Abstract
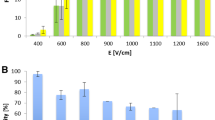
Efficient electroporation of cells in physical contact induces cell fusion, and this process is known as electrofusion. It has been shown that appropriate hypotonic treatment of cells before the application of electric pulses can cause a significant increase in electrofusion efficiency. First, the amplitudes of the electric field were determined spectrofluorometrically, where sufficient permeabilization in hypotonic buffer occurred for B16-F1 and CHO cells. In further electrofusion experiments 14 ± 4% of fused cells for B16-F1 and 6 ± 1% for CHO was achieved. These electrofusion efficiencies, determined by double staining and fluorescence microcopy, are comparable to those of other published studies. It was also confirmed that successful electroporation does not necessarily guarantee high electrofusion efficiency due to biological factors involved in the electrofusion process. Furthermore, not only the extension of electrofusion but also cell survival depends on the cell line used. Further studies are needed to improve overall cell survival after electroporation in hypotonic buffer, which was significantly reduced, especially for B16-F1 cells. Another contribution of this report is the description of a simple modification of the adherence method for formation of spontaneous cell contact, while cells preserve their spherical shape.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abe S, Takeda J (1988) Effects of La3+ on surface charges, dielectrophoresis, and electrofusion of barley protoplasts. Plant Physiol 87:389–394
Abidor IG, Barbul AI, Zhelev DV, Doinov P, Bandrina IN, Osipova EM, Sukharev SI (1993) Electrical properties of cell pellets and cell electrofusion in a centrifuge. Biochim Biophys Acta 1152:207–218
Ahkong QF, Lucy JA (1986) Osmotic forces in artificially induced cell fusion. Biochim Biophys Acta 858:206–216
Barrau C, Teissie J, Gabriel B (2004) Osmotically induced membrane tension facilitates the triggering of living cell electropermeabilization. Bioelectrochemistry 63:327–332
Blangero C, Rols MP, Teissié J (1989) Cytoskeletal reorganization during electric-field-induced fusion of Chinese hamster ovary cells grown in monolayers. Biochim Biophys Acta 981:295–302
Castro-Garza J, Barrios-Garcia HB, Cruz-Vega DE, Said-Fernandez S, Carranza-Rosales P, Molina-Torres CA, Vera-Cabrera L (2007) Use of a colorimetric assay to measure differences in cytotoxicity of Mycobacterium tuberculosis strains. J Med Microbiol 56:733–737
Cegovnik U, Novakovic S (2004) Setting optimal parameters for in vitro electrotransfection of B16F1, SA1, LPB, SCK, L929 and CHO cells using predefined exponentially decaying electric pulses. Bioelectrochemistry 62:73–82
Cemazar M, Jarm T, Miklavcic D, Macek-Lebar A, Ihan A, Kopitar NA, Sersa G (1998) Effect of electric-field intensity on electropermeabilization and electrosensitivity of various tumor-cell lines in vitro. Electromagn Biol Med 17:263–272
Chen EH, Grote E, Mohler W, Vignery A (2007) Cell–cell fusion. FEBS Lett 581:2181–2193
Escoffre J-M, Portet T, Wasungu L, Teissie J, Dean D, Rols M-P (2009) What is (still not) known of the mechanism by which electroporation mediates gene transfer and expression in cells and tissues. Mol Biotechnol 41:286–295
Evans EA, Parsegian VA (1986) Thermal–mechanical fluctuations enhance repulsion between bimolecular layers. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83:7132–7136
Finaz C, Lefevre A, Teissie J (1984) Electrofusion. A new, highly efficient technique for generating somatic cell hybrids. Exp Cell Res 150:477–482
Foung S, Perkins S, Kafadar K, Gessner P, Zimmermann U (1990) Development of microfusion techniques to generate human hybridomas. J Immunol Methods 134:35–42
Gabrijel M, Repnik U, Kreft M, Grilc S, Jeras M, Zorec R (2004) Quantification of cell hybridoma yields with confocal microscopy and flow cytometry. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 314:717–723
