Abstract
Background
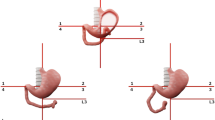
In some series of malrotation small numbers of children are described in whom the position of the duodenojejunal flexure was considered to be normal on straight anteroposterior (AP) view of an upper gastrointestinal (UGI) series.
Objective
The purpose of this study was to illustrate children with disorders of midgut rotation in whom the diagnosis was difficult because on the straight AP view of the UGI series the duodenojejunal flexure was either not clearly depicted or was projected to the left of the midline close to its expected normal position at or close to the level of the duodenal cap.
Materials and methods
We reviewed 111 children with malrotation to determine the frequency that duodenojejunal flexure was not clearly depicted or was close to normal position.
Results
Seven patients had close to normal position of duodenojejunal flexure on AP view. The correct diagnosis was made on initial UGI series in four patients based on other features on AP and lateral views. In two of the other three patients, a repeat UGI series facilitated the correct diagnosis. In the final patient, an abnormal position of a nasojejunal tube suggested the correct diagnosis.
Conclusion
Accurate diagnosis of anomalies of midgut rotation requires careful assessment of the entire duodenal sweep on both AP and lateral views to avoid false-negative interpretations.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Strouse PJ (2000) Disorders of intestinal rotation and fixation (“malrotation”). Pediatr Radiol 34:837–851
Lampl B, Levin TL, Berdon WE et al (2009) Malrotation and midgut volvulus: a historical review and current controversies in diagnosis and management. Pediatr Radiol 39:359–366
Daneman A (2009) Malrotation: the balance of evidence. Pediatr Radiol 39:S164–S166
Long FR, Kramer SS, Markowitz RI et al (1996) Intestinal malrotation in children: tutorial on radiographic diagnosis in difficult cases. Radiology 198:775–780
Long FR, Kramer SS, Markowitz RI et al (1996) Radiographic patterns of intestinal malrotation in children. Radiographics 16:547–556
Katz ME, Siegel MJ, Shackelford GD et al (1987) The position and mobility of the duodenum in children. AJR Am J Roentgenol 148:947–951
Berdon WE, Baker DH, Bull S et al (1970) Midgut malrotation and volvulus. Which films are most helpful? Radiology 96:375–383
Sizemore A, Rabbani KZ, Ladd A et al (2008) Diagnostic performance of the upper gastrointestinal series in the evaluation of children with clinically suspected malrotation. Pediatr Radiol 38:518–528
Dilley AV, Pereira J, Shi EC et al (2000) The radiologist says malrotation: does the surgeon operate? Pediatr Surg Int 16:45–49
Lim-Dunham JE, Ben-Ami T, Yousefzadeh DK (1999) Manual epigastric compression during upper gastrointestinal examination of neonates: value in diagnosis of intestinal malrotation and volvulus. AJR Am J Roentgenol 173:979–983
Blumberg K (1997) Intestinal malrotation. Radiology 202:584
Koplewitz BZ, Daneman A (1999) The lateral view: a useful adjunct in the diagnosis of malrotation. Pediatr Radiol 29:144–145
Slovis T, Strouse PJ (2009) Malrotation: some answers but more questions. Pediatr Radiol 39:315–316
Chao HC, Kong MS, Chen N et al (2000) Sonographic features related to volvulus in neonatal intestinal malrotation. J Ultrasound Med 19:371–376
Shimanuki Y, Aihara T, Takano H et al (1996) Clockwise whirlpool sign at color Doppler US: an objective and definite sign of midgut volvulus. Radiology 199:261–264
Yousefzadeh DK (2009) The position of the duodenojejunal junction: the wrong horse to back in diagnosing or excluding malrotation. Pediatr Radiol 39:S172–S177
Menten R, Reding R, Godding V et al (2012) Sonographic assessment of the retroperitoneal position of the third part of the duodenum: an indicator of normal intestinal rotation. Pediatr Radiol 42:941–945
Taylor GA (2011) CT appearance of the duodenum and mesenteric vessels in children with normal and abnormal bowel rotation. Pediatr Radiol 41:1378–1383
Gent R (2009) The role of ultrasound in the diagnosis of malrotation. Presentation at the 12th World Congress of the World Federation of Ultrasound in Medicine and Biology. Sydney, Australia, 30 August
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tang, V., Daneman, A., Navarro, O.M. et al. Disorders of midgut rotation: making the correct diagnosis on UGI series in difficult cases. Pediatr Radiol 43, 1093–1102 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-013-2676-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-013-2676-3