Abstract
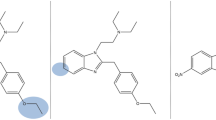
The recent scheduling actions of fentanyl-related substances in both the United States and China have sparked the emergence and proliferation of other generations of “legal” opioids that are structurally distinct from fentanyl, including the recently emerged class of cinnamylpiperazines. In contrast to fentanyl, which contains a piperidine core and a phenethyl moiety, the primary structural components of cinnamylpiperazines are the piperazine core and a cinnamyl moiety. This manuscript reports on the toxicological profile for antemortem and postmortem cases where a cinnamylpiperazine was detected. Samples were quantitatively confirmed using liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. The cases were received between February 2020 and April 2021. Concentrations of 2-methyl AP-237 from four postmortem cases ranged from 820 to 5800 ng/mL, and concentrations of AP-238 from two postmortem cases were 87 and 120 ng/mL. µ-Opioid receptor (MOR) activation potential for 2-methyl AP-237, AP-237, para-methyl AP-237, and AP-238 were studied using a βarr2 recruitment assay. Efficacies (Emax, relative to hydromorphone) and potencies (EC50) were derived and of the compounds tested AP-238 was the most potent compound in the panel with an EC50 of 248 nM. 2-Methyl AP-237 was found to be the most efficacious drug (Emax = 125%) of the tested cinnamylpiperazines; however, it had substantially less efficacy than fentanyl. The in vitro MOR activation potential of the studied cinnamylpiperazines was lower than that of fentanyl and other novel synthetic opioids (NSOs), in line with the relatively higher concentrations observed in postmortem toxicology samples—an important observational link between in vitro pharmacology and in vivo toxicology.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
AAFS Standards Board (2018) Standard practices for method validation in forensic toxicology. https://asb.aafs.org/wp-content/uploads/2018/09/036_Std_Ballot02.pdf. Accessed 4 Nov 2021
AAFS Standards Board (2021) Standard for a quality control program in forensic toxicology laboratories. http://www.asbstandardsboard.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/10/054_Std_e1.pdf. Accessed 13 Dec 2021
Cannaert A, Vasudevan L, Friscia M, Mohr ALA, Wille SMR, Stove CP (2018) Activity-based concept to screen biological matrices for opiates and (synthetic) opioids. Clin Chem 64:1221–1229
Carrano RA, Kimura KK, McCurdy DH (1975a) Analgesic and tolerance studies with AP-237, a new analgesic. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther 213:41–57
Carrano RA, Kimura KK, Landes RC, McCurdy DH (1975b) General pharmacology of a new analgesic-AP-237. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther 213:28–40
Drug Enforcement Administration (2018) Schedules of controlled substances: temporary placement of fentanyl-related substances in schedule I. Temporary amendment; temporary scheduling order. Fed Reg 83:5188–5192
EMCDDA (2019) EU early warning system formal notification: AP-237. May 3, 2019. https://ewsd.wiv-isp.be/Library%20fact%20sheets%20NPS%202018/EU-EWS-RCS-FN-2019-0017_AP-237.pdf. Accessed 27 Mar 2020
EMCDDA (2020) EU early warning system situation report. https://www.aekwien.at/documents/263869/449604/200629_EU+EARLY+WARNING+SYSTEM+SITUATION+REPORT+June.pdf. Accessed 28 Apr 2021
Furlan D (1985) US patent for methyl-piperazino derivatives with analgesic activity patent. December 31, 1985. https://patents.justia.com/patent/4562191. Accessed 10 January 2021
Irikura T, Masuzawa K, Nishino K, Kitagawa M, Uchida H, Ichinoseki N et al (1968) New analgetic agents. V. 1-Butyryl-4-cinnamylpiperazine hydrochloride and related compounds. J Med Chem 11:801–804
Iula DM, Layle NK (2021) Standardized naming system for the cinnamylpiperazine class of synthetic opioids. September 21, 2021. https://www.caymanchem.com/news/standardized-naming-cinnamylpiperazine-synthetic-opioids. Accessed 4 Nov 2021
Kersten BP, McLaughlin ME (2015) Toxicology and management of novel psychoactive drugs. J Pharm Pract 28:50–65
Krotulski AJ, Fogarty MF, Logan BK (2019a) 2-Methyl-AP-237. https://www.npsdiscovery.org/wp-content/uploads/2019a/06/2-Methyl-AP-237_072219_NMSLabs_Report-1.pdf. Accessed 28 Apr 2021
Krotulski AJ, Fogarty MF, Logan BK (2019b) AP-237. September 19, 2019b. https://www.npsdiscovery.org/wp-content/uploads/2019b/09/AP-237_091619_NMSLabs_Report.pdf. Accessed 10 Mar 2020
Krotulski AJ, Fogarty MF, Logan BK (2020a) Para-methyl-AP-237. April 13, 2020a. https://www.npsdiscovery.org/wp-content/uploads/2020a/04/para-Methyl-AP-237_041320_NMSLabs_Report.pdf. Accessed 14 Apr 2020
Krotulski AJ, Fogarty MF, Papsun DM, Logan BK (2020b) AP-238. November 11, 2020b. https://www.npsdiscovery.org/wp-content/uploads/2020b/11/AP-238_111120_CFSRE-Toxicology_Report.pdf?mc_cid=ce629dae0a&mc_eid=61f76987ec. Accessed 12 Nov 2020
