Abstract
Rationale
AKB48 and its fluorinate derivate 5F-AKB48 are two novel synthetic cannabinoids belonging to a structural class with an indazole core structure. They are marketed as incense, herbal preparations or chemical supply for their psychoactive Cannabis-like effects.
Objectives
The present study was aimed at investigating the in vitro and in vivo pharmacological activity of AKB48 and 5F-AKB48 in male CD-1 mice and comparing their in vivo effects with those caused by the administration of Δ9-THC and JWH-018.
Results
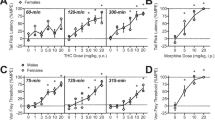
In vitro competition binding experiments performed on mouse and human CB1 and CB2 receptors revealed a nanomolar affinity and potency of the AKB48 and 5F-AKB48. In vivo studies showed that AKB48 and 5F-AKB48, induced hypothermia, increased pain threshold to both noxious mechanical and thermal stimuli, caused catalepsy, reduced motor activity, impaired sensorimotor responses (visual, acoustic and tactile), caused seizures, myoclonia, hyperreflexia and promoted aggressiveness in mice. Moreover, microdialysis study in freely moving mice showed that systemic administration of AKB48 and 5F-AKB48 stimulated dopamine release in the nucleus accumbens. Behavioural, neurological and neurochemical effects were fully prevented by the selective CB1 receptor antagonist/inverse agonist AM 251.
Conclusions
For the first time, the present study demonstrates the overall pharmacological effects induced by the administration of AKB48 and 5F-AKB48 in mice and suggests that the fluorination can increase the power and/or effectiveness of SCBs. Furthermore, this study outlines the potential detrimental effects of SCBs on human health.

















Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AM 251:
-
1-(2,4-Dichlorophenyl)-5-(4-iodophenyl)-4-methyl-N-(piperidin-1-yl)-1H-pyrazole-3-carboxamide
- AKB48:
-
N-(1-Adamantyl)-1-pentyl-1H-indazole-3-carboxamide
- DA:
-
Dopamine
- NAc shell:
-
Nucleus accumbens shell
- Δ9-THC:
-
(−)-Δ9-THC or Dronabinol®
- JWH-018:
-
Naphthalen-1-yl-(1-pentylindol-3-yl)methanone
- 5F-AKB48:
-
N-(1-Adamantyl)-1-(5-fluoropentyl)-1H-indazole-3- carboxamide
References
Barbieri M, Ossato A, Canazza I, Trapella C, Borelli AC, Beggiato S, Rimondo C, Serpelloni G, Ferraro L, Marti M (2016) Synthetic cannabinoid JWH-018 and its halogenated derivatives JWH-018-Cl and JWH-018-Br impair novel object recognition in mice: behavioral, electrophysiological and neurochemical evidence. Neuropharmacology 109:254–269
Bereiter DA, Bereiter DF, Hirata H (2002) Topical cannabinoid agonist, WIN55,212-2, reduces cornea-evoked trigeminal brainstem activity in the rat. Pain 99:547–556
Bortolato M, Aru GN, Frau R, Orru M, Luckey GC, Boi G, Gessa GL (2005) The CB receptor agonist WIN 55,212-2 fails to elicit disruption of prepulse inhibition of the startle in Sprague-Dawley rats. Psychopharmacology 177:264–271
Brents LK, Gallus-Zawada A, Radominska-Pandya A, Vasiljevik T, Prisinzano TE, Fantegrossi WE, Moran JH, Prather PL (2012) Monohydroxylated metabolites of the K2 synthetic cannabinoid JWH-073 retain intermediate to high cannabinoid 1 receptor (CB1R) affinity and exhibit neutral antagonist to partial agonist activity. Biochem Pharmacol 83:952–961
Brents LK, Reichard EE, Zimmerman SM, Moran JH, Fantegrossi WE, Prather PL (2011) Phase I hydroxylated metabolites of the K2 synthetic cannabinoid JWH-018 retain in vitro and in vivo cannabinoid 1 receptor affinity and activity. PLoS One 6:e21917
Carder B, Olson J (1972) Marihuana and shock induced aggression in rats. Physiol Behav 8:599–602
Carlini EA, Gonzales C (1972) Aggressive behaviour induced by marihuana compounds and amphetamine in rats previously made dependent on morphine. Experientia 28:542–544
Carlini EA, Lindsey CJ, Tufik S (1976) Environmental and drug interference with effects of marihuana. Ann N Y Acad Sci 281:229–243
Compton DR, Johnson MR, Melvin LS, Martin BR (1992) Pharmacological profile of a series of bicyclic cannabinoid analogs: classification as cannabimimetic agents. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 260:201–209
Cristino L, de Petrocellis L, Pryce G, Baker D, Guglielmotti V, Di Marzo V (2006) Immunohistochemical localization of cannabinoid type 1 and vanilloid transient receptor potential vanilloid type 1 receptors in the mouse brain. Neuroscience 139:1405–1415
Dasilva MA, Grieve KL, Cudeiro J, Rivadulla C (2012) Endocannabinoid CB1 receptors modulate visual output from the thalamus. Psychopharmacology 219:835–845
De Luca MA, Bimpisidis Z, Melis M, Marti M, Caboni P, Valentini V, Margiani G, Pintori N, Polis I, Marsicano G, Parsons LH, Di Chiara G (2015a) Stimulation OF IN VIVO dopamine transmission and intravenous self-administration in rats and mice by JWH-018, a Spice cannabinoid. Neuropharmacology.
