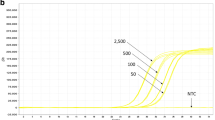
Abstract
Five double-target multiplex plasmids to be used as calibrants for GMO quantification were constructed. They were composed of two modified targets associated in tandem in the same plasmid : (1) a part of the soybean lectin gene and (2) a part of the transgenic construction of the GTS40-3-2 event. Modifications were performed in such a way that each target could be amplified with the same primers as those for the original target from which they were derived but such that each was specifically detected with an appropriate probe. Sequence modifications were done to keep the parameters of the new target as similar as possible to those of its original sequence. The plasmids were designed to be used either in separate reactions or in multiplex reactions. Evidence is given that with each of the five different plasmids used in separate wells as a calibrant for a different copy number, a calibration curve can be built. When the targets were amplified together (in multiplex) and at different concentrations inside the same well, the calibration curves showed that there was a competition effect between the targets and this limits the range of copy numbers for calibration over a maximum of 2 orders of magnitude. Another possible application of multiplex plasmids is discussed.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Permingeat HR, Reggiardo MI, Vallejos RH (2002) J Agric Food Chem 50:4431–4436
James D, Schmidt AM, Wall E, Green M, Masri S (2003) J Agric Food Chem 51:5829–5834
Singh CK, Ojha A, Kachru DN (2007) J AOAC Int 90:1517–1525
Matsuoka T, Kuribara H, Akiyama H, Miura H, Goda Y, Kusakabe Y, Isshiki K, Toyoda M, Hino A (2001) Shokuhin Eiseigaku Zasshi 42:24–32
García-Cañas V, González R, Cifuentes A (2004) Electrophoresis 25:2219–2226
Germini A, Zanetti A, Salati C, Rossi S, Forre C, Schmid S, Marchelli R, Fogher C (2004) J Agric Food Chem 52:3275–3280
Shrestha HK, Hwu KK, Wang SJ, Liu LF, Chang MC (2008) J Agric Food Chem 56:8962–8968
Hernandez M, Esteve T, Pla M (2005) J Agric Food Chem 53:7003–7009
Heide BR, Heir E, Holck A (2008) Eur Food Res Technol 227:527–535
Onishi M, Matsuoka T, Kodama T, Kashiwaba K, Futo S, Akiyama H, Maitani T, Furui S, Oguchi T, Hino A (2005) J Agric Food Chem 53:9713–9721
Hamels S, Glouden T, Gillard K, Mazzara M, Debode F, Foti N, Sneyers M, Teresa E, Pla M, Berben G, Moens W, Bertheau Y, Audeon C, van Den Eede G, Remacle J (2009) Eur Food Res Technol 228:1438–2377
Xu J, Zhu SF, Miao HZ, Huang WS, Qiu MY, Huang Y, Fu XP, Li Y (2007) J Agric Food Chem 55:5575–5579
Nadal A, Coll A, La Paz JL, Esteve T, Pla M (2006) Electrophoresis 27:3879–3888
Hernandez M, Rodriguez-Lazaro D, Esteve T, Prat S, Pla M (2003) Anal Biochem 323:164–170
Huang P, Pan TZ (2004) J Agric Food Chem 52:3264–3268
Leimanis S, Hernández M, Fernández S, Boyer F, Burns M, Bruderer S, Glouden T, Harris N, Kaeppeli O, Philipp P, Pla M, Puigdomènech P, Vaitilingom M, Bertheau Y, Remacle J (2006) Plant Mol Biol 61:123–139
Rudi K, Rud I, Holck A (2003) Nucleic Acids Res 31(11):e62
Foti N, Onori R, Donnarumma E, De Santis B, Miraglia M (2006) Eur Food Res Technol 222:209–216
Weighardt F, Barbati C, Paoletti C, Querci M, Kay S, De Beuckeleer M, Van den Eede G (2004) J AOAC Int 87:1342–1355
