Abstract
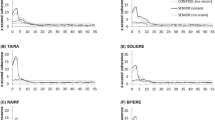
The effect of development and aging on common modulation between bilateral plantarflexors (i.e., the right and left soleus, and the right and left medial gastrocnemius) (bilateral comodulation) and within plantarflexors in one leg (i.e., the right soleus and the right medial gastrocnemius) (unilateral comodulation) was investigated during bipedal quiet standing by comparing electromyography–electromyography (EMG) coherence among three age groups: adult (23–35 years), child (6–8 years), and elderly (60–80 years). The results demonstrate that there was significant coherence between bilateral plantarflexors and within plantarflexors in one leg in the 0- to 4-Hz frequency region in all three age groups. Coherence in this frequency region was stronger in the elderly group than in the adult group, while no difference was found between the adult and child groups. Of particular interest was the finding of significant coherence in bilateral and unilateral EMG recordings in the 8- to 12-Hz frequency region in some subjects in the elderly group, whereas it was not observed in the adult and child groups. These results suggest that aging affects the organization of bilateral and unilateral postural muscle activities (i.e., bilateral and unilateral comodulation) in the plantarflexors during quiet standing.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Basmajian JV, De Luca CJ (1964) Muscle alive. Their functions revealed by electromyography. Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore, p 257
Boonstra TW, Daffertshofer A, van As E, van der Vlugt S, Beek PJ (2006) Bilateral motor unit synchronization is functionally organized. Exp Brain Res. doi:10.1007/s00221-006-0713-2
Boonstra TW, Daffertshofer A, van Ditshuizen JC, van den Heuvel MR, Hofman C, Willigenburg NW, Beek PJ (2008a) Fatigue-related changes in motor-unit synchronization of quadriceps muscles within and across legs. J Electromyogr Kinesiol 18:717–731
Boonstra TW, Roerdink M, Daffertshofer A, van Vugt B, van Werven G, Beek PJ (2008b) Low-alcohol doses reduce common 10- to 15-Hz input to bilateral leg muscles during quiet standing. J Neurophysiol 100:2158–2164
Boonstra TW, van Wijk BCM, Praamstra P, Daffertshofer A (2009) Corticomuscular and bilateral EMG coherence reflect distinct aspects of neural synchronization. Neurosci Lett 463:17–21
Carson RG (2005) Neural pathways mediating bilateral interactions between the upper limbs. Brain Res Bran Res Rev 49(3):641–662
Collins JJ, De Luca CJ, Burrows A, Lipsitz LA (1995) Age-related changes in open-loop and closed-loop postural control mechanisms. Exp Brain Res 104:480–492
Conway BA, Halliday DM, Farmer SF, Shahani U, Maas P, Weir AI, Rosenberg JR (1995) Synchronization between motor cortex and spinal motoneuronal pool during the performance of a maintained motor task in man. J Physiol 489(Pt 3):917–924
Davidson AG, Schieber MH, Buford JA (2007) Bilateral spike-triggered average effects in arm and shoulder muscles from the monkey pontomedullary reticular formation. J Neurosci 27:8053–8058
de Oliveira SC, Gribova A, Donchin O, Bergman H, Vaadia E (2001) Neural interactions between motor cortical hemispheres during bimanual and unimanual arm movements. Eur J Neurosci 14:1881–1896
Eyre JA, Taylor JP, Villagra F, Smith M, Miller S (2001) Evidence of activity-dependent withdrawal of corticospinal projections during human development. Neurolgy 57:1543–1554
Farmer SF, Bremmner FD, Halliday DM, Rosenberg JR, Stephens JA (1993) The frequency content of common synaptic inputs to motoneurones studied during voluntary isometric contraction in man. J Physiol 470:127–155
Farmer SF, Gibbs J, Halliday DM, Harrison LM, James LM, Mayston MJ, Stephens JA (2007) Changes in EMG coherence between long and short thumb abductor muscles during human development. J Physiol 579:389–402
Figura F, Cama G, Capranica L, Guidetti L, Pulejo C (1991) Assessment of static balance in children. J Sports Med Phys Fit 31:235–242
Franz EA, Eliassen JC, Ivry RB, Gazzaniga MS (1996) Dissociation of spatial and temporal coupling in the bimanual movements of callosotomy patients. Psychol Sci 7:306–310
Gatev P, Thomas S, Kepple T, Hallett M (1999) Feedforward ankle strategy of balance during quiet stance in adults. J Physiol 514(Pt 3):915–928
Gibbs J, Harrison LM, Stephens JA (1995) Organization of inputs to motoneurone pools in man. J Physiol 485(Pt 1):245–256