De Luca MA, Castelli MP, Loi B, Porcu A, Martorelli M, Miliano C, Kellett K, Davidson C, Stair LJ, Schifano F, Di Chiara G (2015b) Native CB1 receptor affinity, intrisic activity and accumbens shell dopamine stimulant properties of third generation SPICE/K2 cannabinoids: BB-22, 5F-PB-22, 5F-AKB-48 and STS-135. Neuropharmacology.
Dhawan J, Deng H, Gatley SJ, Makriyannis A, Akinfeleye T, Bruneus M, Dimaio AA, Gifford AN (2006) Evaluation of the in vivo receptor occupancy for the behavioral effects of cannabinoids using a radiolabeled cannabinoid receptor agonist, R-[125/131I]AM2233. Synapse (New York, NY) 60:93–101
Di Chiara G, Bassareo V, Fenu S, De Luca MA, Spina L, Cadoni C, Acquas E, Carboni E, Valentini V, Lecca D (2004) Dopamine and drug addiction: the nucleus accumbens shell connection. Neuropharmacology 47(Suppl 1):227–241
DrugsForum (2012a) AKB-48 (APINACA) drug info. [online] Available at: http://www.drugs-forum.com/forum/showthread.php?t=187522 [Accessed 11 October 2013].
DrugsForum (2012b) Experience with UR-144, 5F-UR-144, AKB-48, & STS-135. [online] Available at: http://www.drugs-forum.com/forum/showthread.php?t=192321 [Accessed 10 October 2013].
EMCDDA (2009) Understanding the ‘spice’ phenomenon. Thematic papers. European Monitoring Centre for Drugs and Drug Addiction. http://www.emcdda.europa.eu/publications/thematic-papers/spice
EMCDDA (2015) European drug report, trends and developments. Thematic papers. European Monitoring Centre for Drugs and Drug Addiction. http://www.emcdda.europa.eu/attachements.cfm/att_239505_EN_TDAT15001ENN.pdf.
Fattore L, Spano S, Cossu G, Deiana S, Fadda P, Fratta W (2005) Cannabinoid CB(1) antagonist SR 141716 A attenuates reinstatement of heroin self-administration in heroin-abstinent rats. Neuropharmacology 48:1097–1104
Gandhi AS, Zhu M, Pang S, Wohlfarth A, Scheidweiler KB, Liu HF, Huestis MA (2013) First characterization of AKB-48 metabolism, a novel synthetic cannabinoid, using human hepatocytes and high-resolution mass spectrometry. AAPS J 15:1091–1098
Gatch MB, Forster MJ (2015) Delta9-Tetrahydrocannabinol-like effects of novel synthetic cannabinoids found on the gray market. Behav Pharmacol 26:460–468
Gomez-Nieto R, Horta-Junior Jde A, Castellano O, Millian-Morell L, Rubio ME, Lopez DE (2014) Origin and function of short-latency inputs to the neural substrates underlying the acoustic startle reflex. Front Neurosci 8:216
Gugelmann H, Gerona R, Li C, Tsutaoka B, Olson KR, Lung D (2014) ‘Crazy monkey’ poisons man and dog: human and canine seizures due to PB-22, a novel synthetic cannabinoid. Clin Toxicol (Phila) 52:635–638
Guindon J, Hohmann AG (2008) Cannabinoid CB2 receptors: a therapeutic target for the treatment of inflammatory and neuropathic pain. Br J Pharmacol 153:319–334
Ham MT, De Jong Y (1975) Absence of interaction between delta9-tetrahydrocannabinol (delta-THC) and cannabidiol (CBD) in aggression, muscle control and body temperature experiments in mice. Psychopharmacologia 41:169–174
Hamdam J, Sethu S, Smith T, Alfirevic A, Alhaidari M, Atkinson J, Ayala M, Box H, Cross M, Delaunois A, Dermody A, Govindappa K, Guillon J-M, Jenkins R, Kenna G, Lemmer B, Meecham K, Olayanju A, Pestel S, Rothfuss A, Sidaway J, Sison-Young R, Smith E, Stebbings R, Tingle Y, Valentin J-P, Williams A, Williams D, Park K, Goldring C (2013) Safety pharmacology—current and emerging concepts. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 273:229–241
Hemelt ME, Keller A (2008) Superior colliculus control of vibrissa movements. J Neurophysiol 100:1245–1254
Herkenham M, Lynn AB, Johnson MR, Melvin LS, de Costa BR, Rice KC (1991) Characterization and localization of cannabinoid receptors in rat brain: a quantitative in vitro autoradiographic study. J Neurosci Off J Soc Neurosci 11:563–583