Trapmann S, Catalani P, Conneely P, Corbisier P, Gancberg D, Hannes E, Guern L, Kramer GN (2002) The certification of reference materials of dry-mixed soya powder with different mass fractions of Roundup Ready soya. Certified reference materials IRMM-410-S. European Commission, DG-JRC, IRMM. http://irmm.jrc.be/rm/cert-reports/IRMM-410s_report.pdf
European Commission (2004) Recommendation 2004/787/EC. Off J Eur Union L 348:18–24
Charels D, Broeders S, Corbisier P, Trapmann S, Schimmels H, Linsinger T, Emons H (2007) J Agric Food Chem 55:3258–3267
Charels D, Broeders S, Corbisier P, Trapmann S, Schimmels H, Linsinger T, Emons H (2007) J Agric Food Chem 55:3268–3274
Burns M, Corbisier P, Wiseman G, Valdivia H, McDonald P, Bowler P, Ohara K, Schimmel H, Charels D, Damant A, Harris N (2006) Eur Food Res Technol 224:249–258
Taverniers I, Van Bockstaele E, De Loose M (2004) Anal Bioanal Chem 378:1198–1207
Block A, Schwarz (2003) Eur Food Res Technol 216:421–427
Mattarucchi E, Weighardt F, Barbati C, Querci M, Van den Eede G (2005) Eur Food Res Technol 221:511–519
Shindo Y, Kuribara H, Matsuoka T, Futo S, Sawada C, Shono J, Akiyama H, Goda Y, Toyoda M, Hino A (2002) J AOAC Int 85:1119–1126
Yang L, Pan A, Zhang K, Yin C, Qian B, Chen J, Huang C, Zhang D (2005) Transgenic Res 14:817–831
Kuribara H, Shindo Y, Matsuoka T, Takubo K, Futo S, Aoki N, Hirao T, Akiyama H, Goda Y, Toyoda M, Hino A (2002) J AOAC Int 85:1077–1089
Yang L, Guo J, Pan A, Zhang H, Zhang K, Wang Z, Zhang D (2007) J Agric Food Chem 55:15–24
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning. A laboratory manual, 2nd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor
Association Française de Normalisation (2005) ISO 21570. Foodstuffs - methods of analysis for the detection of genetically modified organisms and derived products - quantitative nucleic acid based methods. Association Française de Normalisation, Paris
Querci M, Kleter G, Malingreau JP, Broll H, Van den Eede G (2008) Scientific and technical contribution to the development of an overall health strategy in the area of GMOs. JRC-IHCP reference reports. Report EUR 23542 EN. http://ec.europa.eu/dgs/jrc/downloads/jrc_reference_report_2008_11_healthstrategy_gmos.pdf
Love JL, Scholes P, Gilpin B, Savill M, Lin S, Samuel L (2006) J Microbiol Method 67:349–356
European Network of GMO Laboratories (2008) Definition of minimum performance requirements for analytical methods of GMO testing. EU DG-JRC ENGL method performance requirements. EU DG-JRC, Ispra. http://gmo-crl.jrc.ec.europa.eu/guidancedocs.htm
Huang C-C, Pan T-Z (2005) J Agric Food Chem 53:3833–3839
Rønning SB, Vaitilingom M, Berdal KG, Holst-Jensen A (2003) Eur Food Res Technol 216:347–354
Acknowledgements
This research was done within a Belgian research project (S-6140) financed by DG4 and DG6 of the former Belgian Federal Ministry of Agriculture. We are grateful to Aurélie Hosselet (HECE Fleurus) for her technical help and Nicole Wellens (Isogen Life Sciences, De Meern, the Netherlands) for advice with pyrosequencing.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Debode, F., Marien, A., Janssen, E. et al. Design of multiplex calibrant plasmids, their use in GMO detection and the limit of their applicability for quantitative purposes owing to competition effects. Anal Bioanal Chem 396, 2151–2164 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-009-3396-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-009-3396-2