Gabrijel M, Kreft M, Zorec R (2008) Monitoring lysosomal fusion in electrofused hybridoma cells. Biochim Biophys Acta 1778:483–490
Gabrijel M, Bergant M, Kreft M, Jeras M, Zorec R (2009) Fused late endocytic compartments and immunostimulatory capacity of dendritic–tumor cell hybridomas. J Membr Biol 229:11–18
Gillies RJ, Didier N, Denton M (1986) Determination of cell number in monolayer cultures. Anal Biochem 159:109–113
Golzio M, Mora M-P, Raynaud C, Delteil C, Teissié J, Rols M-P (1998) Control by osmotic pressure of voltage-induced permeabilization and gene transfer in mammalian cells. Biophys J 74:3015–3022
Gong J, Avigan D, Chen D, Wu Z, Koido S, Kashiwaba M, Kufe D (2000) Activation of antitumor cytotoxic T lymphocytes by fusions of human dendritic cells and breast carcinoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:2715–2718
Gottfried E, Krieg R, Eichelberg C, Andreesen R, Mackensen A, Krause SW (2002) Characterization of cells prepared by dendritic cell–tumor cell fusion. Cancer Immun 2:15
Hayashi T, Tanaka H, Tanaka J, Wang R, Averbook BJ, Cohen PA, Shu S (2002) Immunogenicity and therapeutic efficacy of dendritic–tumor hybrid cells generated by electrofusion. Clin Immunol 104:14–20
James K, Bell GT (1987) Human monoclonal antibody production. J Immunol Methods 100:5–40
Jantscheff P, Spagnoli G, Zajac P, Rochlitz C (2002) Cell fusion: an approach to generating constitutively proliferating human tumor antigen-presenting cells. Cancer Immunol Immunother 51:367–375
Jaroszeski MJ, Gilbert R, Fallon PG, Heller R (1994) Mechanically facilitated cell–cell electrofusion. Biophys J 67:1574–1581
Jaroszeski MJ, Gilbert R, Heller R (1995) Cytometric detection and quantitation of cell–cell electrofusion products. In: Nickoloff JA (ed) Animal cell electroporation and electrofusion protocols. Humana Press, Totowa, NJ, pp 355–363
Kanduser M, Sentjurc M, Miklavcic D (2006) Cell membrane fluidity related to electroporation and resealing. Eur Biophys J 35:196–204
Knutton S, Jackson D, Graham JM, Micklem KJ, Pasternak CA (1976) Microvilli and cell swelling. Nature 262:52–54
Kotnik T, Bobanovic F, Miklavcic D (1997) Sensitivity of transmembrane voltage induced by applied electric fields—a theoretical analysis. Bioelectrochem Bioenerg 43:6
Lambert IH (2007) Activation and inactivation of the volume-sensitive taurine leak pathway in NIH3T3 fibroblasts and Ehrlich Lettre ascites cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 293:C390–C400
Lee WT, Shimizu K, Kuriyama H, Tanaka H, Kjaergaard J, Shu S (2005) Tumor–dendritic cell fusion as a basis for cancer immunotherapy. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 132:755–764
Macek-Lebar A, Miklavcic D (2001) Cell electropermeabilization to small molecules in vitro: control by pulse parameters. Radiol Oncol 35:10
Mally MI, McKnight ME, Glassy MC (1992) Protocols of electroporation and electrofusion for producing human hybridomas. In: Chang D, Chassy B, Saunders J, Sowers A (eds) Guide to electroporation and electrofusion. Academic Press, San Diego, pp 507–522
Martens S, McMahon HT (2008) Mechanisms of membrane fusion: disparate players and common principles. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 9:543–556
Marty M, Sersa G, Garbay JR, Gehl J, Collins CG, Snoj M, Billard V, Geertsen PF, Larkin JO, Miklavcic D, Pavlovic I, Paulin-Kosir SM, Cemazar M, Morsli N, Rudolf Z, Robert C, O’Sullivan GC, Mir LM (2006) Electrochemotherapy—an easy, highly effective and safe treatment of cutaneous and subcutaneous metastases: results of ESOPE (European Standard Operating Procedures of Electrochemotherapy) study. EJC Suppl 4:3–13
Matibiri EA, Mantell SH (1995) Comparative effects of fusion facilitators on electrofusion attributes of N. tabacum mesophyll protoplasts. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Culture 40:125–131
