Abstract.
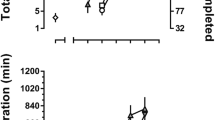
Rationale: 2β-propanoyl-3β-(4-tolyl)-tropane (PTT) is a cocaine analog with high affinity at and selectivity for the dopamine transporter (DAT). 2β-propanoyl-3β-(2-naphthyl)-tropane (HD-23), like cocaine, binds with approximately equal affinity to the DAT, the serotonin transporter, and the norepinephrine transporter but has over a 100-fold higher affinity for these monoamine transporters than cocaine. The reinforcing effects of these drugs have not been evaluated in cocaine-naïve non-human primates. Objective: The primary goal of the present study was to examine the reinforcing effects of PTT and HD-23 in rhesus monkeys before and after a history of intravenous cocaine self-administration. Methods: Monkeys (n=4) were initially trained to respond under a fixed-ratio 30 schedule of food presentation. When responding was stable, saline, PTT (0.001–0.03 mg/kg per injection), and HD-23 (0.0003–0.0056 mg/kg per injection) were made available for self-administration for least five sessions per dose. Next, a cocaine dose-effect function (0.0003–0.3 mg/kg per injection) was determined and then PTT and HD-23 dose-effect curves were redetermined. Results: When substituted for food, neither drug maintained responding significantly higher than saline during 3-h (PTT and HD-23) or 22-h (PTT) sessions. After determining the cocaine dose-effect function, PTT and HD-23 functioned as reinforcers in one of four monkeys, when substituted for food during daily 3-h sessions. However, when PTT was made available during 22-h sessions, it had reinforcing effects in three of the four monkeys tested. Conclusions: These results indicate that the reinforcing effects of PTT were slightly modified by a brief history of cocaine reinforcement, and that the weak reinforcing effects were most apparent when the drug was available under unlimited-access conditions.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lile, J., Morgan, D., Freedland, C. et al. Self-administration of two long-acting monoamine transport blockers in rhesus monkeys. Psychopharmacology 152, 414–421 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002130000554
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002130000554