Abstract
Rationale
Although the antidepressant and anxiolytic effects of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors and serotonin–noradrenaline reuptake inhibitors are well-documented, less is known about their cognitive effects.
Objective
Escitalopram, a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor, and atomoxetine, a selective noradrenaline reuptake inhibitor, were used to evaluate the interaction between noradrenergic and serotonergic neurotransmission in the modulation of contextual fear conditioning in rats.
Methods
Contextual fear-conditioning test was used to investigate the acute effects of escitalopram, alone or in combination with atomoxetine, in different stages of learning and memory in rats. Furthermore, microdialysis in freely moving animals was used to investigate the effect of escitalopram on serotonin, dopamine, and noradrenaline levels in the rat hippocampus.
Results
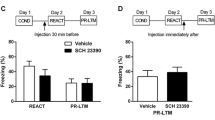
Escitalopram significantly increased conditioned responses when applied before the acquisition, but decreased responses, when applied before the recall test. When administered during memory consolidation, escitalopram dose-dependently enhanced conditioned responding. These effects were blocked by atomoxetine. Escitalopram (at a dose that affects memory consolidation) increased hippocampal serotonin levels fourfold without changing dopamine or noradrenaline. Atomoxetine, at dose levels that blocked the effects of escitalopram on contextual fear conditioning, increased the extracellular levels of noradrenaline eightfold but did not change dopamine or serotonin. A combined treatment of escitalopram and atomoxetine caused a significant attenuation of escitalopram-induced increase in serotonin levels, while noradrenaline levels were not affected.
Conclusions
These findings indicate that escitalopram affects fear memory in rats, likely modulated by increases in serotonin levels in the brain. This effect is impaired by atomoxetine, probably due to a noradrenaline-mediated decrease in serotonin levels. Further studies are warranted to study the effects of potential differences among antidepressant therapies on long-term cognitive outcomes.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- 5-HT:
-
Serotonin
- CR:
-
Conditioned fear response
- CS:
-
Conditioned stimulus
- DA:
-
Dopamine
- NA:
-
Noradrenaline
- NAT:
-
Noradrenaline transporter
- SNRIs:
-
Selective noradrenaline reuptake inhibitors
- SSRIs:
-
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors
- 5-HTT:
-
Serotonin transporter
- US:
-
Unconditioned stimulus
References
Adell A, Artigas F (1999) Regulation of the release of 5-hydroxytryptamine in the median raphe nucleus of the rat by catecholaminergic afferents. Eur J Neurosci 11:2305–2311
Allgulander C, Mangano R, Zhang J, Dahl AA, Lepola U, Sjodin I, Emilien G (2004) Efficacy of Venlafaxine ER in patients with social anxiety disorder: a double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group comparison with paroxetine. Hum Psychopharmacol 19:387–396
Altman HJ, Normile HJ (1988) What is the nature of the role of the serotonergic nervous system in learning and memory: prospects for development of an effective treatment strategy for senile dementia. Neurobiol Aging 9:627–638
Altman HJ, Nordy DA, Ogren SO (1984) Role of serotonin in memory: facilitation by alaproclate and zimeldine. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 84:496–502
Anagnostaras SG, Gale GD, Fanselow MS (2001) Hippocampus and contextual fear conditioning: recent controversies and advances. Hippocampus 11:8–17
Archer T, Ogren SO, Johansson G, Ross SB (1984) The effect of acute zimeldine and alaproclate administration on the acquisition of two-way active avoidance: comparison with other antidepressant agents, test of selectivity and sub-chronic studies. Psychopharmacol Berl 84:188–195
Arenas MC, Vinader-Caerols C, Monleon S, Martos AJ, Everss E, Ferrer-Ano A, Parra A (2006) Are the effects of the antidepressants amitriptyline, maprotiline, and fluoxetine on inhibitory avoidance state-dependent? Behav Brain Res 166:150–158