Ho WS, Patel S, Thompson JR, Roberts CJ, Stuhr KL, Hillard CJ (2010) Endocannabinoid modulation of hyperaemia evoked by physiologically relevant stimuli in the rat primary somatosensory cortex. Br J Pharmacol 160:736–746
Hohmann AG, Tsou K, Walker JM (1999) Cannabinoid suppression of noxious heat-evoked activity in wide dynamic range neurons in the lumbar dorsal horn of the rat. J Neurophysiol 81:575–583
Holm NB, Nielsen LM, Linnet K (2015) CYP3A4 mediates oxidative metabolism of the synthetic cannabinoid AKB-48. AAPS J 17:1237–1245
Irwin S (1968) Comprehensive observational assessment: Ia. A systematic, quantitative procedure for assessing the behavioral and physiologic state of the mouse. Psychopharmacologia 13:222–257
Jenkins S, Worthington M, Harris J, Clarke RW (2004) Differential modulation of withdrawal reflexes by a cannabinoid in the rabbit. Brain Res 1012:146–153
Karinen R, Tuv SS, Oiestad EL, Vindenes V (2015) Concentrations of APINACA, 5F-APINACA, UR-144 and its degradant product in blood samples from six impaired drivers compared to previous reported concentrations of other synthetic cannabinoids. Forensic Sci Int 246:98–103
Koch M (1999) The neurobiology of startle. Prog Neurobiol 59:107–128
Koller VJ, Ferk F, Al-Serori H, Misik M, Nersesyan A, Auwarter V, Grummt T, Knasmuller S (2015) Genotoxic properties of representatives of alkylindazoles and aminoalkyl-indoles which are consumed as synthetic cannabinoids. Food and chemical toxicology: an international journal published for the British Industrial Biological Research Association 80:130–136
Lapoint J, James LP, Moran CL, Nelson LS, Hoffman RS, Moran JH (2011) Severe toxicity following synthetic cannabinoid ingestion. Clin Toxicol (Phila) 49:760–764
Lecca D, Cacciapaglia F, Valentini V, Di Chiara G (2006) Monitoring extracellular dopamine in the rat nucleus accumbens shell and core during acquisition and maintenance of intravenous WIN 55,212-2 self-administration. Psychopharmacology 188:63–74
Macri S, Lanuzza L, Merola G, Ceci C, Gentili S, Valli A, Macchia T, Laviola G (2013) Behavioral responses to acute and sub-chronic administration of the synthetic cannabinoid JWH-018 in adult mice prenatally exposed to corticosterone. Neurotox Res 24:15–28
Malone DT, Taylor DA (2006) The effect of Delta9-tetrahydrocannabinol on sensorimotor gating in socially isolated rats. Behav Brain Res 166:101–109
Mansbach RS, Rovetti CC, Winston EN, Lowe JA 3rd (1996) Effects of the cannabinoid CB1 receptor antagonist SR141716A on the behavior of pigeons and rats. Psychopharmacology 124:315–322
Marshell R, Kearney-Ramos T, Brents LK, Hyatt WS, Tai S, Prather PL, Fantegrossi WE (2014) In vivo effects of synthetic cannabinoids JWH-018 and JWH-073 and phytocannabinoid Delta-THC in mice: inhalation versus intraperitoneal injection. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 124C:40–47
Marsicano G, Lutz B (1999) Expression of the cannabinoid receptor CB1 in distinct neuronal subpopulations in the adult mouse forebrain. Eur J Neurosci 11:4213–4225
Marti M, Mela F, Fantin M, Zucchini S, Brown JM, Witta J, Di Benedetto M, Buzas B, Reinscheid RK, Salvadori S, Guerrini R, Romualdi P, Candeletti S, Simonato M, Cox BM, Morari M (2005) Blockade of nociceptin/Orphanin FQ transmission attenuates symptoms and neurodegeneration associated with Parkinson’s disease. J Neurosci 25:9591–9601
Marti M, Mela F, Guerrini R, Calò G, Bianchi C, Morari M (2004) RAPID COMMUNICATION: blockade of nociceptin/orphanin FQ transmission in rat substantia nigra reverses haloperidol-induced akinesia and normalizes nigral glutamate release. J Neurochem 91:1501–1504
