Abstract
Background
Children with Noonan syndrome are known to have increased risk for lymphatic disorders, the extent and nature of which are poorly understood.
Objective
Our objective was to describe the imaging findings of the central lymphatic abnormalities in children with Noonan syndrome who underwent central lymphatic imaging.
Materials and methods
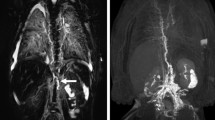
We conducted a single-center retrospective review of all children with a confirmed history of Noonan syndrome who presented for lymphatic imaging over a 5-year period. Imaging evaluation was performed on unenhanced T2-weighted (T2-W) imaging, dynamic-contrast MR lymphangiography or conventional lymphangiography. Two readers evaluated the imaging in consensus for the distribution of fluid on T2-W imaging and for lymphatic flow of intranodal contrast agent and thoracic duct abnormalities on dynamic-contrast MR lymphangiography and conventional lymphangiography. We performed a chart review for clinical history and outcomes.
Results
We identified a total of 10 children, all but one of whom had congenital heart disease. Presenting symptoms included chylothorax (n=9) and ascites (n=1). Nine had T2-W imaging, seven had dynamic-contrast MR lymphangiography, and seven had conventional lymphangiography. All with T2-W imaging had pleural effusions. On both dynamic-contrast MR lymphangiography and conventional lymphangiography, perfusion to the lung was seen (n=6), with intercostal flow also seen on dynamic-contrast MR lymphangiography (n=6). The thoracic duct was not present in three children and the central thoracic duct was not present in three. A double thoracic duct was seen in two children.
Conclusion
Children with Noonan syndrome and clinical evidence of lymphatic dysfunction have central lymphatic abnormalities characterized by retrograde intercostal flow, pulmonary lymphatic perfusion, and thoracic duct abnormalities.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Roberts AE, Allanson JE, Tartaglia M, Gelb BD (2013) Noonan syndrome. Lancet 381:333–342
Matsumoto T, Kudo T, Endo J et al (2015) Transnodal lymphangiography and post-CT for protein-losing enteropathy in Noonan syndrome. Minim Invasive Ther Allied Technol 24:246–249
Hasegawa K, Nagaoka Y, Maruyama H et al (2009) Late-onset lymphedema and protein-losing enteropathy with Noonan syndrome. Clin Pediatr Endocrinol 18:87–93
Tartaglia M, Zampino G, Gelb BD (2010) Noonan syndrome: clinical aspects and molecular pathogenesis. Mol Syndromol 1:2–26
Tsang HY, Cheung YF, Leung MP, Chau KT (2000) Cutaneous oozing of lymphatic fluid after interventional cardiac catheterization in a patient with Noonan syndrome. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv 51:441–443
Baltaxe HA, Lee JG, Ehlers KH, Engle MA (1975) Pulmonary lymphangiectasia demonstrated by lymphangiography in 2 patients with Noonan’s syndrome. Radiology 115:149–153
Keberle M, Mörk H, Jenett M et al (2000) Computed tomography after lymphangiography in the diagnosis of intestinal lymphangiectasia with protein-losing enteropathy in Noonan’s syndrome. Eur Radiol 10:1591–1593
Witt DR, Hoyme HE, Zonana J et al (1987) Lymphedema in Noonan syndrome: clues to pathogenesis and prenatal diagnosis and review of the literature. Am J Med Genet 27:841–856
Hoeffel J, Juncker P, Remy J (1980) Lymphatic vessels dysplasia in Noonan’s syndrome. AJR Am J Roentgenol 134:399–401
Okuda I, Udagawa H, Takahashi J et al (2009) Magnetic resonance-thoracic ductography: imaging aid for thoracic surgery and thoracic duct depiction based on embryological considerations. Gen Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 57:640–646
Takahashi H, Kuboyama S, Abe H et al (2003) Clinical feasibility of noncontrast-enhanced magnetic resonance lymphography of the thoracic duct. Chest 124:2136–2142
Dori Y, Keller MS, Rychik J, Itkin M (2014) Successful treatment of plastic bronchitis by selective lymphatic embolization in a Fontan patient. Pediatrics 134:e590–e595
Dori Y, Keller MS, Rome JJ et al (2016) Percutaneous lymphatic embolization of abnormal pulmonary lymphatic flow as treatment of plastic bronchitis in patients with congenital heart disease. Circulation 133:1160–1170
Chavhan GB, Amaral JG, Temple M, Itkin M (2017) MR lymphangiography in children: technique and potential applications. Radiographics 37:1775–1790
Savla JJ, Itkin M, Rossano JW, Dori Y (2017) Post-operative chylothorax in patients with congenital heart disease. J Am Coll Cardiol 69:2410–2422
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
None
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Biko, D.M., Reisen, B., Otero, H.J. et al. Imaging of central lymphatic abnormalities in Noonan syndrome. Pediatr Radiol 49, 586–592 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-018-04337-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-018-04337-6