Abstract
Introduction
To validate the usefulness of the packages available for automated hippocampal volumetry, we measured hippocampal volumes using one manual and two recently developed automated volumetric methods.
Methods
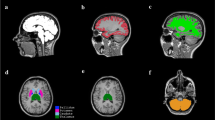
The study included T1-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of 21 patients with chronic major depressive disorder (MDD) and 20 normal controls. Using coronal turbo field echo (TFE) MRI with a slice thickness of 1.3 mm, the hippocampal volumes were measured using three methods: manual volumetry, surface-based parcellation using FreeSurfer, and individual atlas-based volumetry using IBASPM. In addition, the intracranial cavity volume (ICV) was measured manually.
Results
The absolute left hippocampal volume of the patients with MDD measured using all three methods was significantly smaller than the left hippocampal volume of the normal controls (manual P = 0.029, FreeSurfer P = 0.035, IBASPM P = 0.018). After controlling for the ICV, except for the right hippocampal volume measured using FreeSurfer, both measured hippocampal volumes of the patients with MDD were significantly smaller than the measured hippocampal volumes of the normal controls (right manual P = 0.019, IBASPM P = 0.012; left manual P = 0.003, FreeSurfer P = 0.010, IBASPM P = 0.002),. In the intrarater reliability test, the intraclass correlation coefficients (ICCs) were all excellent (manual right 0.947, left 0.934; FreeSurfer right 1.000, left 1.000; IBASPM right 1.000, left 1.000). In the test of agreement between the volumetric methods, the ICCs were right 0.846 and left 0.848 (manual and FreeSurfer), and right 0.654 and left 0.717 (manual and IBASPM).
Conclusion
The automated hippocampal volumetric methods showed good agreement with manual hippocampal volumetry, but the volume measured using FreeSurfer was 35% larger and the agreement was questionable with IBASPM. Although the automated methods could detect hippocampal atrophy in the patients with MDD, the results indicate that manual hippocampal volumetry is still the gold standard, while the automated volumetric methods need to be improved.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Geuze E, Vermetten E, Bremner JD (2005) MR-based in vivo hippocampal volumetrics: 2. Findings in neuropsychiatric disorders. Mol Psychiatry 10:160–184
Geuze E, Vermetten E, Bremner JD (2005) MR-based in vivo hippocampal volumetrics: 1. Review of methodologies currently employed. Mol Psychiatry 10:147–159
Alemán-Gómez Y, Melie-García L, Valdés-Hernandez P (2006) IBASPM: toolbox for automatic parcellation of brain structures. Presented at the 12th Annual Meeting of the Organization for Human Brain Mapping, 11–15 June 2006, Florence, Italy. Available on CD-Rom in NeuroImage, vol. 27, no. 1
Carmichael OT, Aizenstein HA, Davis SW, Becker JT, Thompson PM, Meltzer CC, Liu Y (2005) Atlas-based hippocampus segmentation in Alzheimer’s disease and mild cognitive impairment. Neuroimage 27:979–990
Chupin M, Mukuna-Bantumbakulu AR, Hasboun D, Bardinet E, Baillet S, Kinkingnehun S, Lemieux L, Dubois B, Garnero L (2007) Anatomically constrained region deformation for the automated segmentation of the hippocampus and the amygdala: method and validation on controls and patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Neuroimage 34:996–1019
Csernansky JG, Joshi S, Wang L, Haller JW, Gado M, Miller JP, Grenander U, Miller MI (1998) Hippocampal morphometry in schizophrenia by high dimensional brain mapping. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95:11406–11411
Duchesne S, Pruessner JC, Collins DL (2002) Appearance-based segmentation of medial temporal lobe structures. Neuroimage 17:515–531
Fischl B, Salat DH, Busa E, Albert M, Dieterich M, Haselgrove C, van der Kouwe A, Killiany R, Kennedy D, Klaveness S, Montillo A, Makris N, Rosen B, Dale AM (2002) Whole brain segmentation: automated labeling of neuroanatomical structures in the human brain. Neuron 33:341–355