Marti M, Ossato A, Trapella C, Seri C, Rimondo C, Serpelloni G (2013) JWH-018 and its N-pentyl-halogenated derivates impair sensory motor functions in mice. First Monothematic Congress of the Italian Society of Pharmacology: “Old and new drugs of abuse, issues and research approaches” Verona, Italy.
Martin RS, Secchi RL, Sung E, Lemaire M, Bonhaus DW, Hedley LR, Lowe DA (2003) Effects of cannabinoid receptor ligands on psychosis-relevant behavior models in the rat. Psychopharmacology 165:128–135
Martin WJ, Hohmann AG, Walker JM (1996) Suppression of noxious stimulus-evoked activity in the ventral posterolateral nucleus of the thalamus by a cannabinoid agonist: correlation between electrophysiological and antinociceptive effects. J Neurosci Off J Soc Neurosci 16:6601–6611
Mattsson JL, Spencer PJ, Albee RR (1996) A performance standard for clinical and functional observational battery examinations of rats. Int J Toxicol 15:239–254
McQuade D, Hudson S, Dargan PI, Wood DM (2013) First European case of convulsions related to analytically confirmed use of the synthetic cannabinoid receptor agonist AM-2201. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 69:373–376
Miczek KA (1978) delta9-tetrahydrocannabinol: antiaggressive effects in mice, rats, and squirrel monkeys. Science (New York, NY) 199:1459–1461
Miczek KA, de Almeida RMM, Kravitz EA, Rissman EF, de Boer SF, Raine A (2007). Neurobiology of Escalated Aggression and Violence. The Journal of Neuroscience. 27:11803–6
Miliano C, Serpelloni G, Rimondo C, Mereu M, Marti M, De Luca MA (2016) Neuropharmacology of new psychoactive substances (NPS): focus on the rewarding and reinforcing properties of Cannabimimetics and amphetamine-like stimulants. Front Neurosci 10:153. doi:10.3389/fnins.2016.00153
Morales M, Bonci A (2012) Getting to the core of addiction: hooking CB2 receptor into drug abuse? Nat Med 18:504–505
Nagai H, Egashira N, Sano K, Ogata A, Mizuki A, Mishima K, Iwasaki K, Shoyama Y, Nishimura R, Fujiwara M (2006) Antipsychotics improve Delta9-tetrahydrocannabinol-induced impairment of the prepulse inhibition of the startle reflex in mice. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 84:330–336
NFLIS (2013) Annual Report. Thematic paper. U.S. Department Of Justice, D. E. A., Office Of Diversion Control, National Forensic Laboratory Information System. http://www.deadiversion.usdoj.gov/nflis/NFLIS2013AR.pdf
Nordstedt C, Fredholm BB (1990) A modification of a protein-binding method for rapid quantification of cAMP in cell-culture supernatants and body fluid. Anal Biochem 189:231–234
Odoardi S, Romolo FS, Strano-Rossi S (2016) A snapshot on NPS in Italy: distribution of drugs in seized materials analysed in an Italian forensic laboratory in the period 2013-2015. Forensic Sci Int 265:116–120
Ossato A, Canazza I, Trapella C, Vincenzi F, De Luca MA, Rimondo C, Varani K, Borea PA, Serpelloni G, Marti M (2016) Effect of JWH-250, JWH-073 and their interaction on “tetrad”, sensorimotor, neurological and neurochemical responses in mice. Prog Neuro-Psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 67:31–50
Ossato A, Vigolo A, Trapella C, Seri C, Rimondo C, Serpelloni G, Marti M (2015) JWH-018 impairs sensorimotor functions in mice. Neuroscience 300:174–188
Papanastassiou AM, Fields HL, Meng ID (2004) Local application of the cannabinoid receptor agonist, WIN 55,212-2, to spinal trigeminal nucleus caudalis differentially affects nociceptive and non-nociceptive neurons. Pain 107:267–275
Patel S, Gerrits R, Muthian S, Greene AS, Hillard CJ (2002) The CB1 receptor antagonist SR141716 enhances stimulus-induced activation of the primary somatosensory cortex of the rat. Neurosci Lett 335:95–98
