative comparisons of 16S rRNA gene sequence libraries from environmental samples. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:4374–4376
Snaidr J, Amann R, Huber I, Ludwig W, Schleifer KH (1997) Phylogenetic analysis and in situ identification of bacteria in activated sludge. Appl Environ Microbiol 63:2884–2896
Song B, Young LY, Palleroni NJ (1998) Identification of denitrifier strain T1 as Thauera aromatica and proposal for emendation of the genus Thauera definition. Int J Syst Bacteriol 48:889–894
Song B, Palleroni NJ, Haggblom MM (2000) Isolation and characterization of diverse halobenzoate-degrading denitrifying bacteria from soils and sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:3446–3453
Thompson JD, Higgins DG, Gibson TJ (1994) CLUSTAL W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weigh matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res 22:4673–4680
US Environmental Protection Agency (1993) Manual: nitrogen control. EPA Office of Research and Development, Cincinnati, EPA/625/R-93/010
van Schie PM, Young LY (1998) Isolation and characterization of phenol-degrading denitrifying bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:2432–2438
Wagner M, Loy A, Nogueira R, Purkhold U, Lee N, Daims H (2002) Microbial community composition and function in wastewater treatment plants. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 81:665–680
Wu WM, Gu B, Fields MW, Gentile M, Ku YK, Yan H, Tiquias S, Yan T, Nyman J, Zhou J, Jardine PM, Criddle CS (2005) Uranium (VI) reduction by denitrifying biomass. Bioremediation Journal 9:1–13
Zhou J, Bruns MA, Tiedje JM (1996) DNA recovery from soils of diverse composition. Appl Environ Microbiol 62:316–322
Zumstein E, Moletta R, Godon JJ (2000) Examination of two years of community dynamics in an anaerobic bioreactor using fluorescence polymerase chain reaction (PCR) single-strand conformation polymorphism analysis. Environ Microbiol 2:69–78
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by The US Department of Energy under the Natural and Accelerated Bioremediation Research program. The authors especially thank Dr. Raj Rajan and Mr. Daniel W. Wagner, Ecovation, Inc., Victor, NY, for their great contribution to the design, fabrication, and start-up of the FBR system and Ms. Tonia Mehlhorn for her support of the field work. We also appreciate Ms. Hui Yang, Mr. Kenneth Lowe, and Dr. Bobette Nourse for assistance in sample analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hwang, C., Wu, WM., Gentry, T.J. et al. Changes in bacterial community structure correlate with initial operating conditions of a field-scale denitrifying fluidized bed reactor. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 71, 748–760 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-005-0189-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-005-0189-1