Aston-Jones G, Rajkowski J, Cohen J (2000) Locus coeruleus and regulation of behavioral flexibility and attention. Prog Brain Res 126:165–182
Austin MP, Mitchell P, Goodwin GM (2001) Cognitive deficits in depression: possible implications for functional neuropathology. Br J Psychiatry 178:200–206
Buckley MJ (2005) The role of the perirhinal cortex and hippocampus in learning, memory, and perception. Q J Exp Psychol B 58:246–268
Buhot MC, Martin S, Segu L (2000) Role of serotonin in memory impairment. Ann Med 32:210–221
Burghardt NS, Sullivan GM, McEwen BS, Gorman JM, Ledoux JE (2004) The selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor citalopram increases fear after acute treatment but reduces fear with chronic treatment: a comparison with tianeptine. Biol Psychiatry 55:1171–1178
Burghardt NS, Bush DE, McEwen BS, Ledoux JE (2007) Acute selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors increase conditioned fear expression: blockade with a 5-HT(2C) receptor antagonist. Biol Psychiatry 62:1111–1118
Bylund DB, U'Prichard DC (1983) Characterization of alpha 1- and alpha 2-adrenergic receptors. Int Rev Neurobiol 24:343–431
Bymaster FP, Katner JS, Nelson DL, Hemrick-Luecke SK, Threlkeld PG, Heiligenstein JH, Morin SM, Gehlert DR, Perry KW (2002) Atomoxetine increases extracellular levels of norepinephrine and dopamine in prefrontal cortex of rat: a potential mechanism for efficacy in attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Neuropsychopharmacology 27:699–711
Carter RB (1991) Differentiating analgesic and non-analgesic drug activities on rat hot plate: effect of behavioral endpoint. Pain 47:211–220
Conrad LC, Leonard CM, Pfaff DW (1974) Connections of the median and dorsal raphe nuclei in the rat: an autoradiographic and degeneration study. J Comp Neurol 156:179–205
Consolo S, Bertorelli R, Russi G, Zambelli M, Ladinsky H (1994) Serotonergic facilitation of acetylcholine release in vivo from rat dorsal hippocampus via serotonin 5-HT3 receptors. J Neurochem 62:2254–2261
De BT, Nefkens F, Van HA (1994) The alpha 2-adrenoceptor antagonist Org 3770 enhances serotonin transmission in vivo. Eur J Pharmacol 253:R5–R6
Fanselow MS (1980) Conditioned and unconditional components of post-shock freezing. Pavlov J Biol Sci 15:177–182
Fanselow MS (2000) Contextual fear, gestalt memories, and the hippocampus. Behav Brain Res 110:73–81
Fendt M, Fanselow MS (1999) The neuroanatomical and neurochemical basis of conditioned fear. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 23:743–760
Frankland PW, Bontempi B (2005) The organization of recent and remote memories. Nat Rev Neurosci 6:119–130
Ghose S, Fujita M, Morrison P, Uhl G, Murphy DL, Mozley PD, Schou M, Halldin C, Innis R (2005) Specific in vitro binding of (S, S)-[3H]MeNER to norepinephrine transporters. Synapse 56:100–104
Gobert A, Rivet JM, Cistarelli L, Melon C, Millan MJ (1999) Buspirone modulates basal and fluoxetine-stimulated dialysate levels of dopamine, noradrenaline and serotonin in the frontal cortex of freely moving rats: activation of serotonin1A receptors and blockade of alpha2-adrenergic receptors underlie its actions. Neuroscience 93:1251–1262
Graeff FG, Viana MB, Mora PO (1997) Dual role of 5-HT in defense and anxiety. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 21:791–799
Gravius A, Barberi C, Schafer D, Schmidt WJ, Danysz W (2006) The role of group I metabotropic glutamate receptors in acquisition and expression of contextual and auditory fear conditioning in rats—a comparison. Neuropharmacology 51:1146–1155
Griebel G, Moreau JL, Jenck F, Misslin R, Martin JR (1994) Acute and chronic treatment with 5-HT reuptake inhibitors differentially modulate emotional responses in anxiety models in rodents. Psychopharmacol Berl 113:463–470
Griebel G, Blanchard DC, Agnes RS, Blanchard RJ (1995) Differential modulation of antipredator defensive behavior in Swiss-Webster mice following acute or chronic administration of imipramine and fluoxetine. Psychopharmacol Berl 120:57–66
Hajos-Korcsok E, Robinson DD, Yu JH, Fitch CS, Walker E, Merchant KM (2003) Rapid habituation of hippocampal serotonin and norepinephrine release and anxiety-related behaviors, but not plasma corticosterone levels, to repeated footshock stress in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 74:609–616
