Abstract
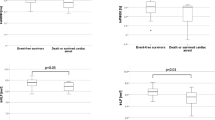
Previous studies have reported that patients with mitral valve prolapse (MVP) may display autonomic dysfunction. Measurement of heart rate variability (HRV) and P-wave dispersion (PWD) may provide insights into the functional state of the autonomic nervous system. Heart rate variability (HRV) has been used as a noninvasive marker of autonomic activity. However, to the authors’ knowledge, PWD has not been studied in the context of MVP. This study aimed to examine HRV and PWD in patients with MVP and to determine whether differences exist between symptomatic and asymptomatic patients. The study population consisted of 54 healthy children (17 boys and 37 girls) ages 6–18 years and 76 patients with MVP (20 boys and 56 girls) ages 6–18 years. The duration and dispersion of the P-wave were measured by surface 12-lead electrocardiograms (ECGs). Heart rate variability was quantified using both time-domain and frequency-domain analyses of Holter ECGs. The minimum duration of the P-wave was significantly lower in the MVP patients (42.4 ± 10.0 ms) than in the control subjects (54.4 ± 12.8 ms) (p < 0.01), and the PWD was significantly increased in the MVP group (42.7 ± 10.8 ms) compared with the control subjects (31.8 ± 10.9 ms) (p < 0.01). However, no significant differences were found between the symptomatic and asymptomatic patients. In addition, the HRV parameters were not statistically different between the two groups. In conclusion, although HRV parameters were not significantly different between the MVP and control groups, the findings show that PWD was increased for the children with MVP. However, no relationship could be established between PWD and clinical symptoms.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association (1998) ACC/AHA guidelines for the management of patients with valvular heart disease: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines (Committee on Management of Patients with Valvular Heart Disease). J Am Coll Cardiol 32:1486–1588
Boudoulas H, Reynolds JC, Mazzaferri E, Wooley CF (1980) Metabolic studies in mitral valve prolapse syndrome: a neuroendocrine–cardiovascular process. Circulation 61:1200–1205
Boudoulas H, Reynolds JC, Mazzaferri E, Wooley CF (1983) Mitral valve prolapse syndrome: the effect of adrenergic stimulation. J Am Coll Cardiol 2:638–644
Cheema AN, Ahmed MW, Kadish AH, Goldberger JJ (1995) Effects of autonomic stimulation and blockade on signal-averaged P-wave duration. J Am Coll Cardiol 26:497–502
Davies AO, Mares A, Pool JL, Taylor AA (1987) Mitral valve prolapse with symptoms of beta-adrenergic hypersensitivity: beta 2-adrenergic receptor supercoupling with desensitization on isoproterenol exposure. Am J Med 82:193–201
Devereux RB, Jones EC, Roman MJ, Howard BV, Fabsitz RR, Liu JE, Palmieri V, Welty TK, Lee ET (2001) Prevalence and correlates of mitral valve prolapse in a population-based sample of American Indians: the strong heart study. Am J Med 111:679–685
Digeos-Hasnier S, Copie X, Paziaud O, Abergel E, Guize L, Diebold B, Jeunemaître X, Berrebi A, Piot O, Lavergne T, Le Heuzey JY (2005) Abnormalities of ventricular repolarization in mitral valve prolapse. Ann Noninvasive Electrocardiol 10:297–304
Dilaveris PE, Gialafos EJ, Sideris SK, Theopistou AM, Andrikopoulos GK, Kyriakidis M, Gialafos JE, Toutouzas PK (1998) Simple electrocardiographic markers for the prediction of paroxysmal idiopathic atrial fibrillation. Am Heart J 135:733–738
Freed LA, Levy D, Levine RA, Larson MG, Evans JC, Fuller DL, Lehman B, Benjamin EJ (1999) Prevalence and clinical outcome of mitral valve prolapse. N Engl J Med 341:1–7
Frisinghelli A, Turiel M, Milletich A, Crema C, Malliani A (1992) The role of mitral regurgitation in the neurovegetative regulation of mitral valve prolapse. Cardiologia 37:781–783