Krotulski AJ, Varnum SJ, Logan BK (2020c) Sample mining and data mining: combined real-time and retrospective approaches for the identification of emerging novel psychoactive substances. J Forensic Sci 65:550–562
Krotulski AJ, Papsun DM, Kacinko SL, Logan BK (2020d) Isotonitazene quantitation and metabolite discovery in authentic forensic casework. J Anal Toxicol 44:521–530
Krotulski AJ, Papsun DM, Noble C, Kacinko SL, Logan BK (2021a) Brorphine-investigation and quantitation of a new potent synthetic opioid in forensic toxicology casework using liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. J Forensic Sci 66:664–676
Krotulski AJ, Papsun DM, Walton SE, Logan BK (2021b) Metonitazene in the United States-forensic toxicology assessment of a potent new synthetic opioid using liquid chromatography mass spectrometry. Drug Test Anal. https://doi.org/10.1002/dta.3115
Krotulski AJ, Walton SE, Mohr ALA, Logan BK, Trend Report: Q3 (2021c) NPS discovery at CFSRE. https://www.npsdiscovery.org/wp-content/uploads/2021c/10/2021c-Q3_NPS-Opioids_Trend-Report.pdf. Accessed 25 Oct 2021
Ljubljana NFL (2019) Analytical report: 2-methyl AP-237. J Chem Inf Model. https://doi.org/10.1021/ci100384d
NDEWS Weekly Briefing, Issue 5. https://ndews.org/?wysija-page=1&controller=email&action=view&email_id=37&wysijap=subscriptions. Accessed 5 May 2021
UNODC (2019) China: announcement to place all fentanyl-related substances under national control. https://www.unodc.org/LSS/announcement/Details/f2adea68-fbed-4292-a4cc-63771c943318. Accessed 3 Aug 2021
Nishimura N, Kiuchi M, Kanetake Y, Takahashi T (1970) Clinical exaluation of a new analgesic agent Ap-237 Masui. Jpn J Anesthesiol 19:653–656
Resnik K, Brandão P, Alves EA (2021) DARK classics in chemical neuroscience: bucinnazine. ACS Chem Neurosci 12:3527–3534
Tao Q, Wang W-P (1986) Experimental study on the dependence-producting properties of Qiang Tong Ding (AP-237). Chin J Clin Pharmacol 1986(2):83–90
UNODC (2020) The growing complexity of the opioid crisis. Global SMART Update, Vol 24. Vienna. https://www.unodc.org/documents/scientific/Global_SMART_Update_2020-Vol.24-Eng-Final.pdf.
Vandeputte MM, Cannaert A, Stove CP (2020) In vitro functional characterization of a panel of non-fentanyl opioid new psychoactive substances. Arch Toxicol 94(11):3819–3830
Vasudevan L, Vandeputte M, Deventer M, Wouters E, Cannaert A, Stove CP (2020) Assessment of structure-activity relationships and biased agonism at the Mu opioid receptor of novel synthetic opioids using a novel, stable bio-assay platform. Biochem Pharmacol 177:113910
Wu S-D, Zhang Z-H, Jin J-Z, Kong J, Wang W, Zhang Q et al (2004) Effects of narcotic analgesic drugs on human Oddi’s sphincter motility. World J Gastroenterol 10:2901–2904
Yu Z-Q, Zhang C-L, Xu Y-J, Chang M-J, Jin J-J, Luo L et al (2015) Chronopharmacology of analgesic effect and tolerance induced by six narcotic analgesics in mice. Drug Res 65:141–146
Yu Z, Li X, Feng C, Lei K, He W, Zhang C et al (2020) Circadian variations in the pharmacokinetics of bucinnazine in rats. Biol Rhythm Res 51:758–769
Acknowledgements
The authors of this manuscript would like to thank the following partners for their contributions: Donna Iula from Cayman Chemical, for gifting of the cinnamylpiperazine reference standards to the Stove group; Christine Murphy from Carolinas Medical Center; Sarah Buxon de Quintana from the LA County Medical Examiner – Coroner office (CA); Michael Yeh from the Georgia Poison Center; Darinka Mileusnic from the Knox County Regional Forensic Center; Di Wang from the Morris County Medical Examiner's Office (NJ); Kelly Boulos from the District 23 Medical Examiner’s Office (NJ), Amy Turenne from the Lake County Coroner's Office (OH); and Robert Johnson from the Tarrant County Medical Examiner’s Office (TX). Daria Morozova is acknowledged for her help in conducting the in vitro experiments.
Funding
Funding for this study was received from the National Institute of Justice, Office of Justice Programs, U.S. Department of Justice (Award Number 2020-DQ-BX-0007, “Real-Time Sample-Mining and Data-Mining Approaches for the Discovery of Novel Psychoactive Substances (NPS)”). The opinions, findings, conclusions and/or recommendations expressed in this publication are those of the author(s) and do not necessarily reflect those of the Department of Justice. M.M.V. and C.P.S. acknowledge the Research Foundation Flanders (FWO) (grant numbers 1S81520N and G069419N, respectively) for funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to report.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fogarty, M.F., Vandeputte, M.M., Krotulski, A.J. et al. Toxicological and pharmacological characterization of novel cinnamylpiperazine synthetic opioids in humans and in vitro including 2-methyl AP-237 and AP-238. Arch Toxicol 96, 1701–1710 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-022-03257-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-022-03257-7