McIntosh TJ, Advani S, Burton RE, Zhelev DV, Needham D, Simon SA (1995) Experimental tests for protrusion and undulation pressures in phospholipid bilayers. Biochemistry 34:8520–8532
McIntosh TJ, Kulkarni KG, Simon SA (1999) Membrane fusion promoters and inhibitors have contrasting effects on lipid bilayer structure and undulations. Biophys J 76:2090–2098
Mekid H, Mir LM (2000) In vivo cell electrofusion. Biochim Biophys Acta 1524:118–130
Miklavcic D, Towhidi L (2010) Numerical study of the electroporation pulse shape effect on molecular uptake of biological cells. Radiol Oncol 44:8
Mir LM (2009) Nucleic acids electrotransfer-based gene therapy (electrogenetherapy): past, current, and future. Mol Biotechnol 43:167–176
Mizukami Y, Kito H, Okauchi M (1993) Factors affecting the electrofusion efficiency of Porphyra protoplasts. J Appl Psychol 5:29–36
Neil GA, Zimmermann U (1993) Electrofusion. Methods Enzymol 220:174–196
Neumann E, Sowers AE, Jordan CA (1989) Electroporation and electrofusion in cell biology. Springer-Verlag, New York
O’Hare MJ, Ormerod MG, Imrie PR, Peacock JH, Asche W (1989) Electropermeabilization and electrosensitivity of different types of mammalian cells. In: Neumann E, Sowers AE, Jordan CA (eds) Electroporation and electrofusion in cell biology. Plenum Press, New York, pp 319–330
Ohno-Shosaku T, Okada Y (1985) Electric pulse-induced fusion of mouse lymphoma cells: roles of divalent cations and membrane lipid domains. J Membr Biol 85:269–280
Pucihar G, Miklavcic D, Kotnik T (2009) A time-dependent numerical model of transmembrane voltage inducement and electroporation of irregularly shaped cells. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 56:1491–1501
Ramos C, Bonenfant D, Teissie J (2002) Cell hybridization by electrofusion on filters. Anal Biochem 302:213–219
Rols MP, Teissie J (1989) Ionic-strength modulation of electrically induced permeabilization and associated fusion of mammalian cells. Eur J Biochem 179:109–115
Rols MP, Teissie J (1990) Modulation of electrically induced permeabilization and fusion of Chinese hamster ovary cells by osmotic pressure. Biochemistry 29:4561–4567
Rubinsky B, Onik G, Mikus P (2007) Irreversible electroporation: a new ablation modality–clinical implications. Technol Cancer Res Treat 6:37–48
Salomskaite-Davalgiene S, Cepurniene K, Satkauskas S, Venslauskas MS, Mir LM (2009) Extent of cell electrofusion in vitro and in vivo is cell line dependent. Anticancer Res 29:3125–3130
Salvi A, Quillan J, Sadée W (2002) Monitoring intracellular pH changes in response to osmotic stress and membrane transport activity using 5-chloromethylfluorescein. AAPS J 4:21–28
Schmitt JJ, Zimmermann U (1989) Enhanced hybridoma production by electrofusion in strongly hypo-osmolar solutions. Biochim Biophys Acta 983:42–50
Schnettlera R, Zimmermann U (1992) Zinc ions stimulate electrofusion of Hansenula polymorpha protoplasts. FEMS Microbiol Lett 106:47–51
Scott-Taylor TH, Pettengell R, Clarke I, Stuhler G, La Barthe MC, Walden P, Dalgleish AG (2000) Human tumour and dendritic cell hybrids generated by electrofusion: potential for cancer vaccines. Biochim Biophys Acta 1500:265–279
Sowers AE (1986) A long-lived fusogenic state is induced in erythrocyte ghosts by electric pulses. J Cell Biol 102:1358–1362
Sowers AE (1989) Evidence that electrofusion yield is controlled by biologically relevant membrane factors. Biochim Biophys Acta 985:334–338
Stenger DA, Kubiniec RT, Purucker WJ, Liang H, Hui SW (1988) Optimization of electrofusion parameters for efficient production of murine hybridomas. Hybridoma 7:505–518
Stenger DA, Kaler KV, Hui SW (1991) Dipole interactions in electrofusion. Contributions of membrane potential and effective dipole interaction pressures. Biophys J 59:1074–1084
Stevens RH, Macy E, Morrow C, Saxon A (1979) Characterization of a circulating subpopulation of spontaneous antitetanus toxoid antibody producing B cells following in vivo booster immunization. J Immunol 122:2498–2504