Harrison BJ, Olver JS, Norman TR, Burrows GD, Wesnes KA, Nathan PJ (2004) Selective effects of acute serotonin and catecholamine depletion on memory in healthy women. J Psychopharmacol 18:32–40
Hashimoto S, Inoue T, Koyama T (1996) Serotonin reuptake inhibitors reduce conditioned fear stress-induced freezing behavior in rats. Psychopharmacol Berl 123:182–186
Hashimoto S, Inoue T, Koyama T (1999) Effects of conditioned fear stress on serotonin neurotransmission and freezing behavior in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 378:23–30
Hyttel J (1994) Pharmacological characterization of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors. Int Clin Psychopharmacol 1:19–26
Inoue T, Koyama T, Yamashita I (1993) Effect of conditioned fear stress on serotonin metabolism in the rat brain. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 44:371–374
Inoue T, Tsuchiya K, Koyama T (1994) Regional changes in dopamine and serotonin activation with various intensity of physical and psychological stress in the rat brain. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 49:911–920
Inoue T, Hashimoto S, Tsuchiya K, Izumi T, Ohmori T, Koyama T (1996a) Effect of citalopram, a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor, on the acquisition of conditioned freezing. Eur J Pharmacol 311:1–6
Inoue T, Tsuchiya K, Koyama T (1996b) Serotonergic activation reduces defensive freezing in the conditioned fear paradigm. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 53:825–831
Inoue T, Li XB, Abekawa T, Kitaichi Y, Izumi T, Nakagawa S, Koyama T (2004) Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor reduces conditioned fear through its effect in the amygdala. Eur J Pharmacol 497:311–316
Inoue T, Nakagawa S, Izumi T, Kitaichi Y, Koyama T (2006) Effect of combined treatment with noradrenaline and serotonin reuptake inhibitors on conditioned freezing. Eur J Pharmacol 540:91–95
Kalueff AV, Murphy DL (2007) The importance of cognitive phenotypes in experimental modeling of animal anxiety and depression. Neural Plast 2007:52087
Knierim JJ (2003) Hippocampus and memory. Can we have our place and fear it too? Neuron 37:372–374
Kobayashi K, Ikeda Y, Haneda E, Suzuki H (2008) Chronic fluoxetine bidirectionally modulates potentiating effects of serotonin on the hippocampal mossy fiber synaptic transmission. J Neurosci 28:6272–6280
Koponen H, Allgulander C, Erickson J, Dunayevich E, Pritchett Y, Detke MJ, Ball SG, Russell JM (2007) Efficacy of duloxetine for the treatment of generalized anxiety disorder: implications for primary care physicians. Prim Care Companion J Clin Psychiat 9:100–107
Ledoux JE (1993) Emotional memory systems in the brain. Behav Brain Res 58:69–79
Ledoux JE (1995) Emotion: clues from the brain. Annu Rev Psychol 46:209–235
Ledoux JE (2000) Emotion circuits in the brain. Annu Rev Neurosci 23:155–184
Li XB, Inoue T, Hashimoto S, Koyama T (2001) Effect of chronic administration of flesinoxan and fluvoxamine on freezing behavior induced by conditioned fear. Eur J Pharmacol 425:43–50
Lorens SA, Guldberg HC (1974) Regional 5-hydroxytryptamine following selective midbrain raphe lesions in the rat. Brain Res 78:45–56
Majlessi N, Naghdi N (2002) Impaired spatial learning in the Morris water maze induced by serotonin reuptake inhibitors in rats. Behav Pharmacol 13:237–242
Maren S, Quirk GJ (2004) Neuronal signaling of fear memory. Nat Rev Neurosci 5:844–852
Maren S, Anagnostaras SG, Fanselow MS (1998) The startled seahorse: is the hippocampus necessary for contextual fear conditioning? Trends Cogn Sci 2:39–42
Meneses A (1999) 5-HT system and cognition. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 23:1111–1125
Meneses A (2002) Tianeptine: 5-HT uptake sites and 5-HT(1–7) receptors modulate memory formation in an autoshaping Pavlovian/instrumental task. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 26:309–319
Meoni P, Hackett D, Lader M (2004) Pooled analysis of venlafaxine XR efficacy on somatic and psychic symptoms of anxiety in patients with generalized anxiety disorder. Depress Anxiety 19:127–132