Ghanei A, Soltanian-Zadeh H, Windham JP (1998) Segmentation of the hippocampus from brain MRI using deformable contours. Comput Med Imaging Graph 22:203–216
Haller JW, Banerjee A, Christensen GE, Gado M, Joshi SC, Miller MI, Sheline YI, Vannier MW, Csernansky JG (1997) Three-dimensional hippocampal MR morphometry with high-dimensional transformation of a neuroanatomical atlas. Radiology 202:504–510
Hsu YY, Schuff N, Du AT, Mark K, Zhu X, Hardin D, Weiner MW (2002) Comparison of automated and manual MRI volumetry of hippocampus in normal aging and dementia. J Magn Reson Imaging 16:305–310
Jack CR Jr (1994) MRI-based hippocampal volume measurements in epilepsy. Epilepsia 35 [Suppl 6]:S21–S29
Jack CR Jr, Bentley MD, Twomey CK, Zinsmeister AR (1990) MR imaging-based volume measurements of the hippocampal formation and anterior temporal lobe: validation studies. Radiology 176:205–209
Jack CR Jr, Sharbrough FW, Twomey CK, Cascino GD, Hirschorn KA, Marsh WR, Zinsmeister AR, Scheithauer B (1990) Temporal lobe seizures: lateralization with MR volume measurements of the hippocampal formation. Radiology 175:423–429
Jack CR Jr, Theodore WH, Cook M, McCarthy G (1995) MRI-based hippocampal volumetrics: data acquisition, normal ranges, and optimal protocol. Magn Reson Imaging 13:1057–1064
Jack CR Jr, Twomey CK, Zinsmeister AR, Sharbrough FW, Petersen RC, Cascino GD (1989) Anterior temporal lobes and hippocampal formations: normative volumetric measurements from MR images in young adults. Radiology 172:549–554
Luft AR, Skale JM, Welte D, Kolb R, Klose U (1996) Reliability and exactness of MRI-based volumetry: a phantom study. J Magn Reson Imaging 6:700–704
Devanand DP, Pradhaban G, Liu X, Khandji A, De Santi S, Segal S, Rusinek H, Pelton GH, Honig LS, Mayeux R, Stern Y, Tabert MH, de Leon MJ (2007) Hippocampal and entorhinal atrophy in mild cognitive impairment: prediction of Alzheimer disease. Neurology 68:828–836
Grundman M, Sencakova D, Jack CR Jr, Petersen RC, Kim HT, Schultz A, Weiner MF, DeCarli C, DeKosky ST, van Dyck C, Thomas RG, Thal LJ (2002) Alzheimer’s Disease Cooperative Study: brain MRI hippocampal volume and prediction of clinical status in a mild cognitive impairment trial. J Mol Neurosci 19:23–27
Jack CR Jr, Petersen RC, Xu YC, O’Brien PC, Smith GE, Ivnik RJ, Boeve BF, Waring SC, Tangalos EG, Kokmen E (1999) Prediction of AD with MRI-based hippocampal volume in mild cognitive impairment. Neurology 52:1397–1403
Pantel J, O’Leary DS, Cretsinger K, Bockholt HJ, Keefe H, Magnotta VA, Andreasen NC (2000) A new method for the in vivo volumetric measurement of the human hippocampus with high neuroanatomical accuracy. Hippocampus 10:752–758
Walhovd KB, Fjell AM, Reinvang I, Lundervold A, Dale AM, Eilertsen DE, Quinn BT, Salat D, Makris N, Fischl B (2005) Effects of age on volumes of cortex, white matter and subcortical structures. Neurobiol Aging 26:1261–1270
Tzourio-Mazoyer N, Landeau B, Papathanassiou D, Crivello F, Etard O, Delcroix N, Mazoyer B, Joliot M (2002) Automated anatomical labeling of activations in SPM using a macroscopic anatomical parcellation of the MNI MRI single-subject brain. Neuroimage 15:273–289
Han X, Fischl B (2007) Atlas renormalization for improved brain MR image segmentation across scanner platforms. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 26:479–486
Beck AT, Ward CH, Mendelson M, Mock J, Erbaugh J (1961) An inventory for measuring depression. Arch Gen Psychiatry 4:561–571
Hamilton M (1960) A rating scale for depression. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 23:56–62
Oldfield RC (1971) The assessment and analysis of handedness: the Edinburgh inventory. Neuropsychologia 9:97–113
Kruggel F (2006) MRI-based volumetry of head compartments: normative values of healthy adults. Neuroimage 30:1–11
