Abstract
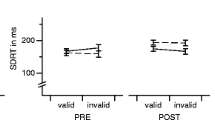
We have previously shown that 0.5mg haloperidol (IV) increased latent inhibition in one of two visual tasks. The present study analysed the effects of a higher dose of haloperidol (1.0 mg, IV) on latent inhibition in these two visual tasks in healthy volunteers in a randomised controlled trial. In the task where 0.5 mg haloperidol had enhanced latent inhibition, 1.0 mg had the same effect, thus replicating the previous result. In the task where 0.5 mg haloperidol had been ineffective, 1.0 mg haloperidol enhanced latent inhibition in high schizotypal subjects only. This indicates that subjects with higher schizotypy scores are more sensitive to dopamine blockade. A comparison of the results from the studies at the two different doses suggests a dose dependence of haloperidol’s effects on latent inhibition that parallels results from animal work.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 10 January 1997 /Final version: 24 April 1997
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Williams, J., Wellman, N., Geaney, D. et al. Haloperidol enhances latent inhibition in visual tasks in healthy people. Psychopharmacology 133, 262–268 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002130050400
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002130050400