Paxinos G, Franklin KBJ (2001) The mouse brain in stereotaxic coordinates. Academic Press, San Diego
Pietr MD, Knutsen PM, Shore DI, Ahissar E, Vogel Z (2010) Cannabinoids reveal separate controls for whisking amplitude and timing in rats. J Neurophysiol 104:2532–2542
Pontieri FE, Tanda G, Di Chiara G (1995) Intravenous cocaine, morphine, and amphetamine preferentially increase extracellular dopamine in the “shell” as compared with the “core” of the rat nucleus accumbens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 92:12304–12308
Porsolt RD, Lemaire M, Dürmüller N, Roux S (2002) New perspectives in CNS safety pharmacology. Fundamental & Clinical Pharmacology 16:197–207
Price TJ, Helesic G, Parghi D, Hargreaves KM, Flores CM (2003) The neuronal distribution of cannabinoid receptor type 1 in the trigeminal ganglion of the rat. Neuroscience 120:155–162
Redfern WS, Strang I, Storey S, Heys C, Barnard C, Lawton K, Hammond TG, Valentin J-P (2005) Spectrum of effects detected in the rat functional observational battery following oral administration of non-CNS targeted compounds. J Pharmacol Toxicol Methods 52:77–82
Reig R, Silberberg G (2014) Multisensory integration in the mouse striatum. Neuron 83:1200–1212
S7A (2001) US Food and Drug Administration Guidance for industry: safety pharmacology studies for human pharmaceuticals (S7 A).
Santacroce R, Corazza O, Martinotti G, Bersani FS, Valeriani G, Di Giannantonio M (2015) Psyclones: a roller coaster of life? Hidden synthetic cannabinoids and stimulants in apparently harmless products. Human psychopharmacology 30:265–271
Schifano F, Orsolini L, Duccio Papanti G, Corkery JM (2015) Novel psychoactive substances of interest for psychiatry. World psychiatry: official journal of the World Psychiatric Association (WPA) 14:15–26
Schneider M, Koch M (2002) The cannabinoid agonist WIN 55,212-2 reduces sensorimotor gating and recognition memory in rats. Behav Pharmacol 13:29–37
Schneir AB, Baumbacher T (2012) Convulsions associated with the use of a synthetic cannabinoid product. J Med Toxicol 8:62–64
Seely KA, Lapoint J, Moran JH, Fattore L (2012) Spice drugs are more than harmless herbal blends: a review of the pharmacology and toxicology of synthetic cannabinoids. Prog Neuro-Psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 39:234–243
Simmons JR, Skinner CG, Williams J, Kang CS, Schwartz MD, Wills BK (2011) Intoxication from smoking “spice”. Ann Emerg Med 57:187–188
Tanda G, Pontieri FE, Frau R, Di Chiara G (1997) Contribution of blockade of the noradrenaline carrier to the increase of extracellular dopamine in the rat prefrontal cortex by amphetamine and cocaine. Eur J Neurosci 9:2077–2085
Takahashi A, Miczek KA (2014) Neurogenetics of aggressive behavior: studies in rodents. Curr Top Behav Neurosci 17:3–44
Tsou K, Brown S, Sanudo-Pena MC, Mackie K, Walker JM (1998) Immunohistochemical distribution of cannabinoid CB1 receptors in the rat central nervous system. Neuroscience 83:393–411
Tzounopoulos T, Rubio ME, Keen JE, Trussell LO (2007) Coactivation of pre- and postsynaptic signaling mechanisms determines cell-specific spike-timing-dependent plasticity. Neuron 54:291–301
Uchiyama N, Kawamura M, Kikura-Hanajiri R, Goda Y (2012) Identification of two new-type synthetic cannabinoids, N-(1-adamantyl)-1-pentyl-1H-indole-3-carboxamide (APICA) and N-(1-adamantyl)-1-pentyl-1H-indazole-3-carboxamide (APINACA), and detection of five synthetic cannabinoids, AM-1220, AM-2233, AM-1241, CB-13 (CRA-13), and AM-1248, as designer drugs in illegal products. Forensic Toxicol 30:114–125
Uchiyama N, Kawamura M, Kikura-Hanajiri R, Goda Y (2013) URB-754: a new class of designer drug and 12 synthetic cannabinoids detected in illegal products. Forensic Sci Int 227:21–32