Lemieux L, Hammers A, Mackinnon T, Liu RS (2003) Automatic segmentation of the brain and intracranial cerebrospinal fluid in T1-weighted volume MRI scans of the head, and its application to serial cerebral and intracranial volumetry. Magn Reson Med 49:872–884
MacLullich AM, Ferguson KJ, Deary IJ, Seckl JR, Starr JM, Wardlaw JM (2002) Intracranial capacity and brain volumes are associated with cognition in healthy elderly men. Neurology 59:169–174
Wolf H, Kruggel F, Hensel A, Wahlund LO, Arendt T, Gertz HJ (2003) The relationship between head size and intracranial volume in elderly subjects. Brain Res 973:74–80
Eritaia J, Wood SJ, Stuart GW, Bridle N, Dudgeon P, Maruff P, Velakoulis D, Pantelis C (2000) An optimized method for estimating intracranial volume from magnetic resonance images. Magn Reson Med 44:973–977
Chey J, Na DG, Tae WS, Ryoo JW, Hong SB (2006) Medial temporal lobe volume of nondemented elderly individuals with poor cognitive functions. Neurobiol Aging 27:1269–1279
Duvernoy HM (1991) The human brain: surface, three-dimensional sectional anatomy, and MRI. Springer-Verlag, New York, NY
Hasboun D, Chantome M, Zouaoui A, Sahel M, Deladoeuille M, Sourour N, Duyme M, Baulac M, Marsault C, Dormont D (1996) MR determination of hippocampal volume: comparison of three methods. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 17:1091–1098
Arndt S, Swayze V, Cizadlo T, O’Leary D, Cohen G, Yuh WT, Ehrhardt JC, Andreasen NC (1994) Evaluating and validating two methods for estimating brain structure volumes: tessellation and simple pixel counting. Neuroimage 1:191–198
Cronbach LJ (1951) Coefficient alpha and the internal structure of tests. Psychometrika 16:297–334
Bland JM, Altman DG (1986) Statistical methods for assessing agreement between two methods of clinical measurement. Lancet 1:307–310
Pitman EJG (1939) A note on normal correlation. Biometrica 31:9–12
Frodl T, Schaub A, Banac S, Charypar M, Jager M, Kummler P, Bottlender R, Zetzsche T, Born C, Leinsinger G, Reiser M, Moller HJ, Meisenzahl EM (2006) Reduced hippocampal volume correlates with executive dysfunctioning in major depression. J Psychiatry Neurosci 31:316–323
Hickie I, Naismith S, Ward PB, Turner K, Scott E, Mitchell P, Wilhelm K, Parker G (2005) Reduced hippocampal volumes and memory loss in patients with early- and late-onset depression. Br J Psychiatry 186:197–202
Neumeister A, Wood S, Bonne O, Nugent AC, Luckenbaugh DA, Young T, Bain EE, Charney DS, Drevets WC (2005) Reduced hippocampal volume in unmedicated, remitted patients with major depression versus control subjects. Biol Psychiatry 57:935–937
O’Brien JT, Lloyd A, McKeith I, Gholkar A, Ferrier N (2004) A longitudinal study of hippocampal volume, cortisol levels, and cognition in older depressed subjects. Am J Psychiatry 161:2081–2090
Videbech P, Ravnkilde B (2004) Hippocampal volume and depression: a meta-analysis of MRI studies. Am J Psychiatry 161:1957–1966
Li YJ, Ga SN, Huo Y, Li SY, Gao XG (2007) Characteristics of hippocampal volumes in healthy Chinese from MRI. Neurol Res 29:803–806
Tae WS, Hong SB (2001) Boundary of amygdala and hippocampus. Am J Psychiatry 158:820–821
Maller JJ, Daskalakis ZJ, Fitzgerald PB (2007) Hippocampal volumetrics in depression: the importance of the posterior tail. Hippocampus 17:1023–1027
Acknowledgement
This study was supported by a research grant from Kangwon National University Hospital.
Conflict of interest statement
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tae, W.S., Kim, S.S., Lee, K.U. et al. Validation of hippocampal volumes measured using a manual method and two automated methods (FreeSurfer and IBASPM) in chronic major depressive disorder. Neuroradiology 50, 569–581 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-008-0383-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-008-0383-9