Grosse P, Cassidy MJ, Brown P (2002) EEG-EMG, MEG-EMG and EMG–EMG frequency analysis: physiological principles and clinical applications. Clin Neurophysiol 113(10):1523–1531
Hatzitaki V, Zisi V, Kollias I, Kioumourtzoglou E (2002) Perceptual-motor contributions to static and dynamic balance control in children. J Mot Behav 34:161–170
Horak FB, Nashner LM, Diener HC (1990) Postural strategies associated with somatosensory and vestibular loss. Exp Brain Res 82:167–177
Jankowsaka E, Hammar I, Slawinska U, Maleszak K, Edgley SA (2003) Neuronal basis of crossed actions from the reticular formation on feline hindlimb motoneurons. J Neurosci 23:1867–1878
Johnson AN, Shinohara M (2012) Corticomuscular coherence with and without additional task in the elderly. J Appl Physiol 112:970–981
Kilner JM, Baker SN, Salenius S, Hari R, Lemon RN (2000) Human cortical muscle coherence is directly related to specific motor parameters. J Neurosci 20:8838–8845
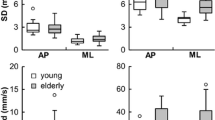
Kouzaki M, Masani K (2012) Postural sway during quiet standing is related to physiological tremor and muscle volume in young and elderly adults. Gait Posture 35:11–17
Laughton CA, Slavin M, Katdare K, Nolan L, Bean JF, Kerrigan DC, Phillips E, Lipsitz LA, Collins JJ (2003) Aging, muscle activity, and balance control: physiologic changes associated with balance impairment. Gait Posture 18:101–108
Lucy S, Hayes K (1985) Postural sway profiles: normal subjects and subjects with cerebellar ataxia. Physiother Can 37:140–148
Maki BE, McIlroy WE (1996) Postural control in the older adult. Clin Geriatr Med 12:635–658
Maki BE, Holliday PJ, Fernie GR (1990) Aging and postural control. A comparison of spontaneous- and induced-sway balance tests. J Am Geriatr Soc 38(1):1–9
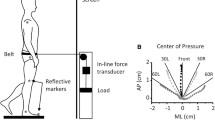
Masani K, Popovic MR, Nakazawa K, Kouzaki M, Nozaki D (2003) Importance of body sway velocity information in controlling ankle extensor activities during quiet stance. J Neurophysiol 90:3774–3782
Masani K, Vette AH, Kouzaki M, Kanehisa H, Fukunaga T, Popovic MR (2007) Larger center of pressure minus center of gravity in the elderly induces larger body acceleration during quiet standing. Neurosci Lett 422:202–206
McAuley JH, Marsden CD (2000) Physiological and pathological tremors and rhythmic central motor control. Brain 123(Pt 8):1545–1567
Mochizuki G, Semmler JG, Ivanova TD, Garland SJ (2006) Low-frequency common modulation of soleus motor unit discharge is enhanced during postural control in humans. Exp Brain Res 175:584–595
Mochizuki G, Ivanova TD, Garland SJ (2007) Factors affecting the common modulation of bilateral motor unit discharge in human soleus muscles. J Neurophysiol 97:3917–3925
Mori S (1973) Discharge patterns of soleus motor units with associated changes in force exerted by foot during quiet stance in man. J Neurophysiol 36:458–471
Mori S (1975) Entrainment of motor-unit discharges as a neuronal mechanism of synchronization. J Neurophysiol 38:859–870
Olivier I, Palluel E, Nougier V (2008) Effects of attentional focus on postural sway in children and adults. Exp Brain Res 185:341–345
Rival C, Ceyte H, Olivier I (2005) Developmental changes of static standing balance in children. Neurosci Lett 376:133–136
Rosenberg JR, Halliday DM, Breeze P, Conway BA (1998) Identification of patterns of neuronal connectivity—partial spectra, partial coherence, and neuronal interactions. J Neurosci Methods 83:57–72
Semmler JG (2002) Motor unit synchronization and neuromuscular performance. Exerc Sport Sci Rev 30:8–14
Shinoda Y, Ohgaki T, Futami T (1986) The morphology of single lateral vestibulospinal tract axons in the lower cervical spinal cord of the cat. J Comp Neurol 249:226–241
Steindl R, Kunz K, Schrott-Fischer A, Scholtz AW (2006) Effect of age and sex on maturation of sensory systems and balance control. Dev Med Child Neurol 48:477–482
Zhang C, Zhu Q, Hua T (2010) Aging of cerebellar Purkinje cells. Cell Tissue Res 341:341–347
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Obata, H., Abe, M.O., Masani, K. et al. Modulation between bilateral legs and within unilateral muscle synergists of postural muscle activity changes with development and aging. Exp Brain Res 232, 1–11 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-013-3702-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-013-3702-2