Stuhler G, Walden P (1994) Recruitment of helper T cells for induction of tumour rejection by cytolytic T lymphocytes. Cancer Immunol Immunother 39:342–345
Sukharev SI, Bandrina IN, Barbul AI, Fedorova LI, Abidor IG, Zelenin AV (1990) Electrofusion of fibroblasts on the porous membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta 1034:125–131
Sukhorukov VL, Arnold WM, Zimmermann U (1993) Hypotonically induced changes in the plasma membrane of cultured mammalian cells. J Membr Biol 132:27–40
Sukhorukov VL, Reuss R, Zimmermann D, Held C, Müller KJ, Kiesel M, Geßner P, Steinbach A, Schenk WA, Bamberg E, Zimmermann U (2005) Surviving high-intensity field pulses: strategies for improving robustness and performance of electrotransfection and electrofusion. J Membr Biol 206:187–201
Sukhorukov VL, Reuss R, Endter JM, Fehrmann S, Katsen-Globa A, Gessner P, Steinbach A, Muller KJ, Karpas A, Zimmermann U, Zimmermann H (2006) A biophysical approach to the optimisation of dendritic–tumour cell electrofusion. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 346:829–839
Teissie J, Blangero C (1984) Direct experimental evidence of the vectorial character of the interaction between electric pulses and cells in cell electrofusion. Biochim Biophys Acta 775:446–448
Teissie J, Ramos C (1998) Correlation between electric field pulse induced long-lived permeabilization and fusogenicity in cell membranes. Biophys J 74:1889–1898
Teissie J, Rols MP (1986) Fusion of mammalian cells in culture is obtained by creating the contact between cells after their electropermeabilization. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 140:258–266
Teissie J, Knutson VP, Tsong TY, Lane MD (1982) Electric pulse-induced fusion of 3T3 cells in monolayer culture. Science 216:537–538
Trontelj K, Rebersek M, Kanduser M, Serbec VC, Sprohar M, Miklavcic D (2008) Optimization of bulk cell electrofusion in vitro for production of human–mouse heterohybridoma cells. Bioelectrochemistry 74:124–129
Urano N, Higashikawa R, Hirai H (1998) Effects of mitochondria on electrofusion of yeast protoplasts. Enzyme Microbial Technol 23:107–112
Usaj M, Trontelj K, Hudej R, Kanducer M, Miklavcic D (2009) Cell size dynamics and viability of cells exposed to hypotonic treatment and electroporation for electrofusion optimization. Radiol Oncol 43:108–119
Vienken J, Zimmermann U (1985) An improved electrofusion technique for production of mouse hybridoma cells. FEBS Lett 182:278–280
Wang J, Lu C (2006) Microfluidic cell fusion under continuous direct current voltage. Appl Physics Lett 89:234102–234103
Wu Y, Montes JG, Sjodin RA (1992) Determination of electric field threshold for electrofusion of erythrocyte ghosts. Comparison of pulse-first and contact-first protocols. Biophys J 61:810–815
Yu X, McGraw PA, House FS, Crowe JE Jr (2008) An optimized electrofusion-based protocol for generating virus-specific human monoclonal antibodies. J Immunol Methods 336:142–151
Zheng Q, Chang DC (1991) Reorganization of cytoplasmic structures during cell–cell fusion. J Cell Sci 100:431–442
Zimmermann U (1982) Electric field–mediated fusion and related electrical phenomena. Biochim Biophys Acta 694:227–277
Zimmermann U, Neil GA (1996) Electromanipulation of cells. CRC, Boca Raton, FL
Zimmermann U, Friedrich U, Mussauer H, Gessner P, Hamel K, Sukhoruhov V (2000) Electromanipulation of mammalian cells: fundamentals and application. IEEE Trans Plasma Sci 28:72–82
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the Slovenian Research Agency (ARRS).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ušaj, M., Trontelj, K., Miklavčič, D. et al. Cell–Cell Electrofusion: Optimization of Electric Field Amplitude and Hypotonic Treatment for Mouse Melanoma (B16-F1) and Chinese Hamster Ovary (CHO) Cells. J Membrane Biol 236, 107–116 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00232-010-9272-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00232-010-9272-3