Gaffney FA, Karlsson ES, Campbell W, Schutte JE, Nixon JV, Willerson JT, Blomqvist CG (1979) Autonomic dysfunction in women with mitral valve prolapse syndrome. Circulation 59:894–901
Gaffney FA, Bastian BC, Lane LB, Taylor WF, Horton J, Schutte JE, Graham RM, Pettinger W, Blomqvist CG (1983) Abnormal cardiovascular regulation in the mitral valve prolapse syndrome. Am J Cardiol 52:316–320
Gunduz H, Arinc H, Kayardi M, Akdemir R, Ozyildirim S, Uyan C (2006) Heart rate turbulence and heart rate variability in patients with mitral valve prolapse. Europace 8:515–520
Han L, Ho TF, Yip WC, Chan KY (2000) Heart rate variability of children with mitral valve prolapse. J Electrocardiol 33:219–224
Helmcke F, Nanda NC, Hsiung MC, Soto B, Adey CK, Goyal RG, Gatewood RP Jr (1987) Color Doppler assessment of mitral regurgitation with orthogonal planes. Circulation 75:175–183
Josephson ME, Kastor JA, Morganroth J (1977) Electrocardiographic left atrial enlargement: electrophysiologic, echocardiographic, and hemodynamic correlates. Am J Cardiol 39:967–971
Kochiadakis GE, Parthenakis FI, Zuridakis EG, Rombola AT, Chrysostomakis SI, Vardas PE (1996) Is there increased sympathetic activity in patients with mitral valve prolapse? Pacing Clin Electrophysiol 19:1872–1876
Leier CV, Jewell GM, Magorien RD, Wepsic RA, Schaal SF (1979) Interatrial conduction (activation) times. Am J Cardiol 44:442–446
Levine RA, Stathogiannis E, Newell JB, Harrigan P, Weyman AE (1988) Reconsideration of echocardiographic standards for mitral valve prolapse: lack of association between leaflet displacement isolated to the apical four-chamber view and independent echocardiographic evidence of abnormality. J Am Coll Cardiol 11:1010–1019
Marks AR, Choong CY, Sanfilippo AJ, Ferré M, Weyman AE (1989) Identification of high-risk and low-risk subgroups of patients with mitral valve prolapse. N Engl J Med 320:1031–1036
Michelucci A, Bagliani G, Colella A, Pieragnoli P, Porciani MC, Gensini G, Padeletti L (2002) P-wave assessment: state of the art update. Card Electrophysiol Rev 6:215–220
Nishimura RA, McGoon MD, Shub C, Miller FA Jr, Ilstrup DM, Tajik AJ (1985) Echocardiographically documented mitral valve prolapse: long-term follow-up of 237 patients. N Engl J Med 313:1305–1309
Pasternac A, Tubau JF, Puddu PE, Król RB, de Champlain J (1982) Increased plasma catecholamine levels in patients with symptomatic mitral valve prolapse. Am J Med 73:783–789
Rubler S, Shah NN, Moallem A (1976) Comparison of left atrial size and pulmonary capillary pressure with P-wave of electrocardiogram. Am Heart J 92:73–78
Taçoy G, Balcioğlu AS, Arslan U, Durakoğlugil E, Erdem G, Ozdemir M, Cengel A (2007) Effect of metoprolol on heart rate variability in symptomatic patients with mitral valve prolapse. Am J Cardiol 99:1568–1570
Terechtchenko L, Doronina SA, Pochinok EM, Riftine A (2003) Autonomic tone in patients with supraventricular arrhythmia associated with mitral valve prolapse in young men. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol 26:444–446
Tükek T, Akkaya V, Atilgan D, Demirel E, Ozcan M, Güven O, Korkut F (2001) Effect of left atrial size and function on P-wave dispersion: a study in patients with paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. Clin Cardiol 24:676–680
Waggoner AD, Adyanthaya AV, Quinones MA, Alexander JK (1976) Left atrial enlargement. Echocardiographic assessment of electrocardiographic criteria. Circulation 54:553–557
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Babaoglu, K., Altun, G. & Binnetoğlu, K. P-Wave Dispersion and Heart Rate Variability in Children with Mitral Valve Prolapse. Pediatr Cardiol 32, 449–454 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00246-011-9892-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00246-011-9892-0