Miyamoto J, Tsuji M, Takeda H, Ohzeki M, Nawa H, Matsumiya T (2004) Characterization of the anxiolytic-like effects of fluvoxamine, milnacipran and risperidone in mice using the conditioned fear stress paradigm. Eur J Pharmacol 504:97–103
Monleon S, Vinader-Caerols C, Arenas MC, Parra A (2008) Antidepressant drugs and memory: insights from animal studies. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 18:235–248
Mørk A, Kreilgaard M, Sanchez C (2003) The R-enantiomer of citalopram counteracts escitalopram-induced increase in extracellular 5-HT in the frontal cortex of freely moving rats. Neuropharmacology 45:167–173
Murchison CF, Zhang XY, Zhang WP, Ouyang M, Lee A, Thomas SA (2004) A distinct role for norepinephrine in memory retrieval. Cell 117:131–143
Nestler EJ, Barrot M, DiLeone RJ, Eisch AJ, Gold SJ, Monteggia LM (2002) Neurobiology of depression. Neuron 34:13–25
O'Leary OF, Bechtholt AJ, Crowley JJ, Valentino RJ, Lucki I (2007) The role of noradrenergic tone in the dorsal raphe nucleus of the mouse in the acute behavioral effects of antidepressant drugs. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 17:215–226
Paxinos G, Watson C (1986) The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates. Academic, San Diego
Phillips RG, Ledoux JE (1992) Differential contribution of amygdala and hippocampus to cued and contextual fear conditioning. Behav Neurosci 106:274–285
Riedel G, Micheau J (2001) Function of the hippocampus in memory formation: desperately seeking resolution. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 25:835–853
Riedel WJ, Klaassen T, Deutz NE, Van SA, van Praag HM (1999) Tryptophan depletion in normal volunteers produces selective impairment in memory consolidation. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 141:362–369
Robbins TW (1997) Arousal systems and attentional processes. Biol Psychol 45:57–71
Sánchez C, Hyttel J (1999) Comparison of the effects of antidepressants and their metabolites on reuptake of biogenic amines and on receptor binding. Cell Mol Neurobiol 19:467–489
Sanchez C, Meier E (1997) Behavioral profiles of SSRIs in animal models of depression, anxiety and aggression. Are they all alike? Psychopharmacology 129:197–205
Schmitt JA, Jorissen BL, Sobczak S, van Boxtel MP, Hogervorst E, Deutz NE, Riedel WJ (2000) Tryptophan depletion impairs memory consolidation but improves focused attention in healthy young volunteers. J Psychopharmacol 14:21–29
Silverstone PH (2004) Qualitative review of SNRIs in anxiety. J Clin Psychiatry 65:19–28
Steckler T, Sahgal A (1995) The role of serotonergic–cholinergic interactions in the mediation of cognitive behavior. Behav Brain Res 67:165–199
Weikop P, Kehr J, Scheel-Kruger J (2004) The role of alpha1- and alpha2-adrenoreceptors on venlafaxine-induced elevation of extracellular serotonin, noradrenaline and dopamine levels in the rat prefrontal cortex and hippocampus. J Psychopharmacol 18:395–403
Yoshioka M, Matsumoto M, Togashi H, Smith CB, Saito H (1992a) Effect of clonidine on the release of serotonin from the rat hippocampus as measured by microdialysis. Neurosci Lett 139:57–60
Yoshioka M, Matsumoto M, Togashi H, Smith CB, Saito H (1992b) Alpha 2-adrenoceptor modulation of 5-HT biosynthesis in the rat brain. Neurosci Lett 139:53–56
Acknowledgements
Liliana C. P. Montezinho was supported by a grant (SFRH/BPD/18389/2004) from Fundação para a Ciência e Tecnologia (F.C.T.), Portugal. The authors would like to thank Anette Frederiksen and Nina Guldhammer for their skillful technical assistance with the microdialysis studies in freely moving rats and Mary Dovlatyan and Chris Schaich for expert assistance with the occupancy determination and Kim Feijgin and Bettina Ullitz for their assistance with the locomotor activity studies.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Montezinho, L.P., Miller, S., Plath, N. et al. The effects of acute treatment with escitalopram on the different stages of contextual fear conditioning are reversed by atomoxetine. Psychopharmacology 212, 131–143 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-010-1917-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-010-1917-5