van Ree JM, Niesink RJ, Nir I (1984) Delta 1-Tetrahydrocannabinol but not cannabidiol reduces contact and aggressive behavior of rats tested in dyadic encounters. Psychopharmacology 84:561–565
Vigolo A, Ossato A, Trapella C, Vincenzi F, Rimondo C, Seri C, Varani K, Serpelloni G, Marti M (2015) Novel halogenated derivates of JWH-018: behavioral and binding studies in mice. Neuropharmacology 95:68–82
Vikingsson S, Josefsson M, Green H (2015) Identification of AKB-48 and 5F-AKB-48 metabolites in authentic human urine samples using human liver microsomes and time of flight mass spectrometry. J Anal Toxicol 39:426–435
Vincenzi F, Targa M, Corciulo C, Tabrizi MA, Merighi S, Gessi S, Saponaro G, Baraldi PG, Borea PA, Varani K (2013) Antinociceptive effects of the selective CB2 agonist MT178 in inflammatory and chronic rodent pain models. Pain 154:864–873
Wegener N, Kuhnert S, Thuns A, Roese R, Koch M (2008) Effects of acute systemic and intra-cerebral stimulation of cannabinoid receptors on sensorimotor gating, locomotion and spatial memory in rats. Psychopharmacology 198:375–385
Wiebelhaus JM, Poklis JL, Poklis A, Vann RE, Lichtman AH, Wise LE (2012) Inhalation exposure to smoke from synthetic “marijuana” produces potent cannabimimetic effects in mice. Drug Alcohol Depend 126:316–323
Wiley JL, Compton DR, Dai D, Lainton JA, Phillips M, Huffman JW, Martin BR (1998) Structure-activity relationships of indole- and pyrrole-derived cannabinoids. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 285:995–1004
Wiley JL, Marusich JA, Huffman JW (2014) Moving around the molecule: relationship between chemical structure and in vivo activity of synthetic cannabinoids. Life Sci 97:55–63
Winton-Brown TT, Allen P, Bhattacharyya S, Borgwardt SJ, Fusar-Poli P, Crippa JA, Seal ML, Martin-Santos R, Ffytche D, Zuardi AW, Atakan Z, McGuire PK (2011) Modulation of auditory and visual processing by delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol and cannabidiol: an FMRI study. Neuropsychopharmacology: official publication of the American College of Neuropsychopharmacology 36:1340–1348
Xi ZX, Peng XQ, Li X, Song R, Zhang HY, Liu QR, Yang HJ, Bi GH, Li J, Gardner EL (2011) Brain cannabinoid CB(2) receptors modulate cocaine’s actions in mice. Nat Neurosci 14:1160–1166
Yoneda T, Kameyama K, Esumi K, Daimyo Y, Watanabe M, Hata Y (2013) Developmental and visual input-dependent regulation of the CB1 cannabinoid receptor in the mouse visual cortex. PLoS One 8:e53082
Acknowledgments
This research has been funded by the Drug Policies Department, Presidency of the Council of Ministers, Italy (project NS-Drugs to M. Marti) and by local funds from the University of Ferrara to M. Marti. All applicable international, national and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed. All procedures performed in the studies involving animals were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institution or practice at which the studies were conducted.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Additional information
Isabella Canazza and Andrea Ossato are equally contributed to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOC 118 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Canazza, I., Ossato, A., Trapella, C. et al. Effect of the novel synthetic cannabinoids AKB48 and 5F-AKB48 on “tetrad”, sensorimotor, neurological and neurochemical responses in mice. In vitro and in vivo pharmacological studies. Psychopharmacology 233, 3685–3709 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-016-4402-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-016-4402-y